Abstract
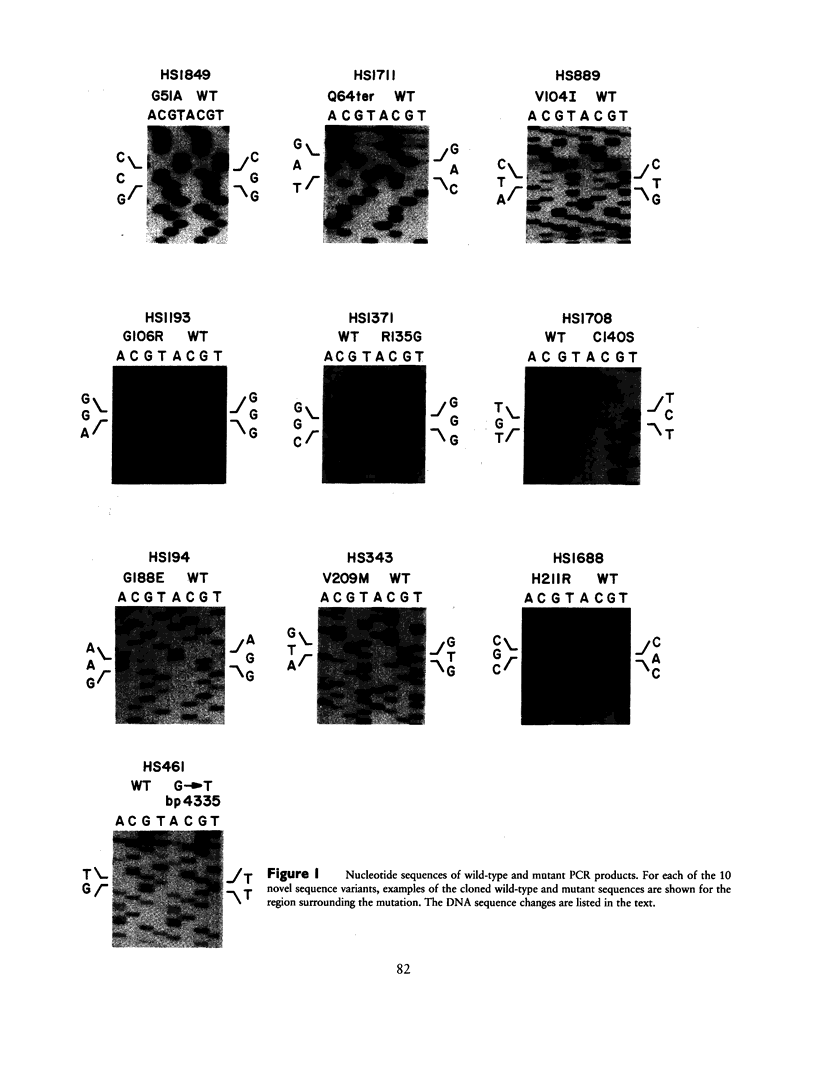
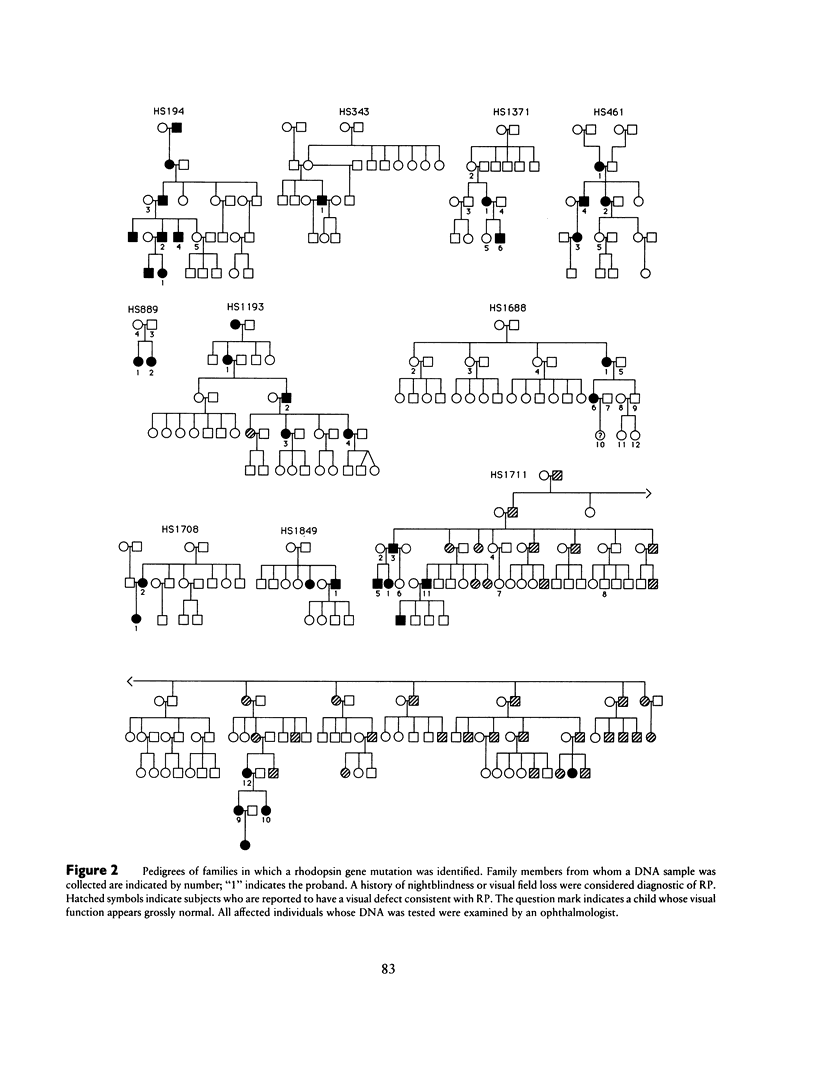
Ten rhodopsin mutations have been found in a screen of 282 subjects with retinitis pigmentosa (RP), 76 subjects with Leber congenital amaurosis, and 3 subjects with congenital stationary night blindness. Eight of these mutations (gly51-to-ala, val104-to-ile, gly106-to-arg, arg135-to-gly, cys140-to-ser, gly188-to-glu, val209-to-met, and his211-to-arg) produce amino acid substitutions, one (gln64-to-ter) introduces a stop codon, and one changes a guanosine in the intron 4 consensus splice donor sequence to thymidine. Cosegregation of RP with gln64-to-ter, gly106-to-arg, arg135-to-gly, cys140-to-ser, gly188-to-glu, his211-to-arg, and the splice site guanosine-to-thymidine indicates that these mutations are likely to cause retinal disease. Val104-to-ile does not cosegregate and is therefore unlikely to be related to retinal disease. The relevance of gly51-to-ala and val209-to-met remains to be determined. The finding of gln64-to-ter in a family with autosomal dominant RP is in contrast to a recent report of a recessive disease phenotype associated with the rhodopsin mutation glu249-to-ter. In the present screen, all of the mutations that cosegregate with retinal disease were found among patients with RP. The mutations described here bring to 35 the total number of amino acid substitutions identified thus far in rhodopsin that are associated with RP. The distribution of the substitutions along the polypeptide chain is significantly nonrandom: 63% of the substitutions involve those 19% of amino acids that are identical among vertebrate visual pigments sequenced to date.
Full text
PDF

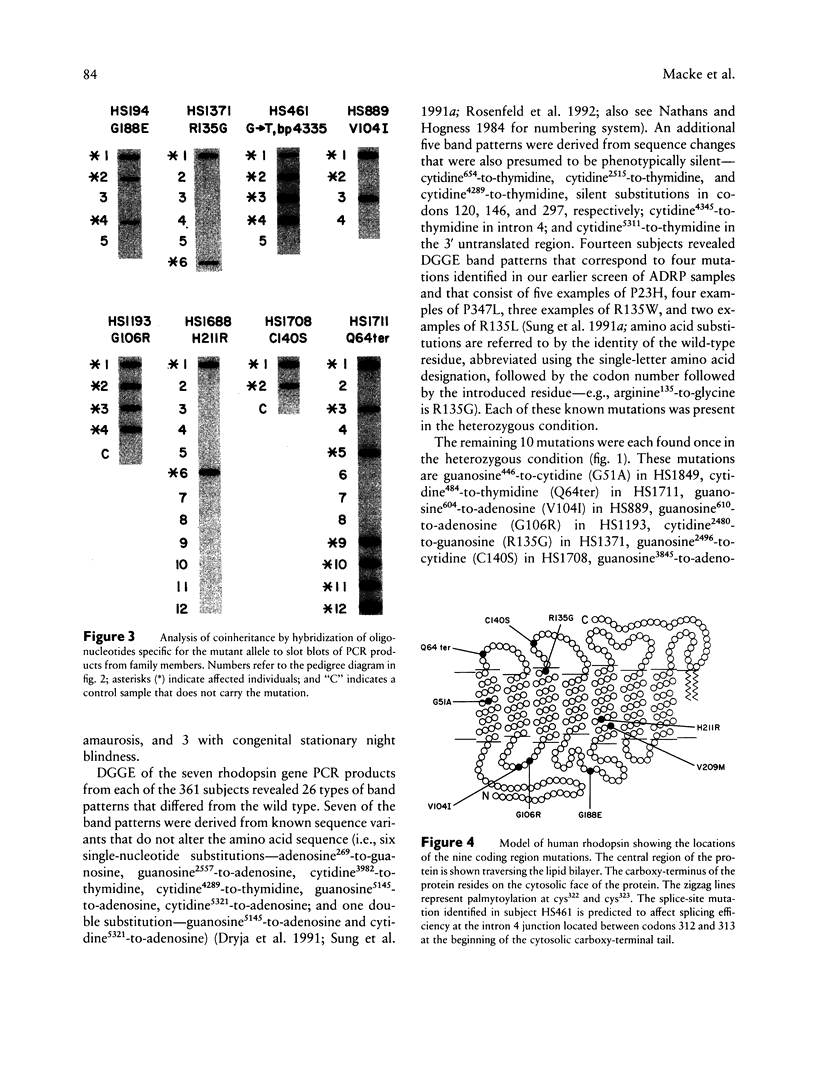
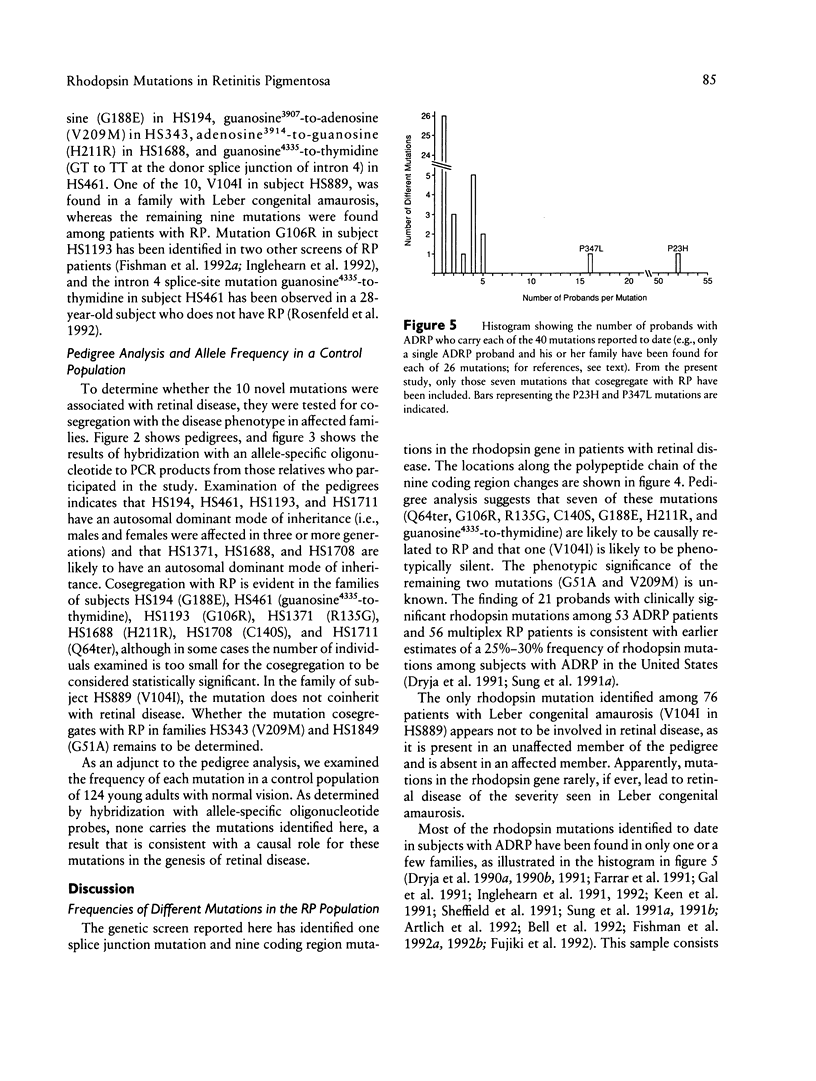
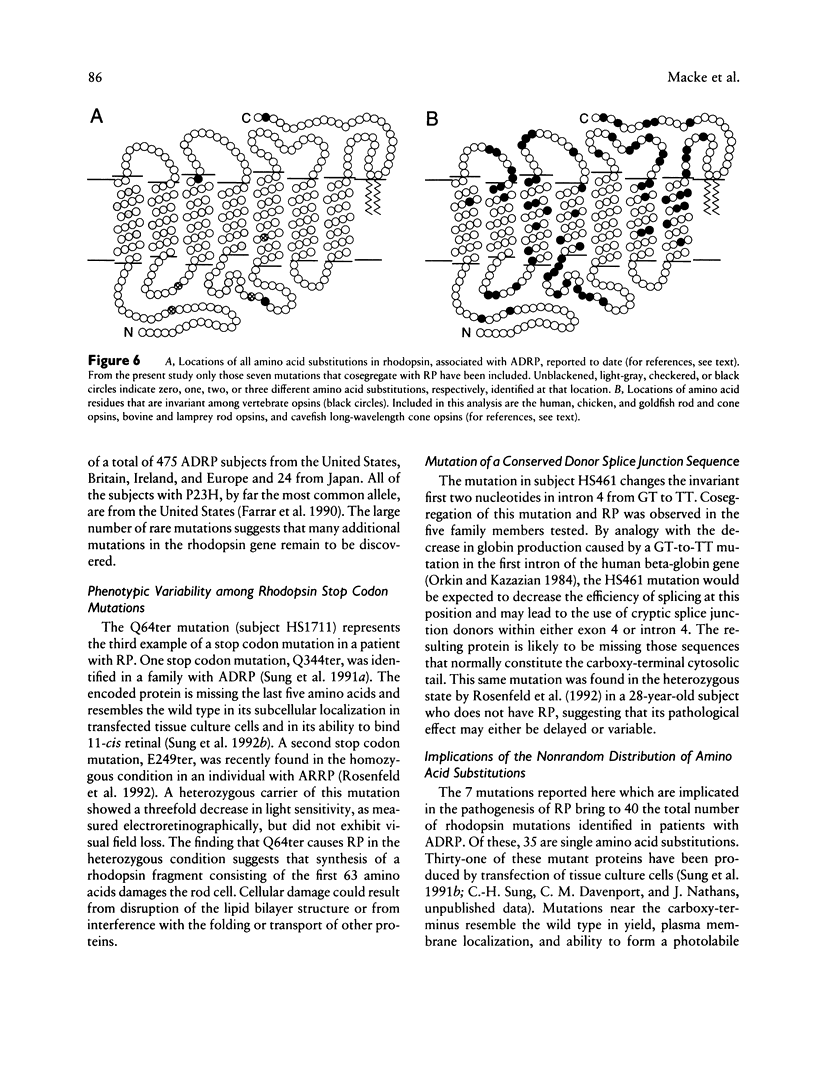
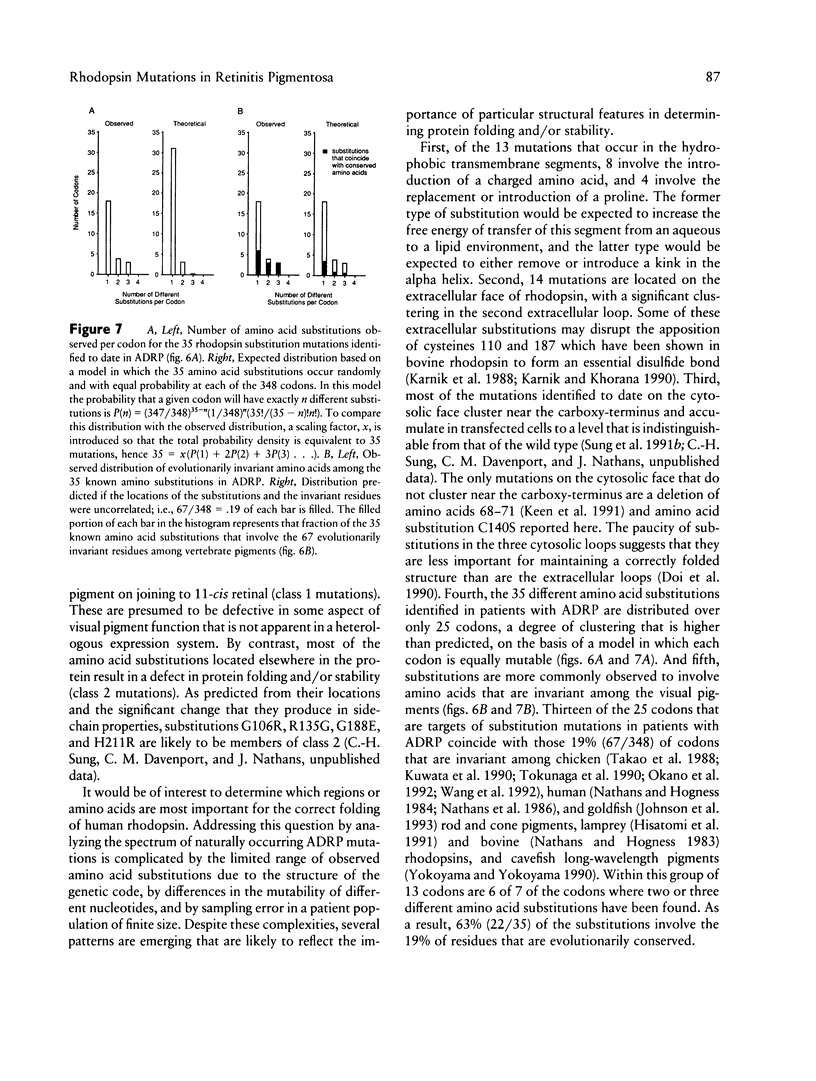


