Abstract
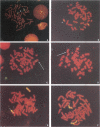
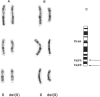
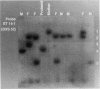
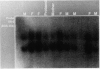
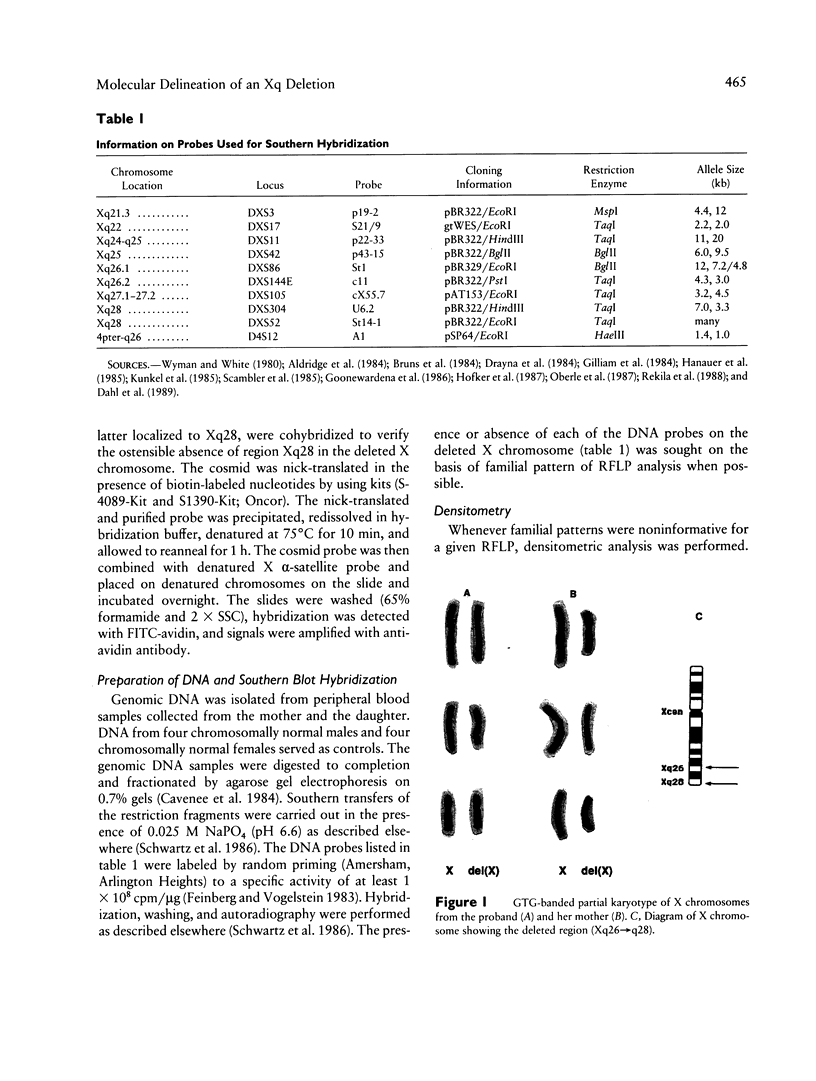
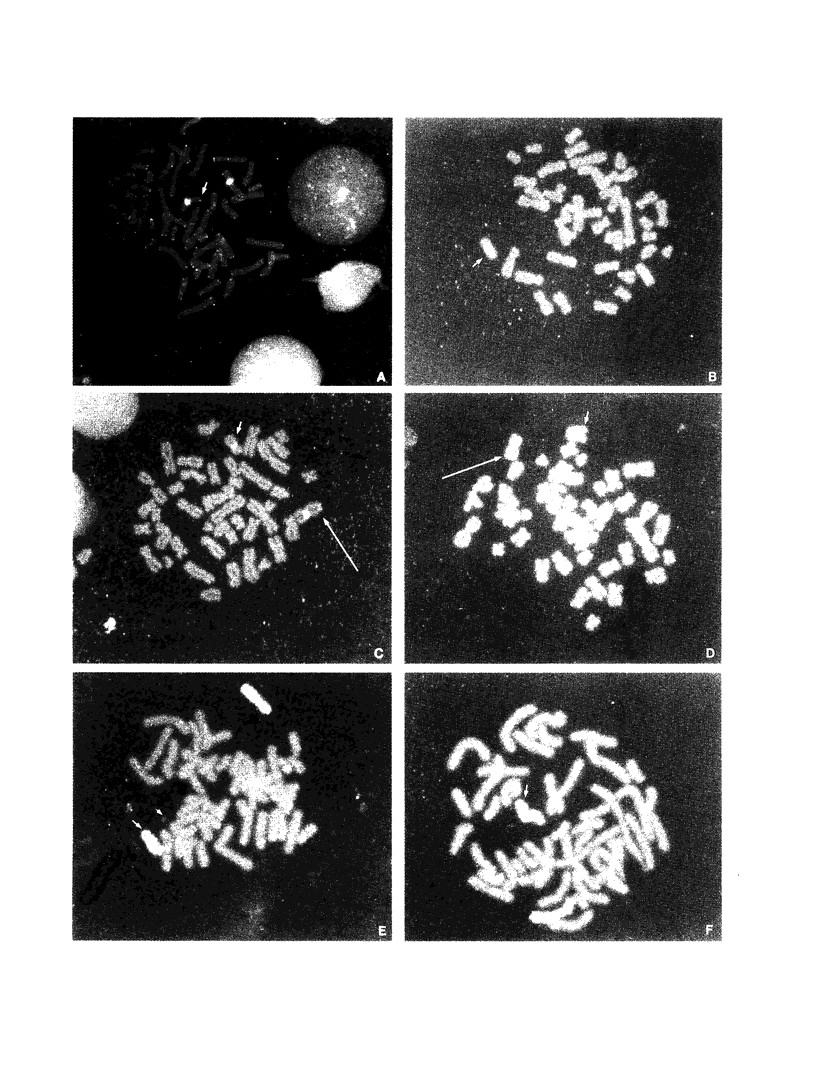
During a routine prenatal diagnosis we detected a female fetus with an apparent terminal deletion of an X chromosome with a karyotype 46,X,del(X)(q25); the mother, who later underwent premature ovarian failure, had the same Xq deletion. To further delineate this familial X deletion and to determine whether the deletion was truly terminal or, rather, interstitial (retaining a portion of the terminal Xq28), we used a combination of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and Southern analyses. RFLP analyses and dosage estimation by densitometry were performed with a panel of nine probes (DXS3, DXS17, DXS11, DXS42, DXS86, DXS144E, DXS105, DXS304, and DXS52) that span the region Xq21 to subtelomeric Xq28. We detected a deletion involving the five probes spanning Xq26-Xq28. FISH with a cosmid probe (CLH 128) that defined Xq28 provided further evidence of a deletion in that region. Analysis with the X chromosome-specific cocktail probes spanning Xpter-qter showed hybridization signal all along the abnormal X, excluding the possibility of a cryptic translocation. However, sequential FISH with the X alpha-satellite probe DXZ1 and a probe for total human telomeres showed the presence of telomeres on both the normal and deleted X chromosomes. From the molecular and FISH analyses we interpret the deletion in this family as 46,X,del(X) (pter-->q26::qter). In light of previous phenotypic-karyotypic correlations, it can be deduced that this region contains a locus responsible for ovarian maintenance.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W., Leach R., Mohandas T., Pearson P., White R. Isolation and regional localization of DNA segments revealing polymorphic loci from human chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):10–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Hammarström-Heeroma K., van Ommen G. B., Pettersson U. A polymorphic locus at Xq27-28 detected by the probe U6.2 [DXS304]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2884–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch N., de Saint Victor J., Richer C. L., Pinsky L., Sitahal S. Premature menopause due to a small deletion in the long arm of the X chromosome: a report of three cases and a review. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Apr 15;142(8):968–972. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90776-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Petit P., van den Berghe H. Fertility in patients with X chromosome deletions. Clin Genet. 