Abstract
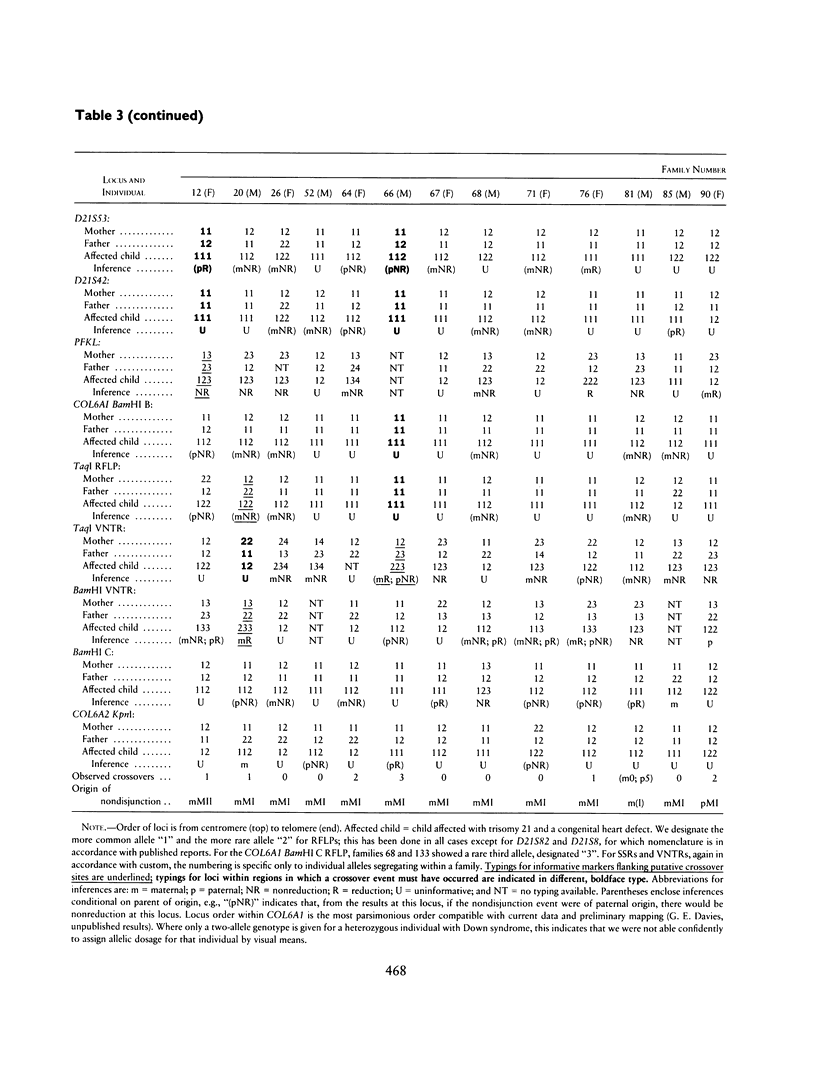
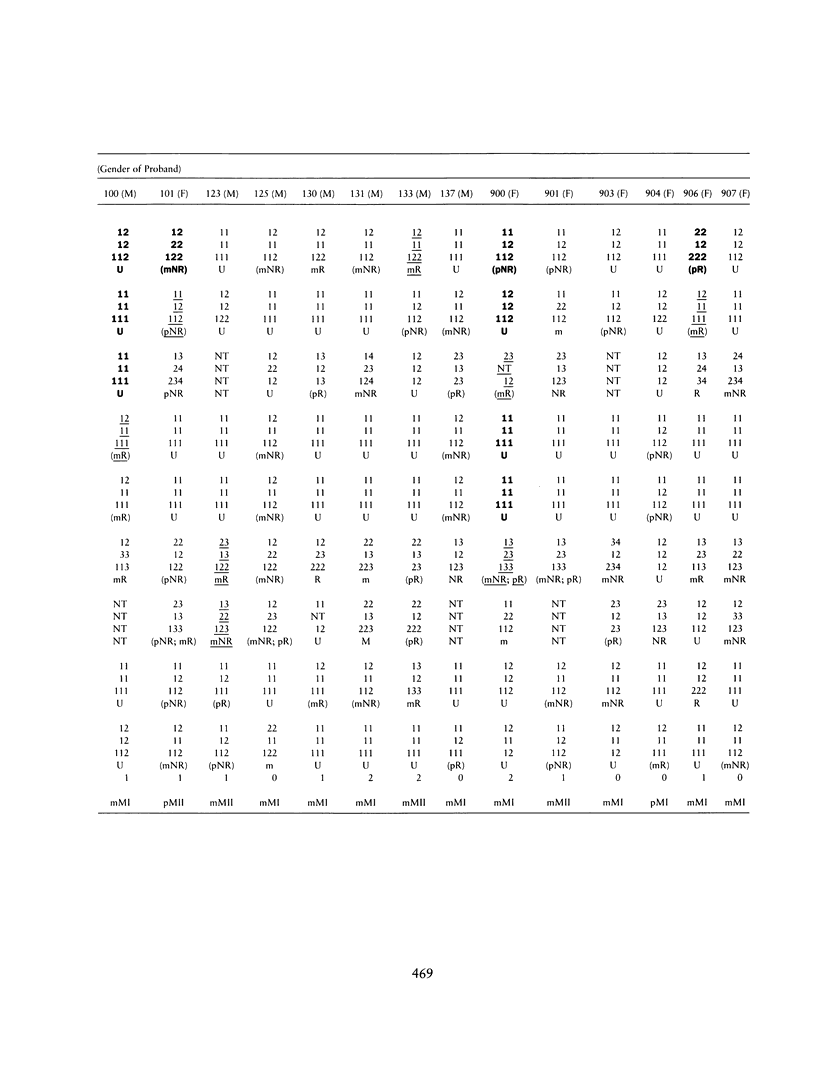
We have used DNA polymorphisms to study meiotic crossovers of chromosome 21q in 27 nuclear families. Each family had a child with Down syndrome and a congenital heart defect. Twenty DNA polymorphisms on chromosome 21 were used to determine parental and meiotic origin of nondisjunction and to identify crossovers. Twenty-four cases were of maternal origin, and three were of paternal origin. Twenty-two unequivocal crossover events were identified. Sixteen crossovers were observed in 22 chromosome pairs nondisjoining at the second meiotic division. Fifty percent of crossover events in MI nondisjunction are detectable by molecular genetic means. Thus, the results suggest that, in this sample, each nondisjoined chromosome 21 pair has been involved in at least one crossover event.
Full text
PDF
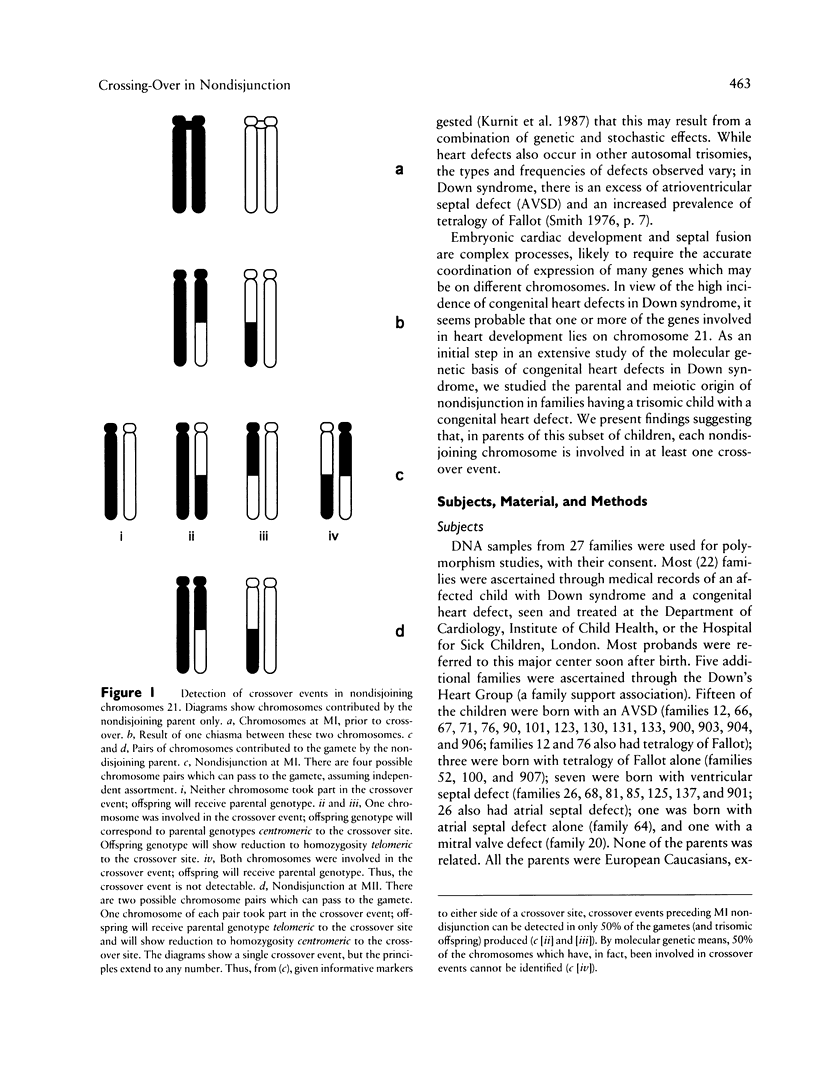
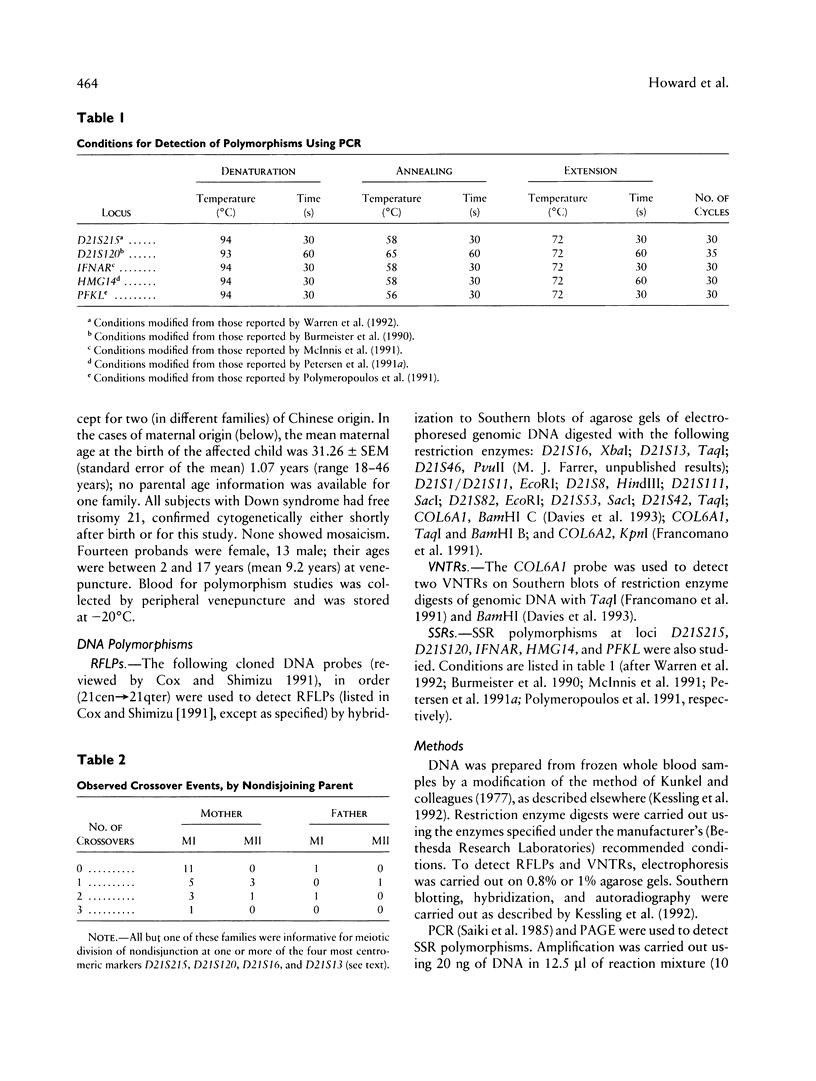

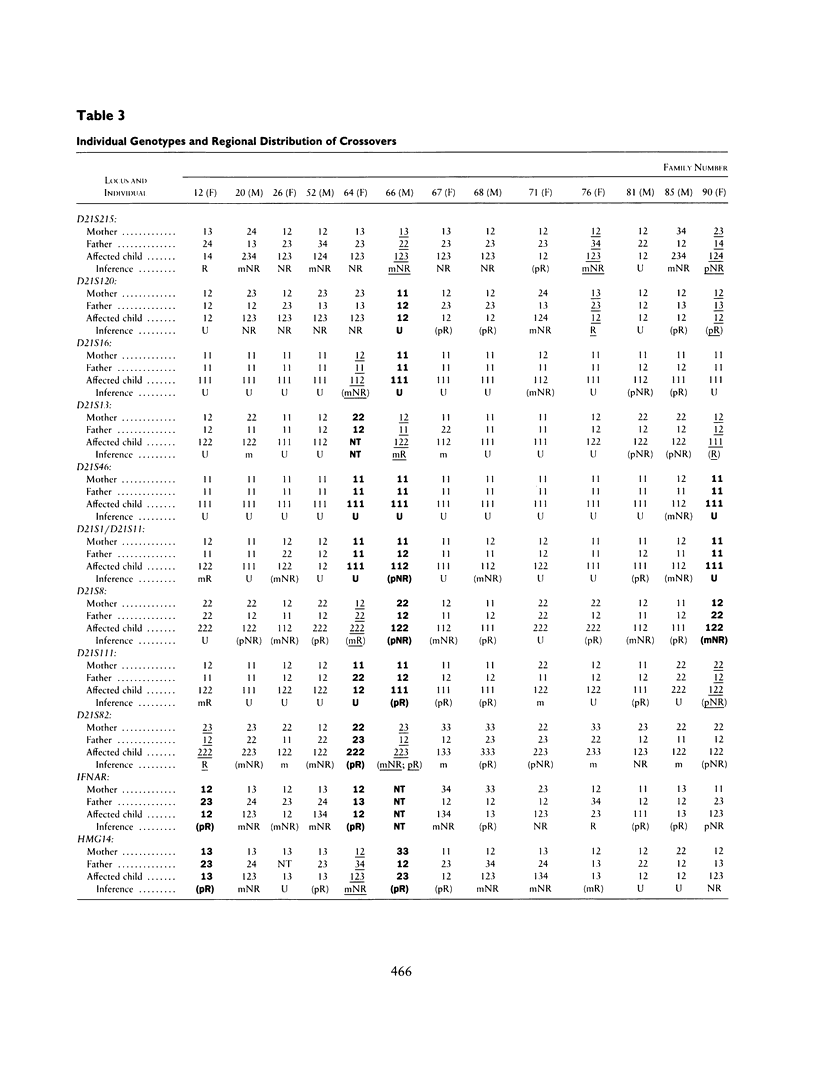