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artlich A., Horn M., Lorenz B., Bhattacharga S., Gal A. Recurrent 3-bp deletion at codon 255/256 of the rhodopsin gene in a German pedigree with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):876–878. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Converse C. A., Collins M. F., Esakowitz L., Kelly K. F., Haites N. E. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (ADRP): a rhodopsin mutation in a Scottish family. J Med Genet. 1992 Sep;29(9):667–668. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.9.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Sandberg M. A., Dryja T. P. Ocular findings in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and a rhodopsin gene defect (Pro-23-His). Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Jan;109(1):92–101. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080010094039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Rosner B., Sandberg M. A., Weigel-DiFranco C., Dryja T. P. Ocular findings in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and rhodopsin, proline-347-leucine. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 May 15;111(5):614–623. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)73708-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi T., Molday R. S., Khorana H. G. Role of the intradiscal domain in rhodopsin assembly and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4991–4995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., McGee T. L., Berson E. L. Mutation spectrum of the rhodopsin gene among patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9370–9374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Olsson J. E., Reichel E., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. Mutations within the rhodopsin gene in patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 8;323(19):1302–1307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011083231903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Reichel E., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Yandell D. W., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):364–366. doi: 10.1038/343364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., Kenna P., Redmond R., McWilliam P., Bradley D. G., Humphries M. M., Sharp E. M., Inglehearn C. F., Bashir R., Jay M. