Abstract
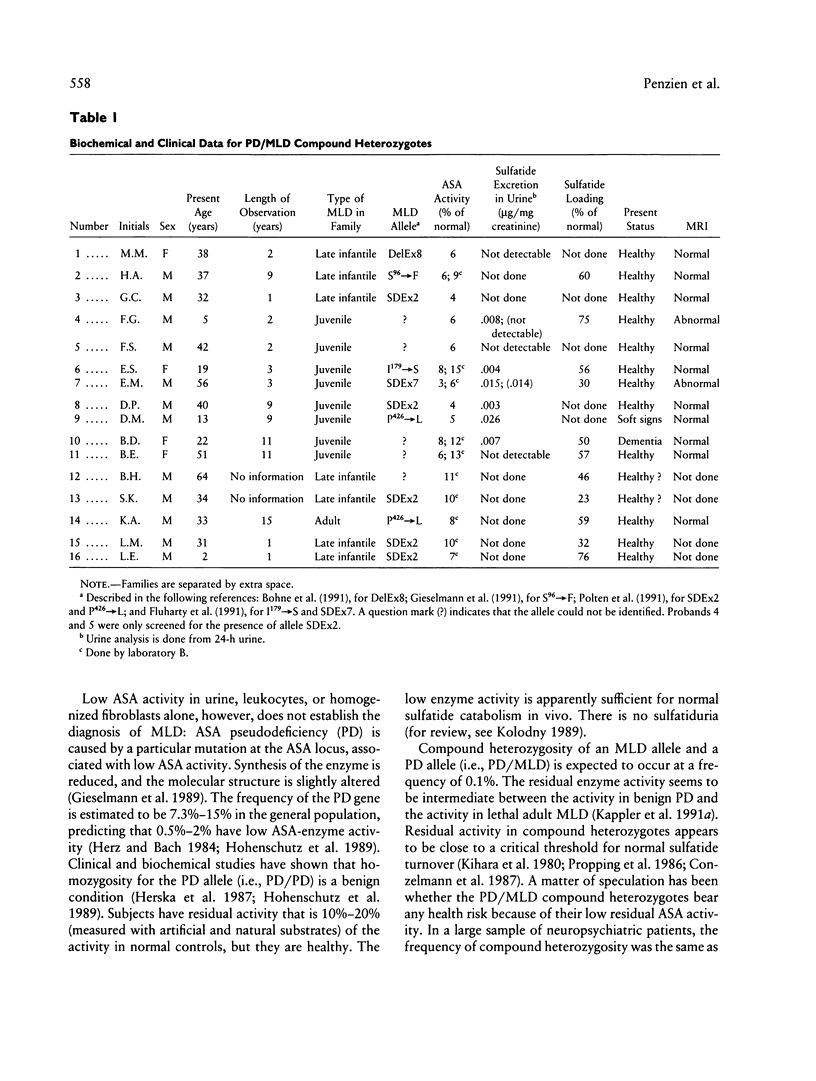
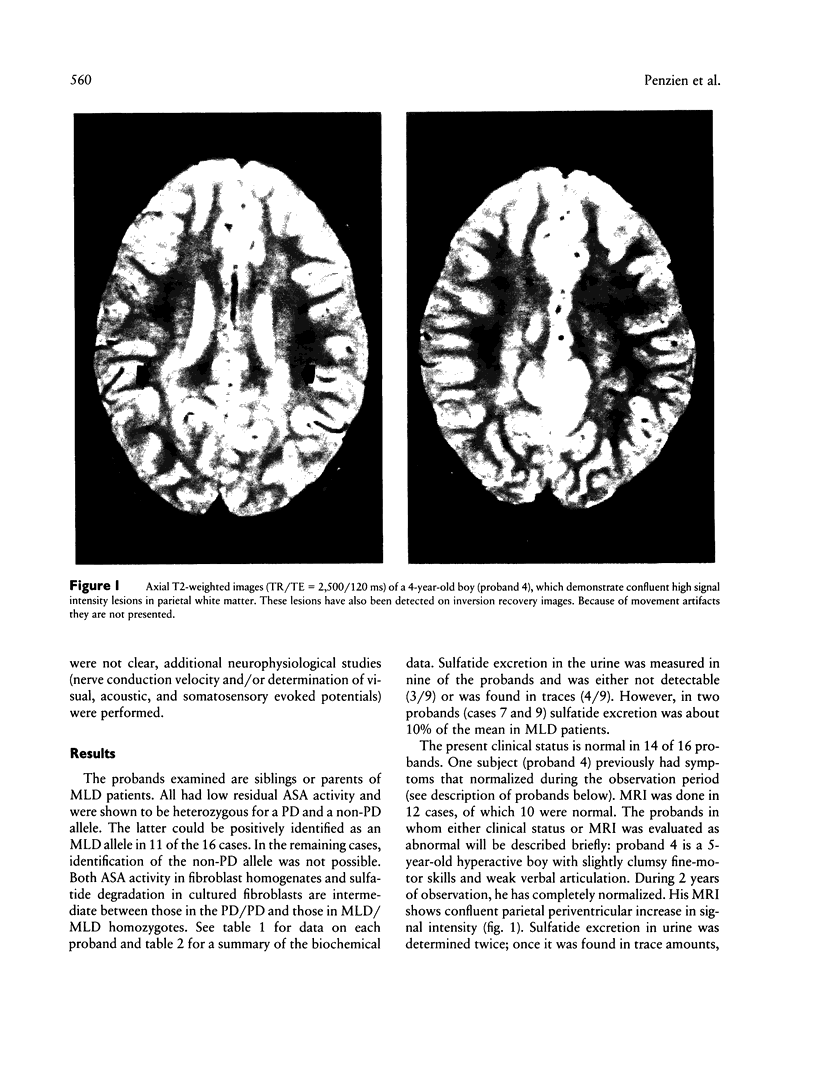
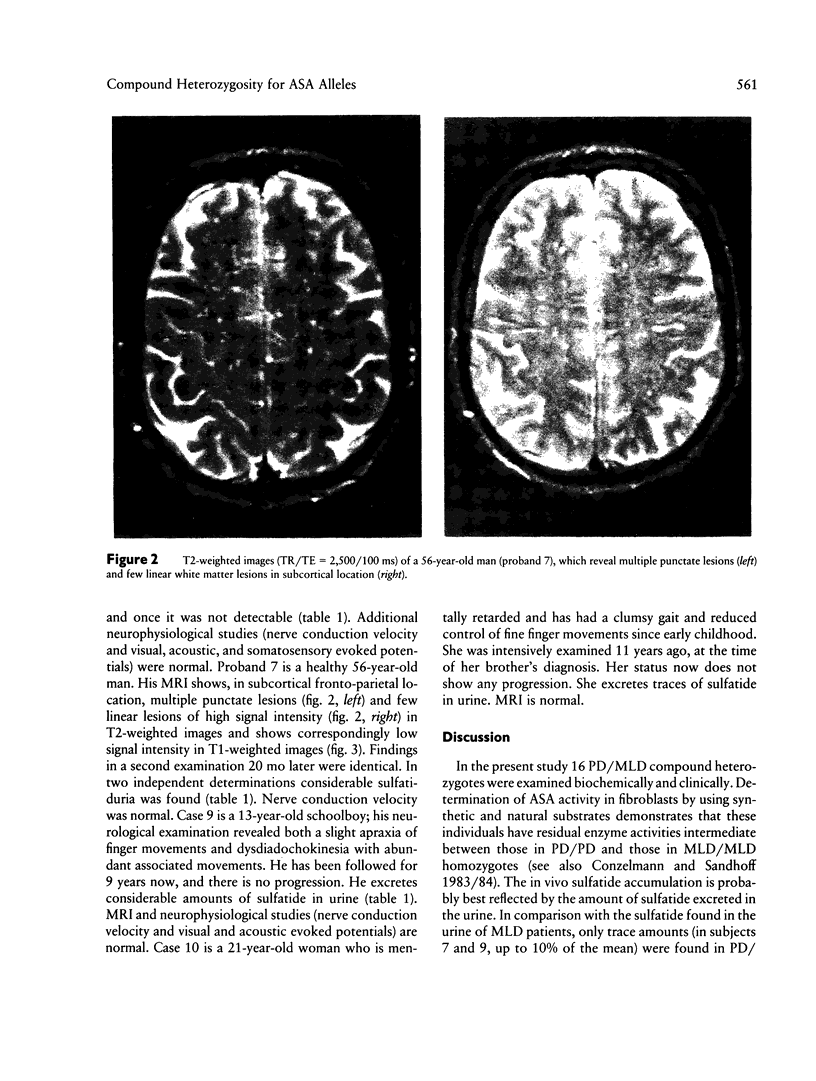
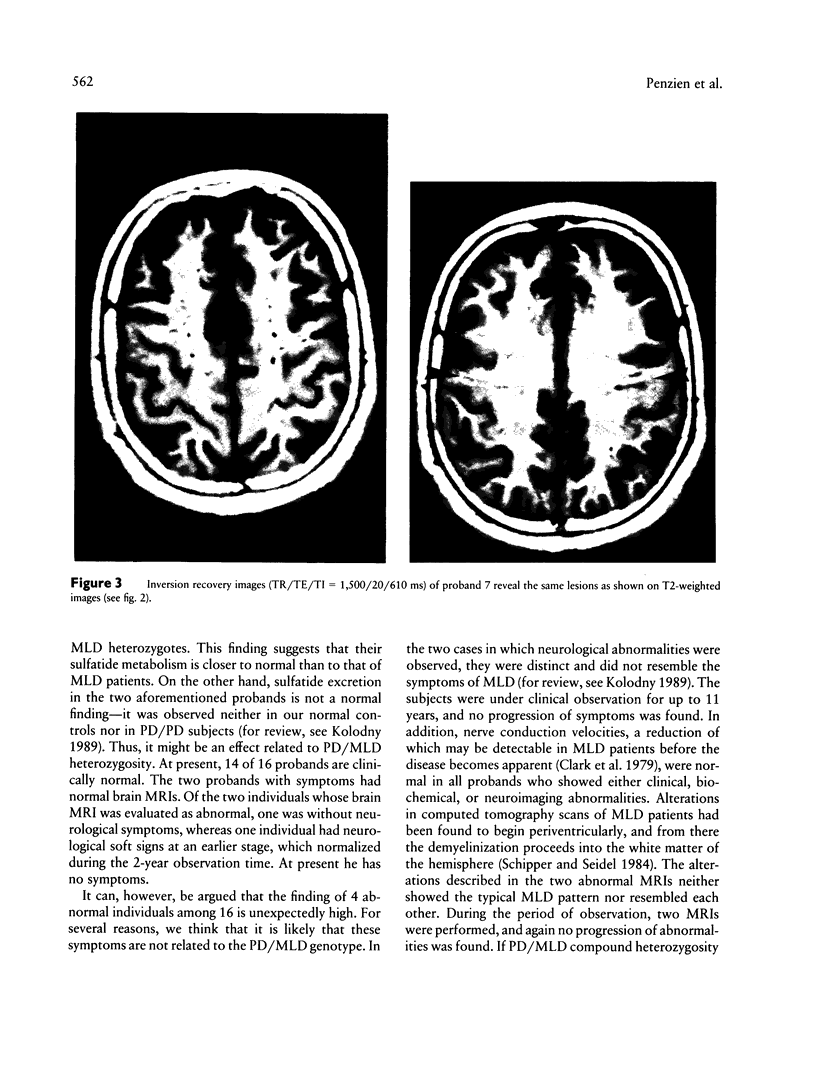
Several allelic mutations at the arylsulfatase A (ASA) locus cause substantial deficiencies of this lysosomal enzyme. Depending on the genetically determined degree of the deficiency, the clinical outcome may be very different—either metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD), a lethal lysosomal storage disorder affecting the nervous system, or, more frequently, the so-called pseudodeficiency (PD), which has no apparent clinical consequence. Because of compound heterozygosity for MLD and PD, 1/1,000 individuals in the population have low residual enzyme activities, which are intermediate between those of MLD patients and those of PD homozygous normal individuals. In order to assess whether PD/MLD compound heterozygotes bear a health risk, we examined clinically and biochemically 16 individuals with this genotype. Of these subjects, two had neurological symptoms and two showed lesions, without clinical symptoms, in magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. None of these symptoms was progressive, nor did they resemble those of MLD. Nerve conduction velocities were normal in these probands, and they secreted only low amounts of sulfatide in the urine. We conclude that the observed neurological symptoms are unrelated to the ASA genotype and that PD/MLD compound heterozygotes are not at an increased risk for developing progressive nervous system diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohne W., von Figura K., Gieselmann V. An 11-bp deletion in the arylsulfatase A gene of a patient with late infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):155–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00204172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. R., Miller R. G., Vidgoff J. M. Juvenile-onset metachromatic leukodystrophy: biochemical and electrophysiologic studies. Neurology. 