1982 Aug;22(2):76–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Scambler P., Robbins T., Ingle C., Williamson R., Davies K. E. The positions of three restriction fragment length polymorphisms on chromosome 4 relative to known genetic markers. Hum Genet. 1984;68(2):154–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00279306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goonewardena P., Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Tolun A., Chotai J., Johnsen E., Pettersson U. Analysis of fragile X-mental retardation families using flanking polymorphic DNA probes. Clin Genet. 1986 Oct;30(4):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W. Chromosome first aid. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):645–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Skraastad M. I., Carpenter N. J., Veenema H., Connor J. M., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Efficient isolation of X chromosome-specific single-copy probes from a cosmid library of a human X/hamster hybrid-cell line: mapping of new probes close to the locus for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X., Worton R. G. Partial gene duplication as a cause of human disease. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(1):3–12. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss C. M., Turksoy R. N., Atkins L., McLaughlin C., Brown L. G., Page D. C. Familial premature ovarian failure due to an interstitial deletion of the long arm of the X chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):125–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Middlesworth W., Ochs H. D., Latt S. A. Specific cloning of DNA fragments absent from the DNA of a male patient with an X chromosome deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4778–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H. Minireview: cryptic translocations and telomere integrity. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):451–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. Recognition of a chromosome truncation site associated with alpha-thalassaemia by human telomerase. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):454–456. doi: 10.1038/353454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naguib K. K., Sundareshan T. S., Bahar A. M., Al-Awadi S. A., Jeryan L. A., Hamdan M. R. Fertility with deletion Xq25: report of three cases; possible exceptions for critical region hypothesis. Fertil Steril. 1988 May;49(5):917–919. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)59907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Wrogemann K., Arveiler B., Hanauer A., Raimondi E., Mandel J. L. Multipoint genetic mapping of the Xq26-q28 region in families with fragile X mental retardation and in normal families reveals tight linkage of markers in q26-q27. Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;77(1):60–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00284716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekilä A. M., Väisänen M. L., Kähkönen M., Leisti J., Winqvist R. A new RFLP with StuI and probe cX55.7 (DXS105) and its usefulness in carrier analysis of fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;80(2):193–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00702869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., Lord R., Bates G., Williamson R. RFLP for D4S12, an anonymous single copy genomic clone at 4pter-4q26 [HGM8 provisional no. D4S12]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):3016–3016. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.3016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. E., McNally E., Leinwand L., Skolnick M. H. A polymorphic human myosin heavy chain locus is linked to an anonymous single copy locus (D17S1) at 17p13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):117–120. doi: 10.1159/000132307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C., Fitch N., Phelan M. C., Richer C. L., Stevenson R. Two sisters with a distal deletion at the Xq26/Xq27 interface: DNA studies indicate that the gene locus for factor IX is present. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00283050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taysi K. Brief clinical report: del(X) (q26) in a phenotypically normal woman and her daughter who also has trisomy 21. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Feb;14(2):367–372. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trunca C., Therman E., Rosenwaks Z. The phenotypic effects of small, distal Xq deletions. Hum Genet. 1984;68(1):87–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00293879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veneman T. F., Beverstock G. C., Exalto N., Mollevanger P. Premature menopause because of an inherited deletion in the long arm of the X-chromosome. Fertil Steril. 1991 Mar;55(3):631–633. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)54199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Lamb J., Harris P. C., Finney R. D., Higgs D. R. A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):868–871. doi: 10.1038/346868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Grouchy J., Thibaud E., Turleau C., Roubin M., Rose F., Cachin O., Rappaport R. Femme 45,X/46,X,del(X)(q25) accouchée d'une fille normale 46,XX. Ann Genet. 1981;24(4):229–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]