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: absence of the rhodopsin proline----histidine substitution (codon 23) in pedigrees from Europe. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):941–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar G. J., Kenna P., Redmond R., Shiels D., McWilliam P., Humphries M. M., Sharp E. M., Jordan S., Kumar-Singh R., Humphries P. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: a mutation in codon 178 of the rhodopsin gene in two families of Celtic origin. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):1170–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A., Stone E. M., Gilbert L. D., Sheffield V. C. Ocular findings associated with a rhodopsin gene codon 106 mutation. Glycine-to-arginine change in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992 May;110(5):646–653. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1992.01080170068026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. A., Vandenburgh K., Stone E. M., Gilbert L. D., Alexander K. R., Sheffield V. C. Ocular findings associated with rhodopsin gene codon 267 and codon 190 mutations in dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992 Nov;110(11):1582–1588. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1992.01080230082026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki K., Hotta Y., Hayakawa M., Sakuma H., Shiono T., Noro M., Sakuma T., Tamai M., Hikiji K., Kawaguchi R. Point mutations of rhodopsin gene found in Japanese families with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (ADRP). Jpn J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;37(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01899733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal A., Artlich A., Ludwig M., Niemeyer G., Olek K., Schwinger E., Schinzel A. Pro-347-Arg mutation of the rhodopsin gene in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):468–470. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90159-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckenlively J. R., Rodriguez J. A., Daiger S. P. Autosomal dominant sectoral retinitis pigmentosa. Two families with transversion mutation in codon 23 of rhodopsin. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991 Jan;109(1):84–91. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1991.01080010086038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatomi O., Iwasa T., Tokunaga F., Yasui A. Isolation and characterization of lamprey rhodopsin cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91537-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglehearn C. F., Bashir R., Lester D. H., Jay M., Bird A. C., Bhattacharya S. S. A 3-bp deletion in the rhodopsin gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):26–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglehearn C. F., Keen T. J., Bashir R., Jay M., Fitzke F., Bird A. C., Crombie A., Bhattacharya S. A completed screen for mutations of the rhodopsin gene in a panel of patients with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):41–45. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S. G., Kemp C. M., Sung C. H., Nathans J. Retinal function and rhodopsin levels in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa with rhodopsin mutations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991 Sep 15;112(3):256–271. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Grant K. B., Zankel T. C., Boehm M. F., Merbs S. L., Nathans J., Nakanishi K. Cloning and expression of goldfish opsin sequences. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 12;32(1):208–214. doi: 10.1021/bi00052a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G. Assembly of functional rhodopsin requires a disulfide bond between cysteine residues 110 and 187. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17520–17524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen T. J., Inglehearn C. F., Lester D. H., Bashir R., Jay M., Bird A. C., Jay B., Bhattacharya S. S. Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa: four new mutations in rhodopsin, one of them in the retinal attachment site. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90119-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp C. M., Jacobson S. G., Roman A. J., Sung C. H., Nathans J. Abnormal rod dark adaptation in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa with proline-23-histidine rhodopsin mutation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992 Feb 15;113(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)71529-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwata O., Imamoto Y., Okano T., Kokame K., Kojima D., Matsumoto H., Morodome A., Fukada Y., Shichida Y., Yasuda K. The primary structure of iodopsin, a chicken red-sensitive cone pigment. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):128–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80465-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A. T., Fitzke F. W., Kemp C. M., Arden G. B., Keen T. J., Inglehearn C. F., Bhattacharya S. S., Bird A. C. Abnormal dark adaptation kinetics in autosomal dominant sector retinitis pigmentosa due to rod opsin mutation. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992 Aug;76(8):465–469. doi: 10.1136/bjo.76.8.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Maniatis T., Lerman L. S. Detection and localization of single base changes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:501–527. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano T., Kojima D., Fukada Y., Shichida Y., Yoshizawa T. Primary structures of chicken cone visual pigments: vertebrate rhodopsins have evolved out of cone visual pigments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5932–5936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Metzenberg A., Das S., Jing B., Gitschier J. Mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene are associated with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):103–106. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Cowley G. S., McGee T. L., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L., Dryja T. P. A null mutation in the rhodopsin gene causes rod photoreceptor dysfunction and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):209–213. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Fishman G. A., Beck J. S., Kimura A. E., Stone E. M. Identification of novel rhodopsin mutations associated with retinitis pigmentosa by GC-clamped denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):699–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Davenport C. M., Hennessey J. C., Maumenee I. H., Jacobson S. G., Heckenlively J. R., Nowakowski R., Fishman G., Gouras P., Nathans J. Rhodopsin mutations in autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6481–6485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. H., Schneider B. G., Agarwal N., Papermaster D. S., Nathans J. Functional heterogeneity of mutant rhodopsins responsible for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8840–8844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Yasui A., Tokunaga F. Isolation and sequence determination of the chicken rhodopsin gene. Vision Res. 1988;28(4):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(88)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga F., Iwasa T., Miyagishi M., Kayada S. Cloning of cDNA and amino acid sequence of one of chicken cone visual pigments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1212–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80915-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., Adler R., Nathans J. A visual pigment from chicken that resembles rhodopsin: amino acid sequence, gene structure, and functional expression. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3309–3315. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama R., Yokoyama S. Convergent evolution of the red- and green-like visual pigment genes in fish, Astyanax fasciatus, and human. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9315–9318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Dreesen J. C., Verdijk M., Knoers N. V., Monnens L. A., Rocchi M., van Oost B. A. Mutations in the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) associated with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):99–102. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]