Abstract
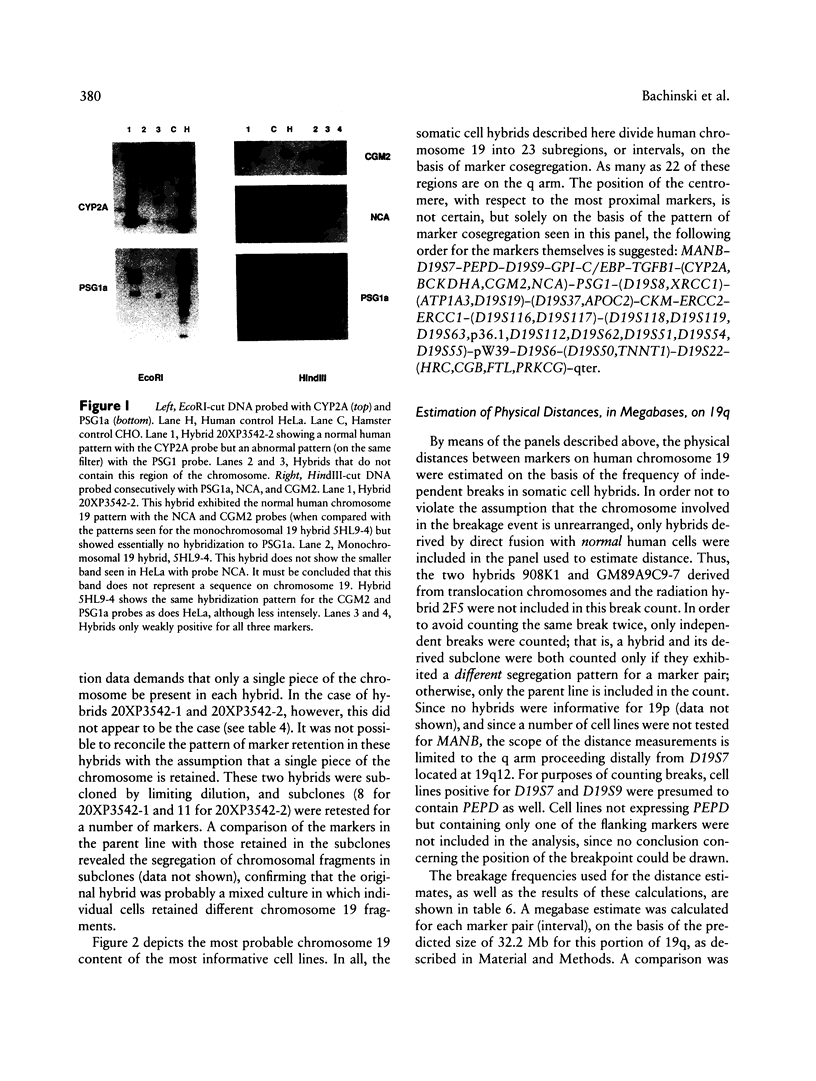
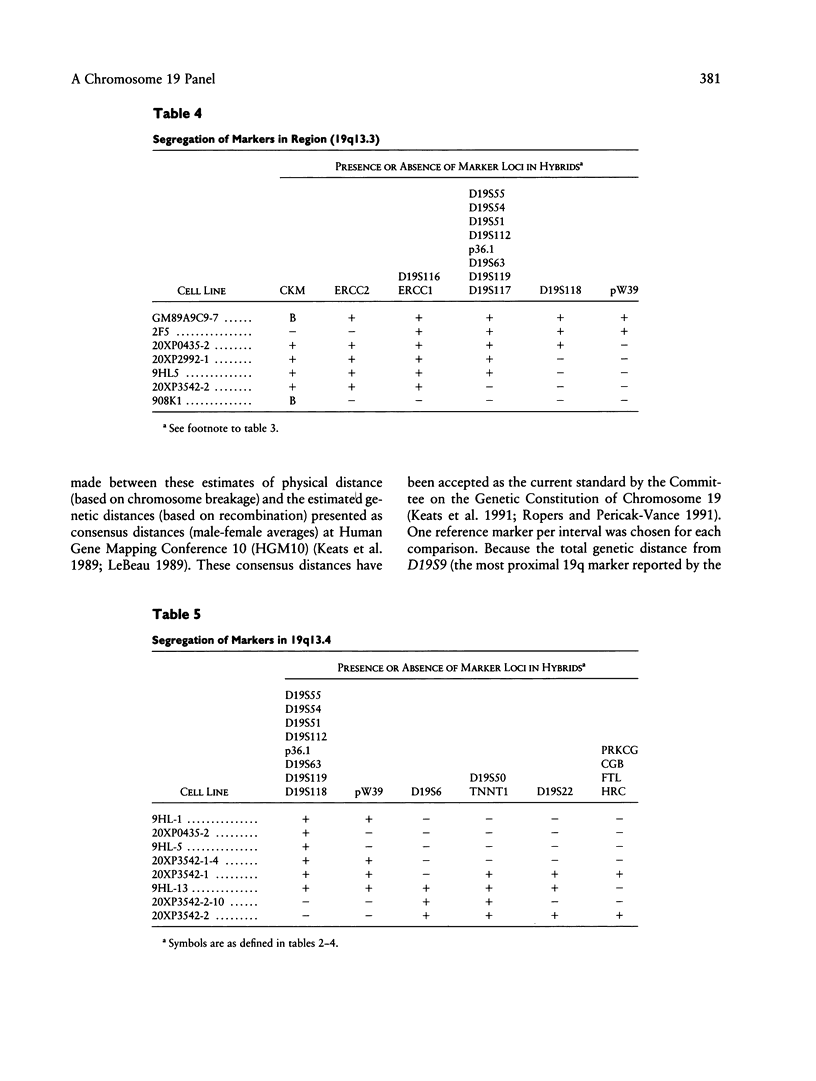
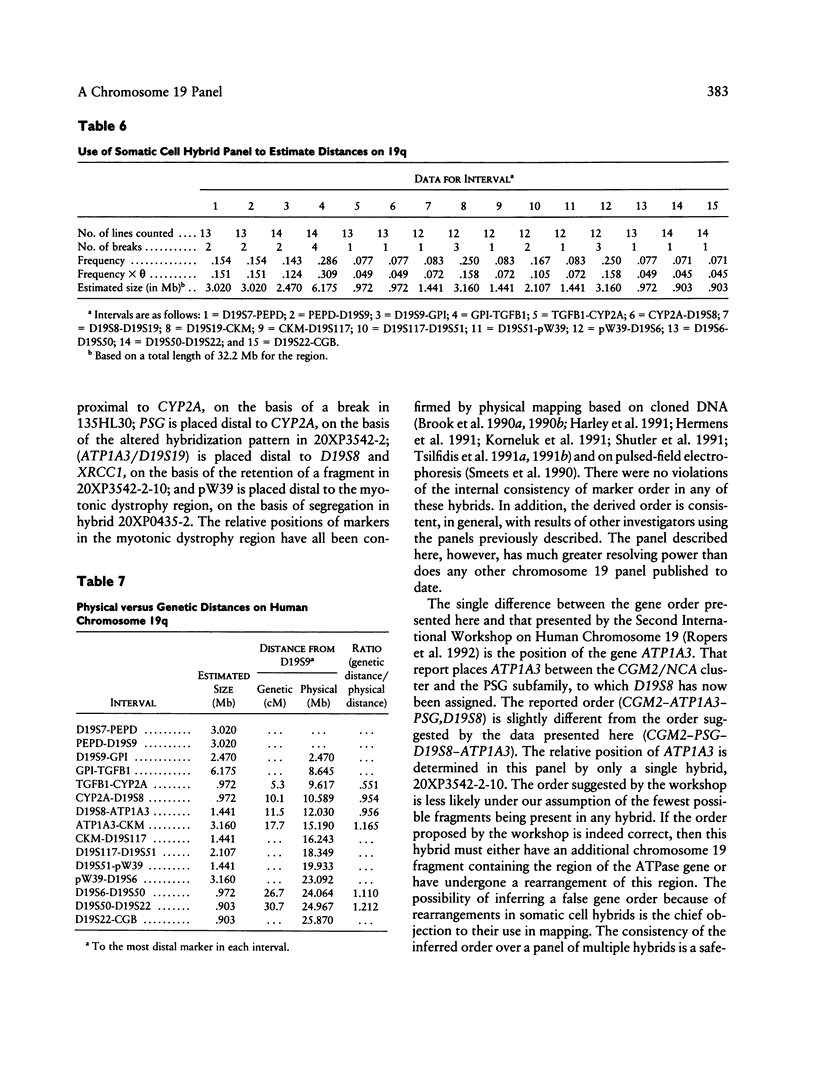
A panel of 22 somatic cell hybrids divides the q arm of human chromosome 19 into 22 ordered subregions. The panel was characterized with respect to 41 genetic markers. In most cases, a single fragment of chromosome 19 was present in each hybrid. In two cell lines the presence of multiple fragments of the chromosome was demonstrated by segregation of these fragments in subclones. On the basis of the results of marker analysis in this panel, the most likely order of the markers tested is MANB-D19S7-PEPD-D19S9-GPI-C/EBP-TGFB1++ +-(CYP2A,BCKDHA,CGM2,NCA)-PSG1-(D19S8, XRCC1)-(ATP1A3,D19S19)-(D19S37,APOC2)-C KM-ERCC2-ERCC1-(D19S116,D19S117)- (D19S118,D19S119, D19S63,p36.1,D19S112,D19S62,D19S51,D19S54, D19S55)-pW39-D19S6-(D19S50,TNNT1)-D19S2 2-(HRC,CGB,FTL,PRKCG)-qter. This gene order is generally consistent with published physical and genetic mapping orders, although some discrepancies exist. By means of a mapping function that relates the frequency of cosegregation of markers to the distance between them, estimates were made of the sizes, in megabases, of the 19q subregions. The relative physical distances between reference markers were compared with published genetic distances for 19q. Excellent correlation was observed, suggesting that the physical distances calculated by this method are predictive of genetic distances in this region of the genome and, therefore, are just as useful in estimating relative positions of markers.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. J., Pericak-Vance M. A., Yamaoka L., Gilbert J., Herbstreith M., Hung W. Y., Lee J. E., Mohandas T., Bruns G., Laberge C. A new probe for the diagnosis of myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1648–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.3029876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Vecoli C., Belcher D. M., Jain S. K., Drysdale J. W. Structural and functional relationships of human ferritin H and L chains deduced from cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11755–11761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Cockburn D., Holt S., Munro E., Van Ommen G. J., Gillard B., Affara N., Ferguson-Smith M., Craig I. Mapping of 12 translocation breakpoints in the Xp21 region with respect to the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(1):28–34. doi: 10.1159/000132581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., Walsh K. V., Shaw D. J. RFLP for a DNA clone which maps to 19q13.2-19qter (D19S63). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1085–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Knight S. J., Roberts S. H., Harley H. G., Walsh K. V., Rundle S. A., Freyne K., Koch M. C., Epstein N. D., Wieringa B. The physical map of chromosome arm 19q: some new assignments, confirmations and re-assessments. Hum Genet. 1991 May;87(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01213095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Skinner M., Roberts S. H., Rettig W. J., Almond J. W., Shaw D. J. Further mapping of markers around the centromere of human chromosome 19. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Walsh K. V., Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., Shaw D. J. A polymorphic DNA clone which maps to 19q13.2-19qter (D19S62). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1086–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1086-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
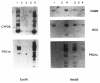
- Brook J. D., Zemelman B. V., Hadingham K., Siciliano M. J., Crow S., Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., Buxton J., Johnson K., Almond J. W. Radiation-reduced hybrids for the myotonic dystrophy locus. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90238-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Reefer J. E. A theory for radiation hybrid (Goss-Harris) mapping: application to proximal 21q markers. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(2-3):99–101. doi: 10.1159/000133212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb D. W., Deaven L. L., Luedemann M., Zhang B., Harris R. A. Assignment of the gene for the E1 alpha subunit of branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase to chromosome 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;50(1):40–41. doi: 10.1159/000132715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk C. T. A simple method for ordering loci using data from radiation hybrids. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. The cDNA for the beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin suggests evolution of a gene by readthrough into the 3'-untranslated region. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):684–687. doi: 10.1038/286684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller L. F., Painter R. B. A Chinese hamster ovary cell line hypersensitive to ionizing radiation and deficient in repair replication. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. New method for mapping genes in human chromosomes. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):680–684. doi: 10.1038/255680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Walsh K. V., Rundle S., Brook J. D., Sarfarazi M., Koch M. C., Floyd J. L., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J. Localisation of the myotonic dystrophy locus to 19q13.2-19q13.3 and its relationship to twelve polymorphic loci on 19q. Hum Genet. 1991 May;87(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01213096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H. Partial reactivation of a human inactive X chromosome in human-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):527–530. doi: 10.1159/000131016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks-Taylor L. R., Bachinski L. L., Siciliano M. J., Fertitta A., Trask B., de Jong P. J., Ledbetter D. H., Darlington G. J. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP alpha) gene (CEBPA) maps to human chromosome 19q13.1 and the related nuclear factor NF-IL6 (C/EBP beta) gene (CEBPB) maps to human chromosome 20q13.1. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermens R., Coerwinkel M., Brunner H., Smeets H., Wieringa B. MspI RFLP at 19q13.3 identified by the anonymous DNA sequence pX75B (D19S112). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1726–1726. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Topham M., Hsieh C. L., Francke U. cDNA and genomic cloning of HRC, a human sarcoplasmic reticulum protein, and localization of the gene to human chromosome 19 and mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):656–669. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90359-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsebos T., Wieringa B., Hochstenbach R., Smeets D., Schepens J., Oerlemans F., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward early diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy: construction and characterization of a somatic cell hybrid with a single human der(19) chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):47–56. doi: 10.1159/000132297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Bruns G. A., Breslow J. L. Isolation and sequence of a human apolipoprotein CII cDNA clone and its use to isolate and map to human chromosome 19 the gene for apolipoprotein CII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Jones P. J., Spurr N., Nimmo E., Davies J., Creed H., Weiss M., Williamson R. Linkage relationships of the protein kinase C gamma gene which exclude it as a candidate for myotonic dystrophy. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(1):13–15. doi: 10.1159/000132577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Buxton J., Nimmo E., Anvret M., Bonduelle M., Williamson B., Savontaus M. L. Recombination events that locate myotonic dystrophy distal to APOC2 on 19q. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):746–751. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Shelbourne P., Davies J., Buxton J., Nimmo E., Siciliano M. J., Bachinski L. L., Anvret M., Harley H., Rundle S. A new polymorphic probe which defines the region of chromosome 19 containing the myotonic dystrophy locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1073–1081. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
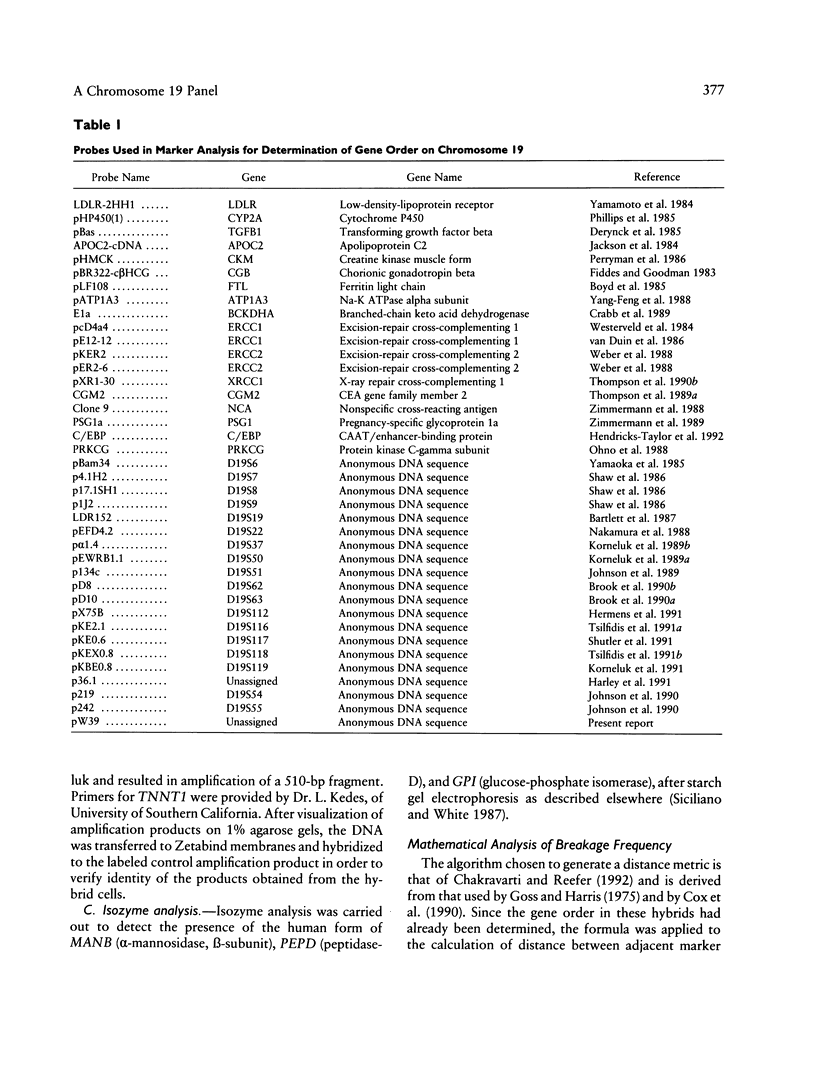
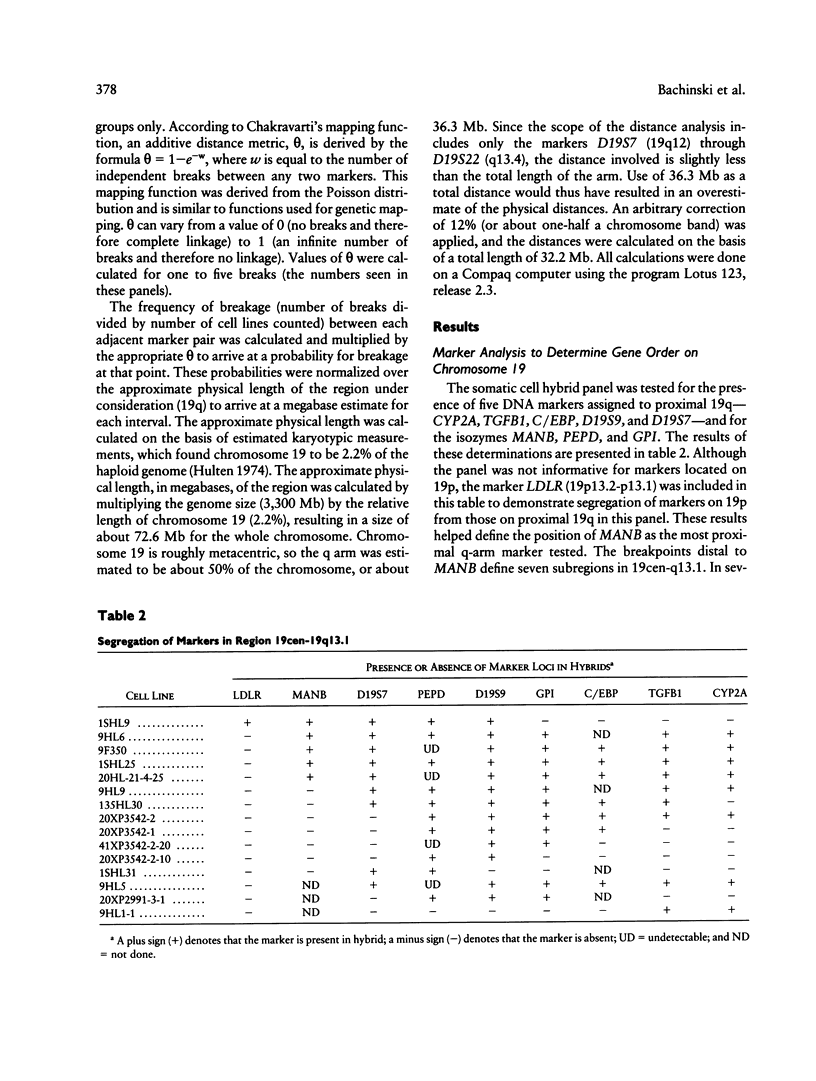
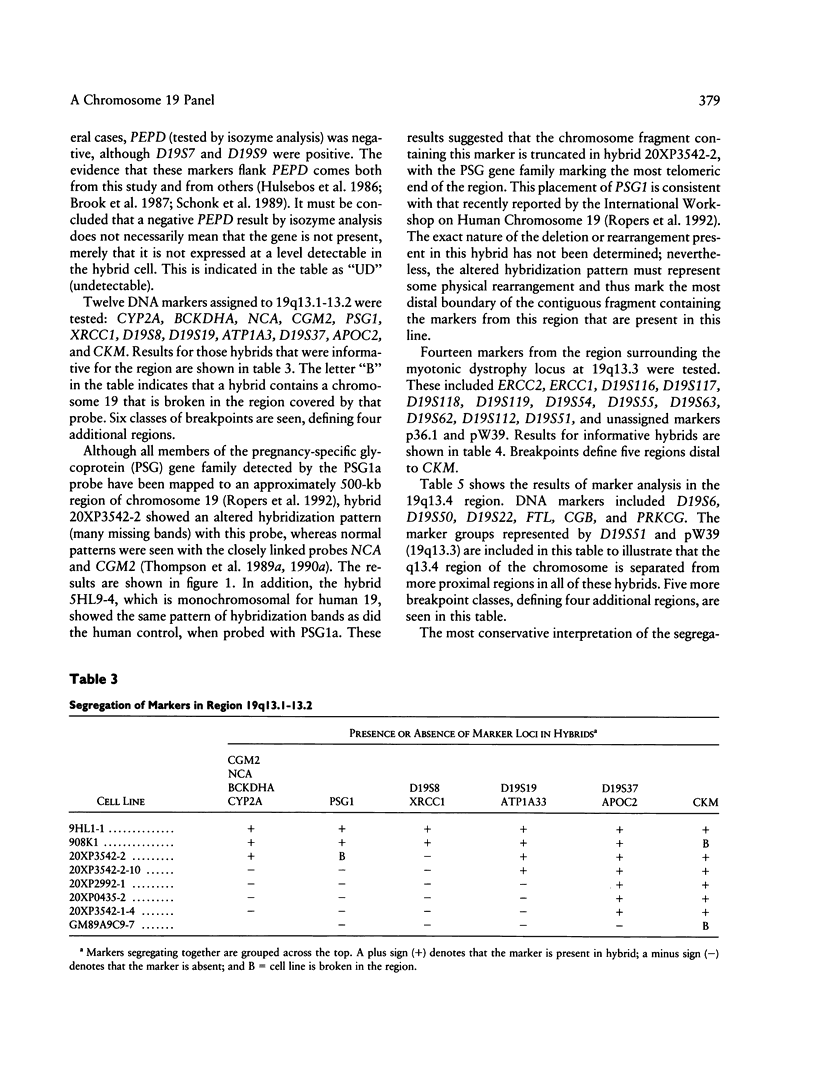
- Korneluk R. G., MacKenzie A. E., Nakamura Y., Dubé I., Jacob P., Hunter A. G. A reordering of human chromosome 19 long-arm DNA markers and identification of markers flanking the myotonic dystrophy locus. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):596–604. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., MacLeod H. L., McKeithan T. W., Brooks J. D., MacKenzie A. E. A chromosome 19 clone from a translocation breakpoint shows close linkage and linkage disequilibrium with myotonic dystrophy. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Tsilfidis C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Bailly J., Surh L. C. A three allele insertion polymorphism is identified by the human chromosome 19q13.3 probe pKBE0.8 (D19S119). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1157–1157. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Ryan D., Jr, Pericak-Vance M. A. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 18 and 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):338–357. doi: 10.1159/000132798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Scott J., Knott T. J., Geller R., Sparkes M. C., Mohandas T. Regional mapping of human chromosome 19: organization of genes for plasma lipid transport (APOC1, -C2, and -E and LDLR) and the genes C3, PEPD, and GPI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3929–3933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauliffe D. P., Lux F. A., Lieu T. S., Sanz I., Hanke J., Newkirk M. M., Bachinski L. L., Itoh Y., Siciliano M. J., Reichlin M. Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosome 19 localization of a human Ro/SS-A autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1379–1391. doi: 10.1172/JCI114582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Fujimoto E., Ballard L., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pEFD4.2 on chromosome 19 [D19S22]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1228–1228. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Akita Y., Konno Y., Imajoh S., Suzuki K. A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC, distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):731–741. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman M. B., Kerner S. A., Bohlmeyer T. J., Roberts R. Isolation and sequence analysis of a full-length cDNA for human M creatine kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):981–989. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90732-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. R., Shephard E. A., Ashworth A., Rabin B. R. Isolation and sequence of a human cytochrome P-450 cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropers H. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Carrano A. V. Report of the Second International Workshop on Human Chromosome 19 mapping 1992. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;60(2):87–95. doi: 10.1159/000133311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonk D., Coerwinkel-Driessen M., van Dalen I., Oerlemans F., Smeets B., Schepens J., Hulsebos T., Cockburn D., Boyd Y., Davis M. Definition of subchromosomal intervals around the myotonic dystrophy gene region at 19q. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Meredith A. L., Sarfarazi M., Harley H. G., Huson S. M., Brook J. D., Bufton L., Litt M., Mohandas T., Harper P. S. Regional localisations and linkage relationships of seven RFLPs and myotonic dystrophy on chromosome 19. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):262–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00282545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shutler G., Tsilfidis C., Leblond S., Korneluk R. G. RFLP identified by the probe pKE0.6 (D19S117) at human chromosome 19q13.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1158–1158. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano M. J., Carrano A. V., Thompson L. H. Assignment of a human DNA-repair gene associated with sister-chromatid exchange to chromosome 19. Mutat Res. 1986 Aug;174(4):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano M. J., White B. F. Isozyme identification of chromosomes in interspecific somatic cell hybrids. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:169–194. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets H., Bachinski L., Coerwinkel M., Schepens J., Hoeijmakers J., van Duin M., Grzeschik K. H., Weber C. A., de Jong P., Siciliano M. J. A long-range restriction map of the human chromosome 19q13 region: close physical linkage between CKMM and the ERCC1 and ERCC2 genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):492–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallings R. L., Olson E., Strauss A. W., Thompson L. H., Bachinski L. L., Siciliano M. J. Human creatine kinase genes on chromosomes 15 and 19, and proximity of the gene for the muscle form to the genes for apolipoprotein C2 and excision repair. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;43(2):144–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Koumari R., Wagner K., Barnert S., Schleussner C., Schrewe H., Zimmermann W., Müller G., Schempp W., Zaninetta D. The human pregnancy-specific glycoprotein genes are tightly linked on the long arm of chromosome 19 and are coordinately expressed. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):848–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Bachinski L. L., Stallings R. L., Dolf G., Weber C. A., Westerveld A., Siciliano M. J. Complementation of repair gene mutations on the hemizygous chromosome 9 in CHO: a third repair gene on human chromosome 19. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):670–679. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Jones N. J., Allen S. A., Carrano A. V. Molecular cloning of the human XRCC1 gene, which corrects defective DNA strand break repair and sister chromatid exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6160–6171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Carrano A. V., Sato K., Salazar E. P., White B. F., Stewart S. A., Minkler J. L., Siciliano M. J. Identification of nucleotide-excision-repair genes on human chromosomes 2 and 13 by functional complementation in hamster-human hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01534495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Brookman K. W. Genetic complementation between UV-sensitive CHO mutants and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 1985 Jun-Jul;150(1-2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Burkhart-Schultz K., Carrano A. V., Siciliano M. J. Correction of a nucleotide-excision-repair mutation by human chromosome 19 in hamster-human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01534738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H. Somatic cell genetics approach to dissecting mammalian DNA repair. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;14(4):264–281. doi: 10.1002/em.2850140409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilfidis C., Shutler G., Leblond S., Korneluk R. G. An SstI RFLP detected by the probe pKE2.1 (D19S116) localized to human chromosome 19q13.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1158–1158. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1158-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilfidis C., Shutler G., Mahadevan M., Korneluk R. G. A frequent HincII polymorphism identified by the human chromosome 19q13.3 probe pKEX0.8 (D19S118). Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1157–1157. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1157-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a human gene, ERCC2, that corrects the nucleotide excision repair defect in CHO UV5 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Brook J. D., Cragg S. J., Hellkuhl B., Jones B. M., Perera P., Roberts S. H., Shaw D. J. Assignment of human ferritin genes to chromosomes 11 and 19q13.3----19qter. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):371–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00291657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka L. H., Bartlett R. J., Ross D. A., Fey G. H., Ledbetter D. H., Bruns G., Pericak-Vance M. A., Herbstreith M. H., Roses A. D. Localization of cloned unique DNA to three different regions of chromosome 19: screen for linkage probes for myotonic dystrophy. J Neurogenet. 1985 Dec;2(6):403–412. doi: 10.3109/01677068509101426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Schneider J. W., Lindgren V., Shull M. M., Benz E. J., Jr, Lingrel J. B., Francke U. Chromosomal localization of human Na+, K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit genes. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):128–138. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Weber B., Ortlieb B., Rudert F., Schempp W., Fiebig H. H., Shively J. E., von Kleist S., Thompson J. A. Chromosomal localization of the carcinoembryonic antigen gene family and differential expression in various tumors. Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2550–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Weiss M., Thompson J. A. cDNA cloning demonstrates the expression of pregnancy-specific glycoprotein genes, a subgroup of the carcinoembryonic antigen gene family, in fetal liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 29;163(3):1197–1209. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]