Abstract
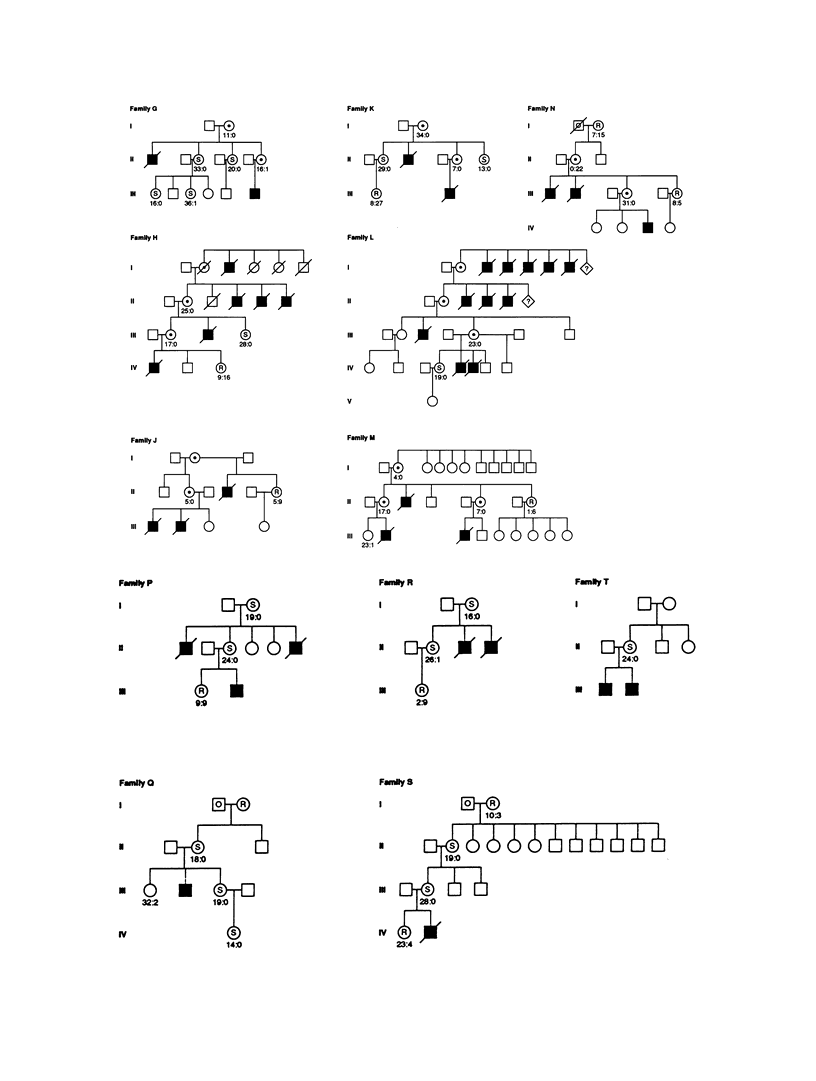
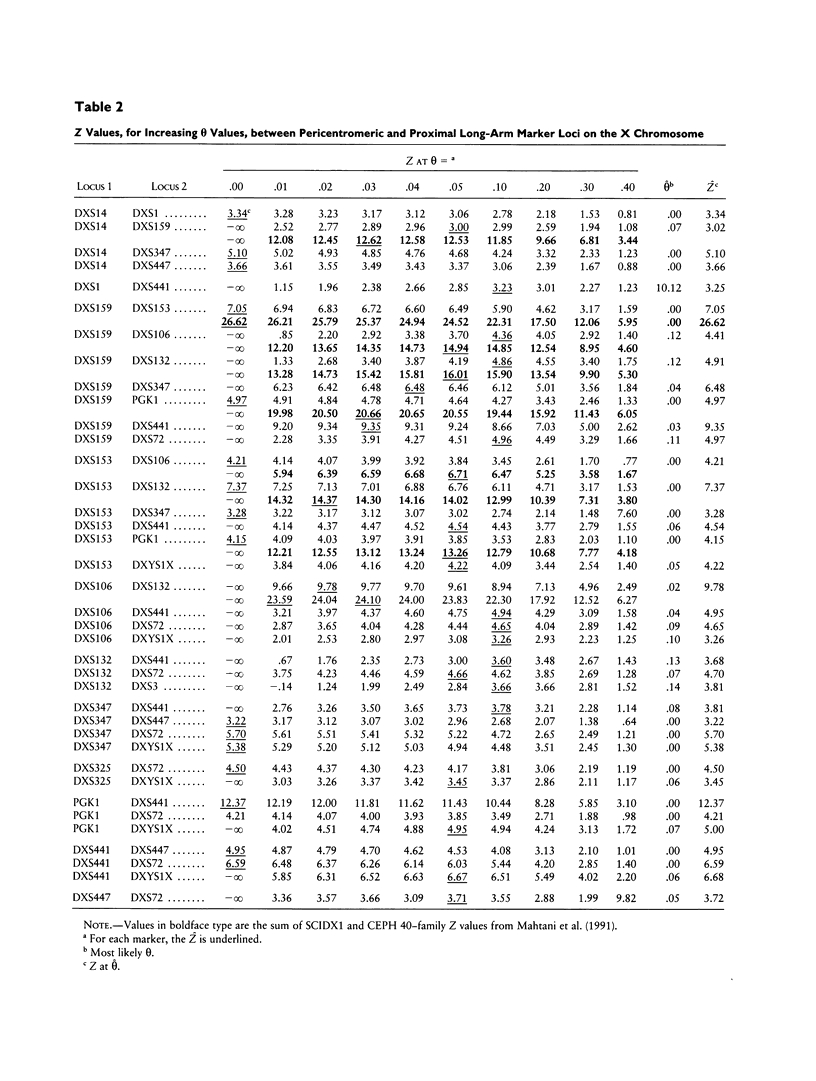
The most common form of human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is inherited as an X-linked recessive genetic defect, MIM 300400. The disease locus, SCIDX1, has previously been placed in Xq13.1-q21.1 by demonstration of linkage to polymorphic markers between DXS159 and DXS3 and by exclusion from interstitial deletions of Xq21.1-q21.3. We report an extension of previous linkage studies, with new markers and a total of 25 SCIDX1 families including female carriers identified by nonrandom X chromosome inactivation in their T lymphocytes. SCIDX1 was nonrecombinant with DXS441, with a lod score of 17.96. Linkage relationships of new markers in the SCIDX1 families were consistent with the linkage map generated in the families of the Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH) and with available physical map data. The most likely locus order was DXS1-(DXS159,DXS153)-DXS106-DXS132-DXS4 53-(SCIDX1,PGK1, DXS325,DXS347,DXS441)-DXS447-DXS72-DXYS 1X-DXS3. The SCIDX1 region now spans approximately 10 Mb of DNA in Xq13; this narrowed genetic localization will assist efforts to identify gene candidates and will improve genetic management for families with SCID.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conley M. E., Buckley R. H., Hong R., Guerra-Hanson C., Roifman C. M., Brochstein J. A., Pahwa S., Puck J. M. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Diagnosis in males with sporadic severe combined immunodeficiency and clarification of clinical findings. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1548–1554. doi: 10.1172/JCI114603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Lavoie A., Briggs C., Brown P., Guerra C., Puck J. M. Nonrandom X chromosome inactivation in B cells from carriers of X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Nov;61(2 Pt 2):S94–S99. doi: 10.1016/s0090-1229(05)80043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fireman P., Johnson H. A., Gitlin D. Presence of plasma cells and gamma-1-M-globulin synthesis in a patient with thymic alymphoplasia. Pediatrics. 1966 Mar;37(3):485–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer A., Landais P., Friedrich W., Morgan G., Gerritsen B., Fasth A., Porta F., Griscelli C., Goldman S. F., Levinsky R. European experience of bone-marrow transplantation for severe combined immunodeficiency. Lancet. 1990 Oct 6;336(8719):850–854. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92348-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti R. A., Meuwissen H. J., Allen H. D., Hong R., Good R. A. Immunological reconstitution of sex-linked lymphopenic immunological deficiency. Lancet. 1968 Dec 28;2(7583):1366–1369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92673-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himelstein B. P., Puck J., August C., Pierson G., Bunin N. T-cell-depleted maternal bone marrow transplantation for siblings with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. J Pediatr. 1993 Feb;122(2):289–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(06)80135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahtani M. M., Lafrenière R. G., Kruse T. A., Willard H. F. An 18-locus linkage map of the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome: genetic framework for mapping X-linked disorders. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Krauss C. M., Puck S. M., Buckley R. H., Conley M. E. Prenatal test for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by analysis of maternal X-chromosome inactivation and linkage analysis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 12;322(15):1063–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004123221508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Conley M. E. Carrier detection in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency based on patterns of X chromosome inactivation. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1172/JCI112967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Smead D. L., Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: localization within the region Xq13.1-q21.1 by linkage and deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):724–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M. Prenatal diagnosis and genetic analysis of X-linked immunodeficiency disorders. Pediatr Res. 1993 Jan;33(1 Suppl):S29–S34. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199305001-00158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Stewart C. C., Nussbaum R. L. Maximum-likelihood analysis of human T-cell X chromosome inactivation patterns: normal women versus carriers of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):742–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram K. T., Barker D. F., Puck J. M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXS441 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1428–1428. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R. New and old immunodeficiencies. Pediatr Res. 1993 Jan;33(1 Suppl):S2–S8. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199305001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tümer Z., Chelly J., Tommerup N., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Tønnesen T., Monaco A. P., Horn N. Characterization of a 1.0 Mb YAC contig spanning two chromosome breakpoints related to Menkes disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):483–489. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verga V., Hall B. K., Wang S. R., Johnson S., Higgins J. V., Glover T. W. Localization of the translocation breakpoint in a female with Menkes syndrome to Xq13.2-q13.3 proximal to PGK-1. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1133–1138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Ledbetter S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS453, DXS454 and DXS458 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4037–4037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonana J., Roberts S. H., Thomas N. S., Harper P. S. Recognition and reanalysis of a cell line from a manifesting female with X linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and an X; autosome balanced translocation. J Med Genet. 1988 Jun;25(6):383–386. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.6.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Basile G., Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Malcolm S., Levinsky R. J., Lau Y. L., Hofker M., Debre M., Fischer A., Griscelli C. Close linkage of the locus for X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency to polymorphic DNA markers in Xq11-q13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7576–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



