Abstract
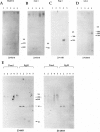
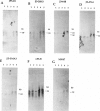
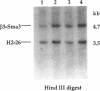
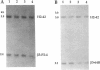
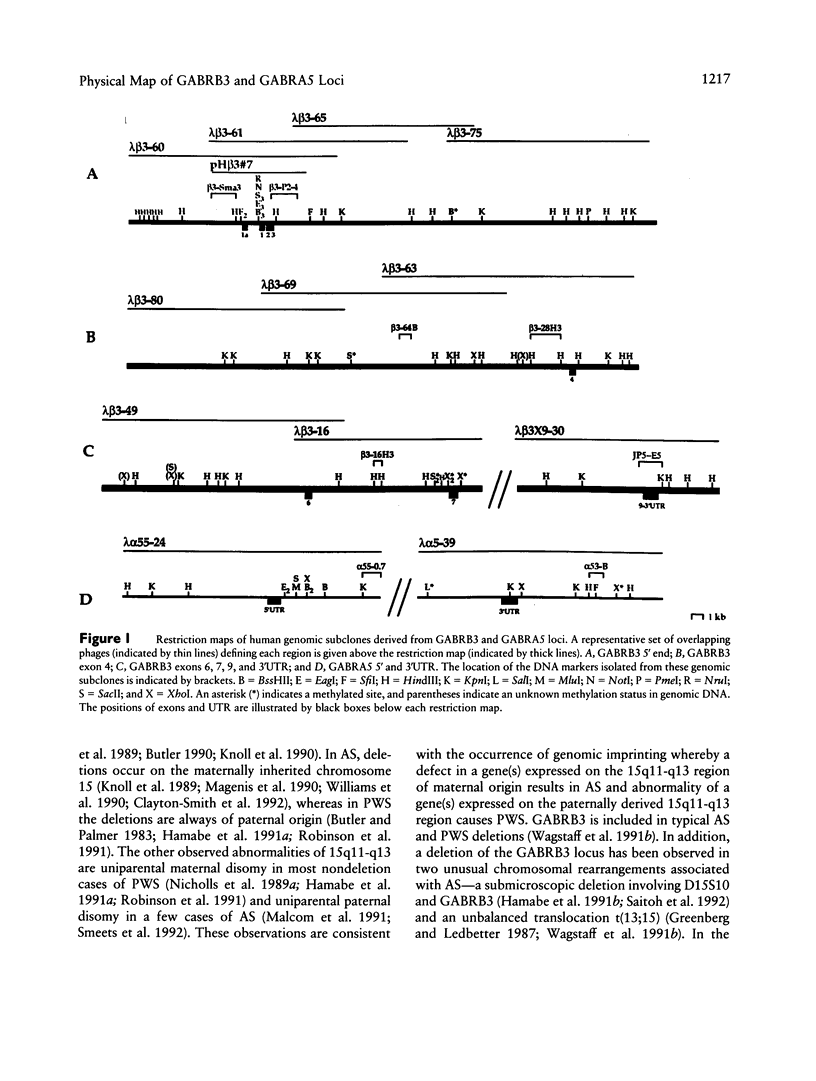
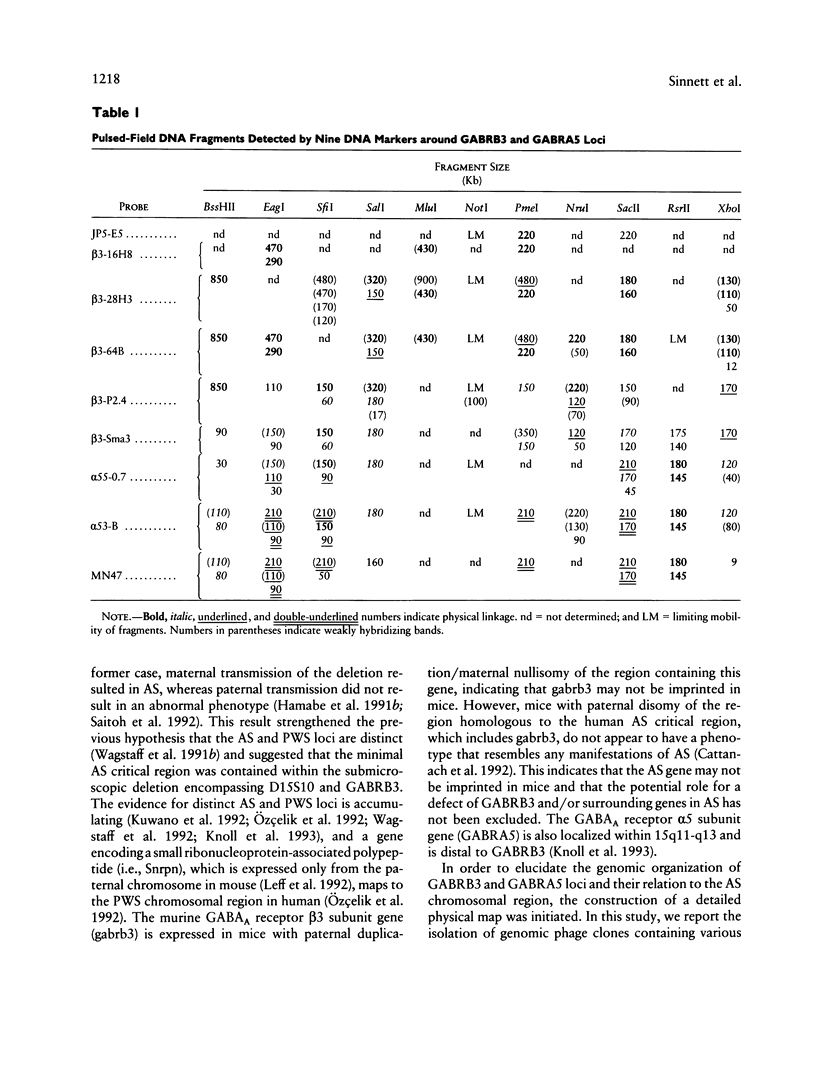
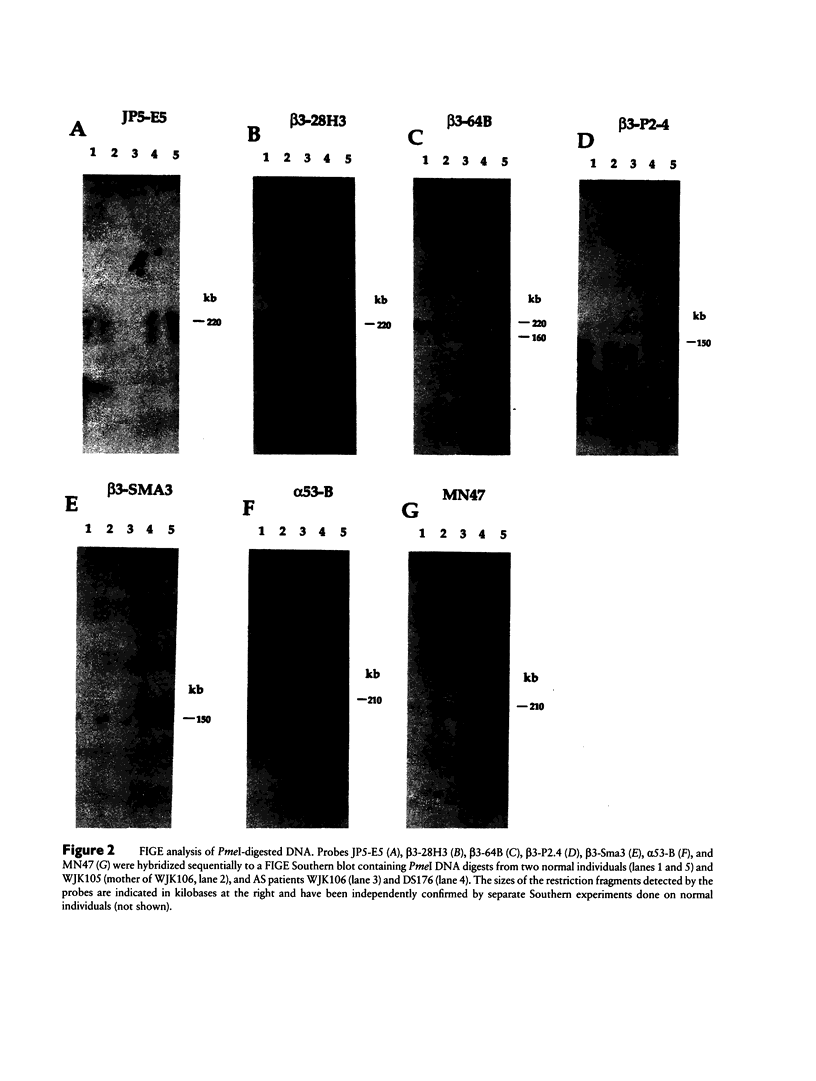
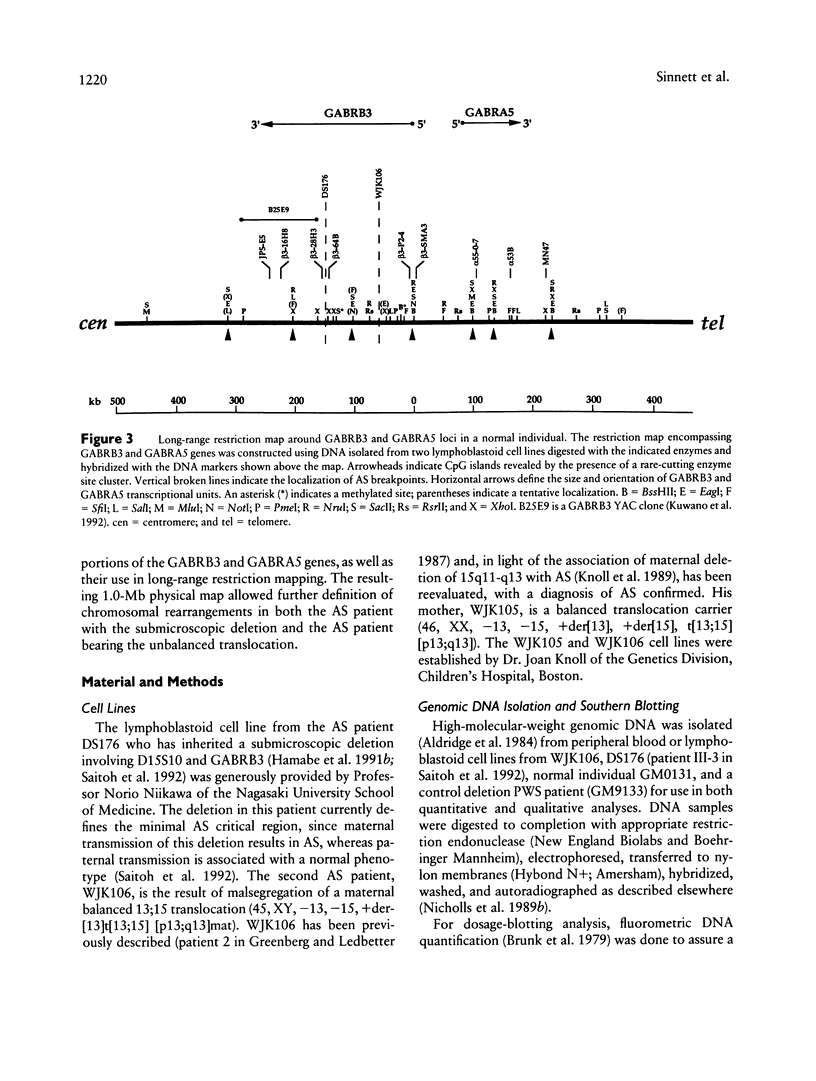
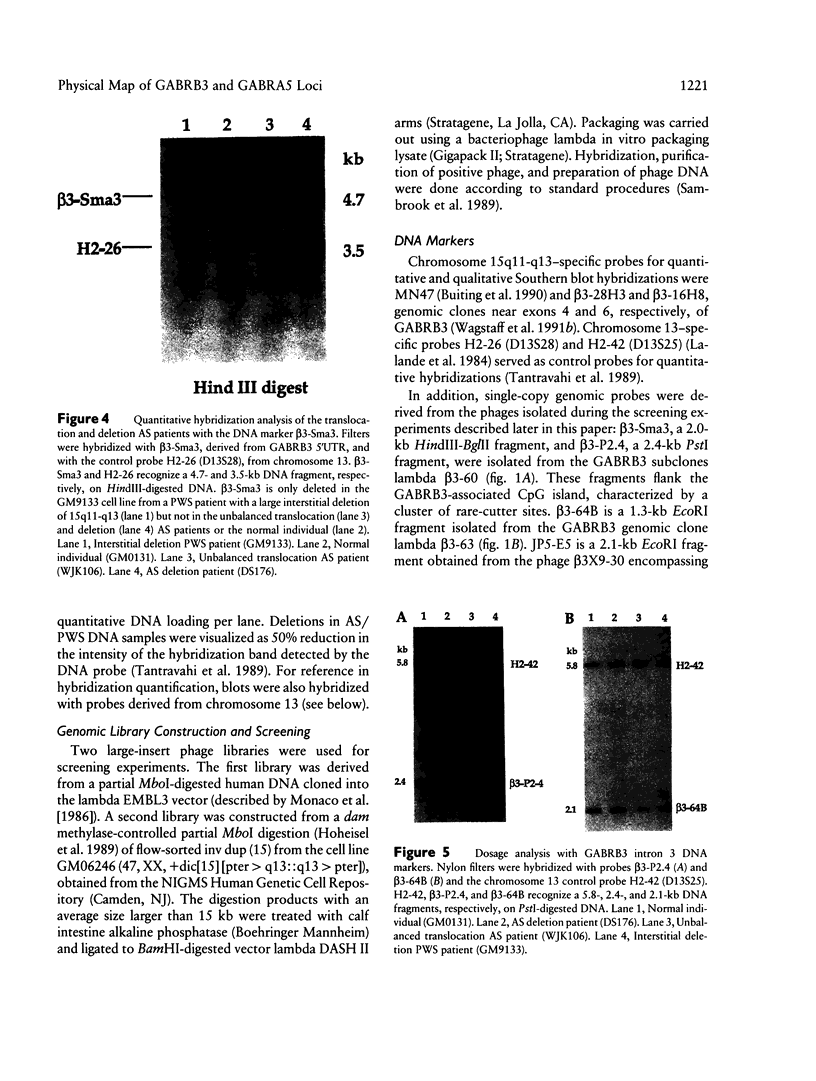
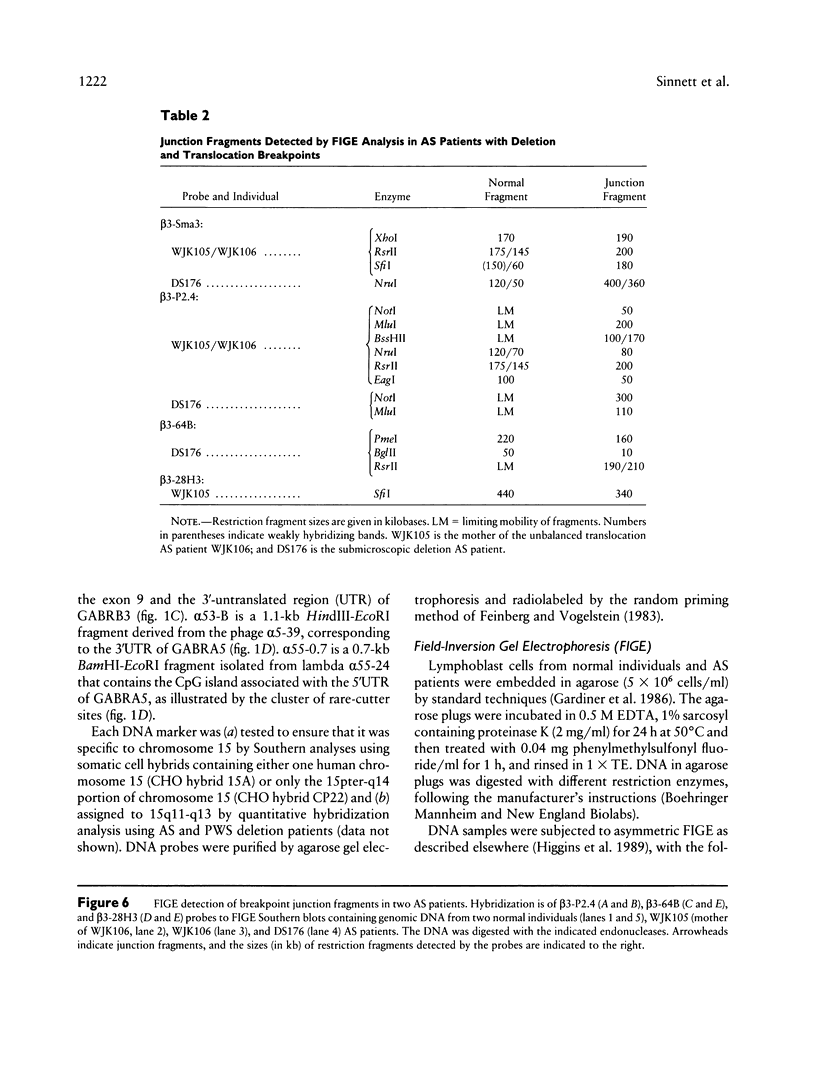
The gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptors are a family of ligand-gated chloride channels constituting the major inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the nervous system. In order to determine the genomic organization of the GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit gene (GABRB3) and alpha 5 subunit gene (GABRA5) in chromosome 15q11-q13, we have constructed a high-resolution physical map using the combined techniques of field-inversion gel electrophoresis and phage genomic library screening. This map, which covers nearly 1.0 Mb, shows that GABRB3 and GABRA5 are separated by less than 100 kb and are arranged in a head-to-head configuration. GABRB3 encompasses approximately 250 kb, while GABRA5 is contained within 70 kb. This difference in size is due in large part to an intron of 150 kb within GABRB3. We have also identified seven putative CpG islands within a 600-kb interval. Chromosomal rearrangement breakpoints--in one Angelman syndrome (AS) patient with an unbalanced translocation and in another patient with a submicroscopic deletion--are located within the large GABRB3 intron. These findings will facilitate chromosomal walking strategies for cloning the regions disrupted by the DNA rearrangements in these AS patients and will be valuable for mapping new genes to the AS chromosomal region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Bond C. T., Douglass J., Herbert E. Two mammalian genes transcribed from opposite strands of the same DNA locus. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1514–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.3547652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H. Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90077-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Duvoisin R. M., Connolly J. G., Wada E., Jensen A., Gardner P. D., Ballivet M., Deneris E. S., McKinnon D. Alpha 3, alpha 5, and beta 4: three members of the rat neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related gene family form a gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4472–4482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Jones K. C., James T. W. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle V. J., Fujita N., Ryder-Cook A. S., Derry J. M., Barnard P. J., Lebo R. V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Bateson A. N., Darlison M. G. Chromosomal localization of GABAA receptor subunit genes: relationship to human genetic disease. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Neumann M., Lüdecke H. J., Senger G., Claussen U., Antich J., Passarge E., Horsthemke B. Microdissection of the Prader-Willi syndrome chromosome region and identification of potential gene sequences. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Palmer C. G. Parental origin of chromosome 15 deletion in Prader-Willi syndrome. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1285–1286. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92745-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Barr J. A., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M., Beechey C. V., Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Jones J. A candidate mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome which shows an absence of Snrpn expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):270–274. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Curristin S., Zoghbi H., O'Hara B., Seldin M. F., Uhl G. R. Identification of a putative gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor subunit rho2 cDNA and colocalization of the genes encoding rho2 (GABRR2) and rho1 (GABRR1) to human chromosome 6q14-q21 and mouse chromosome 4. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90312-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorey T. M., Olsen R. W. Gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16747–16750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forus A., Myklebost O. A physical map of a 1.3-Mb region on the long arm of chromosome 12, spanning the GLI and LRP loci. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Ledbetter D. H. Deletions of proximal 15q without Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):813–820. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabe J., Fukushima Y., Harada N., Abe K., Matsuo N., Nagai T., Yoshioka A., Tonoki H., Tsukino R., Niikawa N. Molecular study of the Prader-Willi syndrome: deletion, RFLP, and phenotype analyses of 50 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):54–63. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabe J., Kuroki Y., Imaizumi K., Sugimoto T., Fukushima Y., Yamaguchi A., Izumikawa Y., Niikawa N. DNA deletion and its parental origin in Angelman syndrome patients. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):64–68. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Hansen M. F., Cavenee W. K., Lalande M. Molecular detection of chromosomal translocations that disrupt the putative retinoblastoma susceptibility locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. C., Wharton R., Elias E., Mandell F., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Clinical heterogeneity associated with deletions in the long arm of chromosome 15: report of 3 new cases and their possible genetic significance. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Fraser C. M. A strong promoter element is located between alternative exons of a gene encoding the human gamma-aminobutyric acid-type A receptor beta 3 subunit (GABRB3). J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4420–4428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Glatt K., Graham J. M., Jr, Kaplan L., Lalande M. Angelman syndrome: three molecular classes identified with chromosome 15q11q13-specific DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):149–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Graham J. M., Jr, Lalande M., Latt S. A. Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes share a common chromosome 15 deletion but differ in parental origin of the deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):285–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Sinnett D., Wagstaff J., Glatt K., Wilcox A. S., Whiting P. M., Wingrove P., Sikela J. M., Lalande M. FISH ordering of reference markers and of the gene for the alpha 5 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor (GABRA5) within the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndrome chromosomal regions. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):183–189. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofuji P., Wang J. B., Moss S. J., Huganir R. L., Burt D. R. Generation of two forms of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor gamma 2-subunit in mice by alternative splicing. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):713–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande M., Dryja T. P., Schreck R. R., Shipley J., Flint A., Latt S. A. Isolation of human chromosome 13-specific DNA sequences cloned from flow sorted chromosomes and potentially linked to the retinoblastoma locus. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Dec;13(4):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen F., Gundersen G., Lopez R., Prydz H. CpG islands as gene markers in the human genome. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1095–1107. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90024-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasham A., Vreugdenhil E., Bateson A. N., Barnard E. A., Darlison M. G. Conserved organization of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor genes: cloning and analysis of the chicken beta 4-subunit gene. J Neurochem. 1991 Jul;57(1):352–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Riccardi V. M., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J., Keenan B. S., Crawford J. D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Brannan C. I., Reed M. L., Ozçelik T., Francke U., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Maternal imprinting of the mouse Snrpn gene and conserved linkage homology with the human Prader-Willi syndrome region. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):259–264. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Kenwrick S., Gamel P., Fisher K., Gitschier J. Evidence for a third transcript from the human factor VIII gene. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):585–589. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Toth-Fejel S., Allen L. J., Black M., Brown M. G., Budden S., Cohen R., Friedman J. M., Kalousek D., Zonana J. Comparison of the 15q deletions in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: specific regions, extent of deletions, parental origin, and clinical consequences. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):333–349. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., Clayton-Smith J., Nichols M., Robb S., Webb T., Armour J. A., Jeffreys A. J., Pembrey M. E. Uniparental paternal disomy in Angelman's syndrome. Lancet. 1991 Mar 23;337(8743):694–697. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90278-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima N., Horiuchi R., Shibuya Y., Fukushige S., Matsubara K., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. Two erbA homologs encoding proteins with different T3 binding capacities are transcribed from opposite DNA strands of the same genetic locus. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Mauron A., Stalder R., Alliod C., Ballivet M. Structure linkage, and sequence of the two genes encoding the delta and gamma subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7975–7979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Glatt K., Hersh J. H., Brewster T. D., Graham J. M., Jr, Wurster-Hill D., Wharton R., Latt S. A. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms within proximal 15q and their use in molecular cytogenetics and the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 May;33(1):66–77. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozçelik T., Leff S., Robinson W., Donlon T., Lalande M., Sanjines E., Schinzel A., Francke U. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N (SNRPN), an expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome critical region. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):265–269. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pembrey M., Fennell S. J., van den Berghe J., Fitchett M., Summers D., Butler L., Clarke C., Griffiths M., Thompson E., Super M. The association of Angelman's syndrome with deletions within 15q11-13. J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;26(2):73–77. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöschl E., Pollner R., Kühn K. The genes for the alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) chains of human basement membrane collagen type IV are arranged head-to-head and separated by a bidirectional promoter of unique structure. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2687–2695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Kunze J., Ladanyi L., Enders H., Klein-Vogler U., Niemann G. Exclusion of the GABAA-receptor beta 3 subunit gene as the Angelman's syndrome gene. Lancet. 1993 Jan 9;341(8837):122–123. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92606-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bottani A., Xie Y. G., Balakrishman J., Binkert F., Mächler M., Prader A., Schinzel A. Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1219–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S., Kubota T., Ohta T., Jinno Y., Niikawa N., Sugimoto T., Wagstaff J., Lalande M. Familial Angelman syndrome caused by imprinted submicroscopic deletion encompassing GABAA receptor beta 3-subunit gene. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91686-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets D. F., Hamel B. C., Nelen M. R., Smeets H. J., Bollen J. H., Smits A. P., Ropers H. H., van Oost B. A. Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome in cousins from a family with a translocation between chromosomes 6 and 15. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):807–811. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203193261206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Webb T., Pembrey M. E., Nichols M., Malcolm S. Maternal origin of deletion 15q11-13 in 25/25 cases of Angelman syndrome. Hum Genet. 1992 Feb;88(4):376–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00215668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Poustka A., Spurr N. K., Seeburg P. H. The murine GABAA receptor delta-subunit gene: structure and assignment to human chromosome 1. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;9(8):561–568. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi U., Nicholls R. D., Stroh H., Ringer S., Neve R. L., Kaplan L., Wharton R., Wurster-Hill D., Graham J. M., Jr, Cantú E. S. Quantitative calibration and use of DNA probes for investigating chromosome abnormalities in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 May;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Chaillet J. R., Lalande M. The GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit gene: characterization of a human cDNA from chromosome 15q11q13 and mapping to a region of conserved synteny on mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90034-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Knoll J. H., Fleming J., Kirkness E. F., Martin-Gallardo A., Greenberg F., Graham J. M., Jr, Menninger J., Ward D., Venter J. C. Localization of the gene encoding the GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit to the Angelman/Prader-Willi region of human chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):330–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagstaff J., Knoll J. H., Glatt K. A., Shugart Y. Y., Sommer A., Lalande M. Maternal but not paternal transmission of 15q11-13-linked nondeletion Angelman syndrome leads to phenotypic expression. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):291–294. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting P., McKernan R. M., Iversen L. L. Another mechanism for creating diversity in gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptors: RNA splicing directs expression of two forms of gamma 2 phosphorylation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9966–9970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox A. S., Warrington J. A., Gardiner K., Berger R., Whiting P., Altherr M. R., Wasmuth J. J., Patterson D., Sikela J. M. Human chromosomal localization of genes encoding the gamma 1 and gamma 2 subunits of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor indicates that members of this gene family are often clustered in the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5857–5861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Gray B. A., Hendrickson J. E., Stone J. W., Cantú E. S. Incidence of 15q deletions in the Angelman syndrome: a survey of twelve affected persons. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Mar;32(3):339–345. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Stone J. W., Gray B. A., Cantu E. S., Ostrer H. Maternal origin of 15q11-13 deletions in Angelman syndrome suggests a role for genomic imprinting. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):350–353. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Fried M. A mouse locus at which transcription from both DNA strands produces mRNAs complementary at their 3' ends. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):275–279. doi: 10.1038/322275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]