1979 Mar;29(3):346–343. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Partial enzyme deficiencies: residual activities and the development of neurological disorders. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(1):58–71. doi: 10.1159/000112332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluharty A. L., Fluharty C. B., Bohne W., von Figura K., Gieselmann V. Two new arylsulfatase A (ARSA) mutations in a juvenile metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) patient. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1340–1350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieselmann V. An assay for the rapid detection of the arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency allele facilitates diagnosis and genetic counseling for metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;86(3):251–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00202403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieselmann V., Fluharty A. L., Tønnesen T., Von Figura K. Mutations in the arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency allele causing metachromatic leukodystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):407–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieselmann V., Polten A., Kreysing J., von Figura K. Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency: loss of a polyadenylylation signal and N-glycosylation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herska M., Moscovich D. G., Kalian M., Gottlieb D., Bach G. Aryl sulfatase A deficiency in psychiatric and neurologic patients. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):629–635. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz B., Bach G. Arylsulfatase A in pseudodeficiency. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):147–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00286589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohenschutz C., Eich P., Friedl W., Waheed A., Conzelmann E., Propping P. Pseudodeficiency of arylsulfatase A: a common genetic polymorphism with possible disease implications. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):45–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00288270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Leinekugel P., Conzelmann E., Kleijer W. J., Kohlschütter A., Tønnesen T., Rochel M., Freycon F., Propping P. Genotype-phenotype relationship in various degrees of arylsulfatase A deficiency. Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;86(5):463–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00194634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Pötter W., Gieselmann V., Kiessling W., Friedl W., Propping P. Phenotypic consequences of low arylsulfatase A genotypes (ASAp/ASAp and ASA-/ASAp): does there exist an association with multiple sclerosis? Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(4-5):228–231. doi: 10.1159/000112165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara H., Ho C. K., Fluharty A. L., Tsay K. K., Hartlage P. L. Prenatal diagnosis of metachromatic leukodystrophy in a family with pseudo arylsulfatase A deficiency by the cerebroside sulfate loading test. Pediatr Res. 1980 Mar;14(3):224–227. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198003000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Vaupel M., Conzelmann E. A simple chromogenic assay for arylsulfatase A. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Apr 30;164(2):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinekugel P., Michel S., Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Quantitative correlation between the residual activity of beta-hexosaminidase A and arylsulfatase A and the severity of the resulting lysosomal storage disease. Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;88(5):513–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00219337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polten A., Fluharty A. L., Fluharty C. B., Kappler J., von Figura K., Gieselmann V. Molecular basis of different forms of metachromatic leukodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):18–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propping P., Friedl W., Huschka M., Schlör K. H., Reimer F., Lee-Vaupel M., Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. The influence of low arylsulfatase A activity on neuropsychiatric morbidity: a large-scale screening in patients. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):244–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00282542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schipper H. I., Seidel D. Computed tomography in late-onset metachromatic leucodystrophy. Neuroradiology. 1984;26(1):39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00328202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen T., Bro P. V., Brøndum Nielsen K., Lykkelund C. Metachromatic leukodystrophy and pseudoarylsulfatase A deficiency in a Danish family. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Mar;72(2):175–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






