Abstract
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) and Cockayne syndrome (CS) are two rare inherited disorders with a clinical and cellular hypersensitivity to the UV component of the sunlight spectrum. Although the two traits are generally considered as clinically and genetically distinct entities, on the biochemical level a defect in the nucleotide excision-repair (NER) pathway is involved in both. Classical CS patients are primarily deficient in the preferential repair of DNA damage in actively transcribed genes, whereas in most XP patients the genetic defect affects both "preferential" and "overall" NER modalities. Here we report a genetic study of two unrelated, severely affected patients with the clinical characteristics of CS but with a biochemical defect typical of XP. By complementation analysis, using somatic cell fusion and nuclear microinjection of cloned repair genes, we assign these two patients to XP complementation group G, which previously was not associated with CS. This observation extends the earlier identification of two patients with a rare combined XP/CS phenotype within XP complementation groups B and D, respectively. It indicates that some mutations in at least three of the seven genes known to be involved in XP also can result in a picture of partial or even full-blown CS. We conclude that the syndromes XP and CS are biochemically closely related and may be part of a broader clinical disease spectrum. We suggest, as a possible molecular mechanism underlying this relation, that the XPGC repair gene has an additional vital function, as shown for some other NER genes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
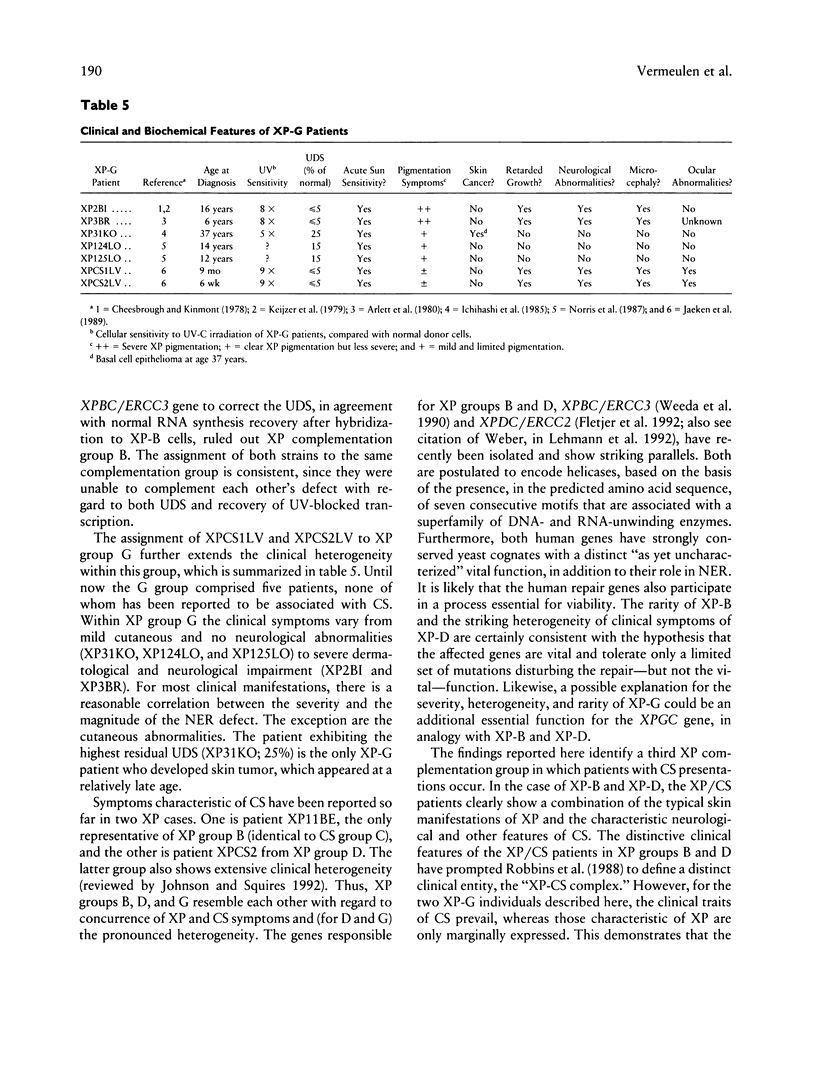
- Arlett C. F., Harcourt S. A., Lehmann A. R., Stevens S., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Morley W. N. Studies on a new case of xeroderma pigmentosum (XP3BR) from complementation group G with cellular sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Carcinogenesis. 1980 Sep;1(9):745–751. doi: 10.1093/carcin/1.9.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A. Gene specific DNA repair. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Nov;12(11):1983–1992. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.11.1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejter W. L., McDaniel L. D., Johns D., Friedberg E. C., Schultz R. A. Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and gene transfer: involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C. Heterogeneity of DNA repair at the gene level. Mutat Res. 1991 Apr;247(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90016-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi M., Fujiwara Y., Uehara Y., Matsumoto A. A mild form of xeroderma pigmentosum assigned to complementation group G and its repair heterogeneity. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Sep;85(3):284–287. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
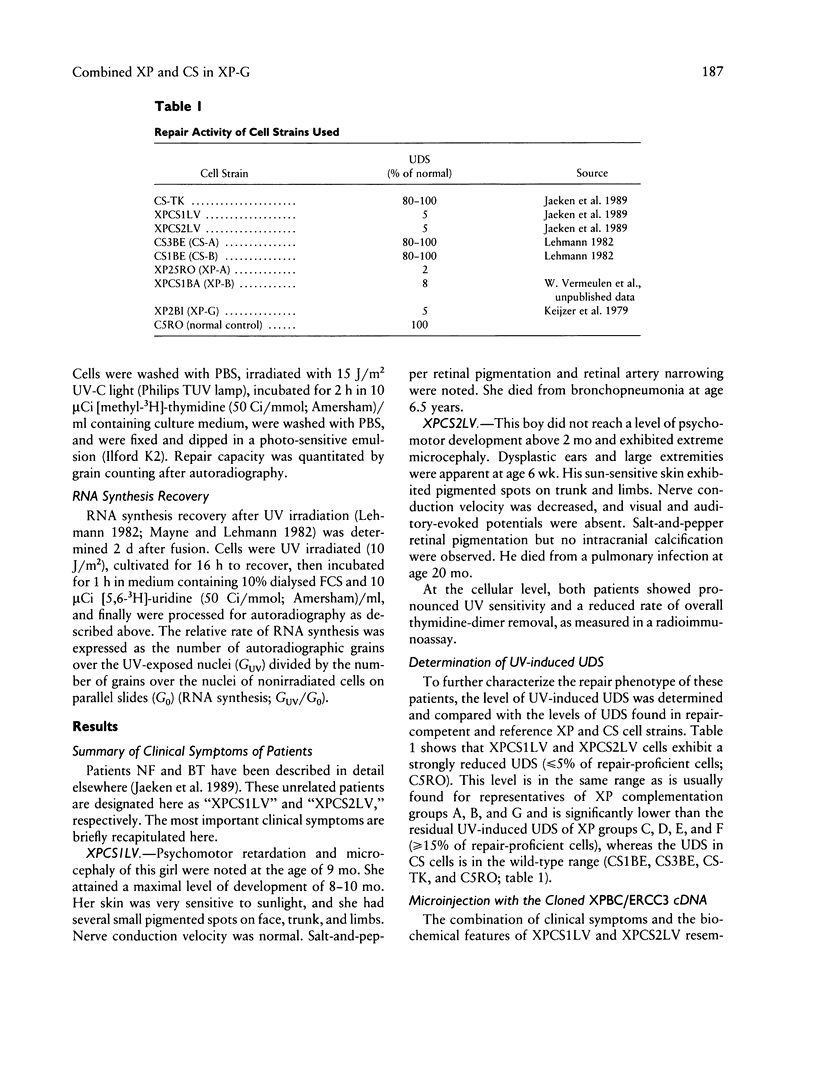
- Jaeken J., Klocker H., Schwaiger H., Bellmann R., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Schweiger M. Clinical and biochemical studies in three patients with severe early infantile Cockayne syndrome. Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;83(4):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00291378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers N. G., Bootsma D. Genetic heterogeneity in ataxia-telangiectasia studied by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2641–2644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Elliott G. C., Squires S., Joysey V. C. Lack of complementation between xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups D and H. Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;81(3):203–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00278989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Squires S. The XPD complementation group. Insights into xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne's syndrome and trichothiodystrophy. Mutat Res. 1992 Mar;273(2):97–118. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90072-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keijzer W., Jaspers N. G., Abrahams P. J., Taylor A. M., Arlett C. F., Zelle B., Takebe H., Kinmont P. D., Bootsma D. A seventh complementation group in excision-deficient xeroderma pigmentosum. Mutat Res. 1979 Aug;62(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafforet D., Dupuy J. M. Photosensibilité et réparation de l'ADN. Possibilité d'une parenté nosologique entre Xéroderma pigmentosum et syndrome de Cockayne. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1978 Dec;35(10 Suppl):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Zeeland A. A., Backendorf C. M., Bridges B. A., Collins A., Fuchs R. P., Margison G. P., Montesano R., Moustacchi E. Workshop on DNA repair. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;273(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
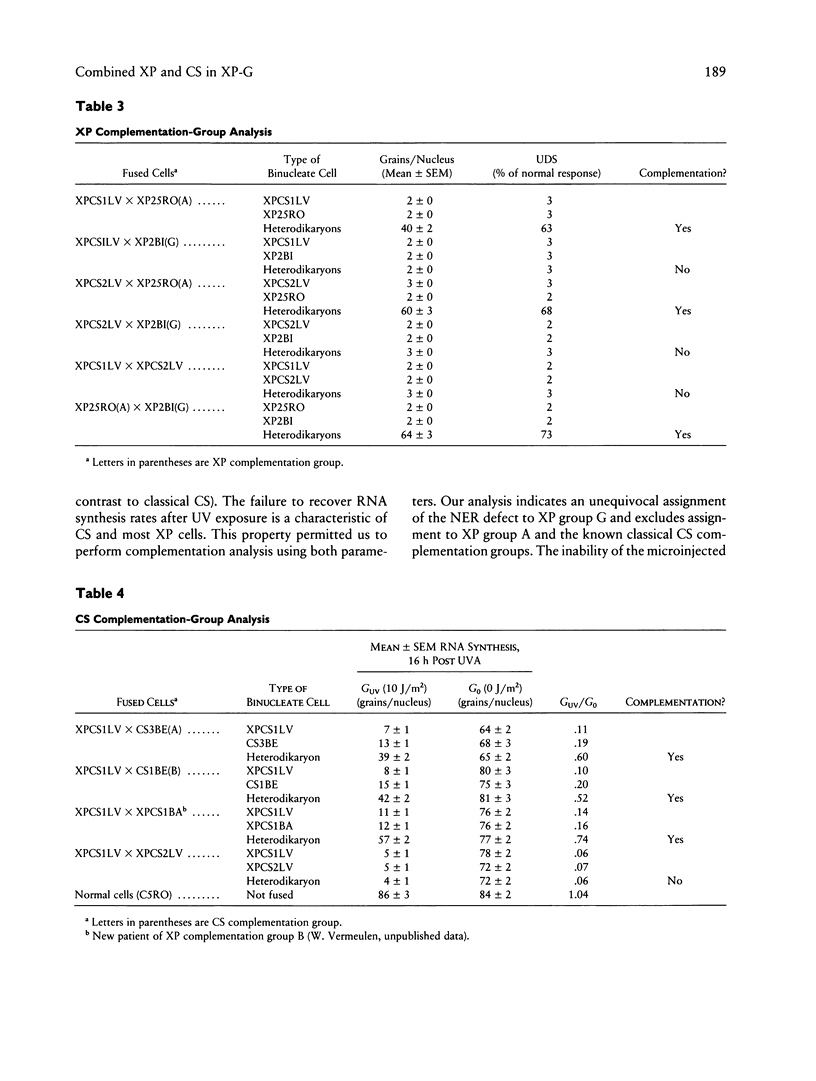
- Lehmann A. R. Three complementation groups in Cockayne syndrome. Mutat Res. 1982 Dec;106(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne L. V., Lehmann A. R. Failure of RNA synthesis to recover after UV irradiation: an early defect in cells from individuals with Cockayne's syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum. Cancer Res. 1982 Apr;42(4):1473–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance M. A., Berry S. A. Cockayne syndrome: review of 140 cases. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jan 1;42(1):68–84. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris P. G., Hawk J. L., Avery J. A., Giannelli F. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group G--report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 1987 Jun;116(6):861–866. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb04906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Brumback R. A., Mendiones M., Barrett S. F., Carl J. R., Cho S., Denckla M. B., Ganges M. B., Gerber L. H., Guthrie R. A. Neurological disease in xeroderma pigmentosum. Documentation of a late onset type of the juvenile onset form. Brain. 1991 Jun;114(Pt 3):1335–1361. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.3.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Kraemer K. H., Lutzner M. A., Festoff B. W., Coon H. G. Xeroderma pigmentosum. An inherited diseases with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):221–248. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Defective DNA repair causes skin cancer and neurodegeneration. JAMA. 1988 Jul 15;260(3):384–388. doi: 10.1001/jama.260.3.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Kawai K., Kumahara Y., Ikenaga M., Okada Y. Genetic complementation groups in cockayne syndrome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Jul;7(4):445–455. doi: 10.1007/BF01542989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., Mullenders L. H., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mayne L. V. The genetic defect in Cockayne syndrome is associated with a defect in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in transcriptionally active DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4707–4711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., van Hoffen A., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mullenders L. H. The residual repair capacity of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C fibroblasts is highly specific for transcriptionally active DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):443–448. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Osseweijer P., de Jonge A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Transient correction of excision repair defects in fibroblasts of 9 xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups by microinjection of crude human cell extracts. Mutat Res. 1986 May;165(3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Stefanini M., Giliani S., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group H falls into complementation group D. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep;255(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
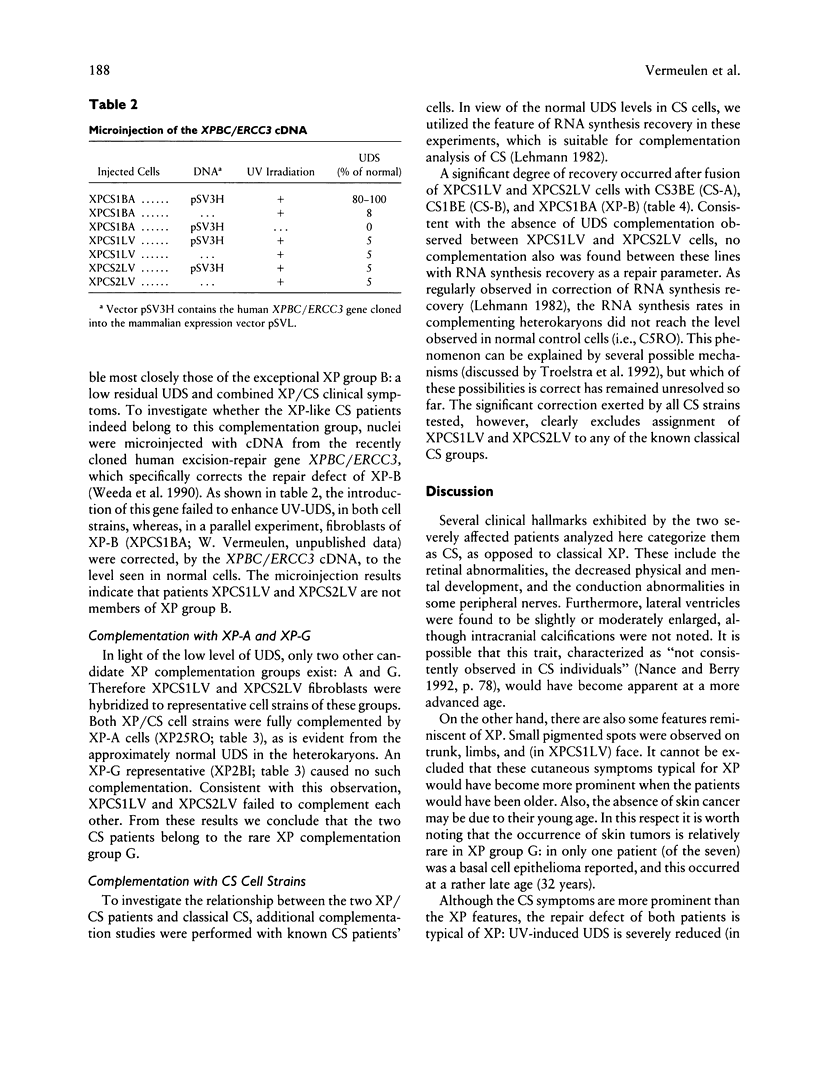
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Vredeveldt G., Mayne L. V., Odijk H., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. The cloned human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-1 fails to correct xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups A through I. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;217(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