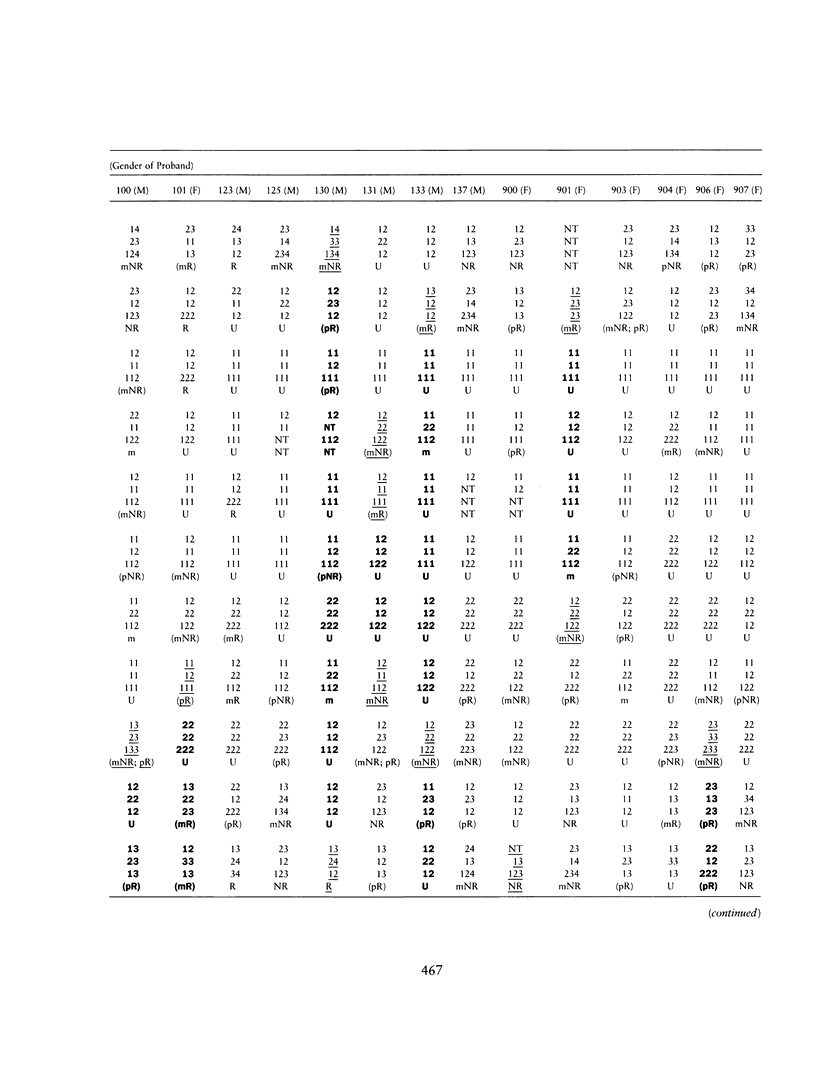


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Petersen M. B., McInnis M. G., Adelsberger P. A., Schinzel A. A., Binkert F., Pangalos C., Raoul O., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Hafez M. The meiotic stage of nondisjunction in trisomy 21: determination by using DNA polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):544–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmelster M., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism located at D21S120. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4969–4969. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Howard C. M., Gorman L. M., Farrer M. J., Holland A. J., Williamson R., Kessling A. M. Polymorphisms and linkage disequilibrium in the COL6A1 and COL6A2 gene cluster: novel DNA polymorphisms in the region of a candidate gene for congenital heart defects in Down's syndrome. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):521–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00217452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francomano C. A., Cutting G. R., McCormick M. K., Chu M. L., Timpl R., Hong H. K., Antonarakis S. E. The COL6A1 and COL6A2 genes exist as a gene cluster and detect highly informative DNA polymorphisms in the telomeric region of human chromosome 21q. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):162–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00204174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galt J., Boyd E., Connor J. M., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Isolation of chromosome-21-specific DNA probes and their use in the analysis of nondisjunction in Down syndrome. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):113–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00293885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T. J., Jacobs P. A. Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:69–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M. Chiasma distribution at diakinesis in the normal human male. Hereditas. 1974;76(1):55–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1974.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M., Lawrie N. M., Laurie D. A. Chiasma-based genetic maps of chromosome 21. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:148–154. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Warren A. C., Taylor E. W., Colyer C. R., Meyers D. A., Antonarakis S. E. Alphoid DNA polymorphisms for chromosome 21 can be distinguished from those of chromosome 13 using probes homologous to both. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessling A., Ouellette S., Bouffard O., Chamberland A., Bétard C., Selinger E., Xhignesse M., Lussier-Cacan S., Davignon J. Patterns of association between genetic variability in apolipoprotein (apo) B, apo AI-CIII-AIV, and cholesterol ester transfer protein gene regions and quantitative variation in lipid and lipoprotein traits: influence of gender and exogenous hormones. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):92–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Layton W. M., Matthysse S. Genetics, chance, and morphogenesis. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):979–995. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Hultén M. A. Further studies on bivalent chiasma frequency in human males with normal karyotypes. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;49(Pt 3):189–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnis M. G., Lutfalla G., Slaugenhaupt S., Petersen M. B., Uze G., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. Linkage mapping of highly informative DNA polymorphisms within the human interferon-alpha receptor gene on chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):573–576. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90064-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer H., Hamers G. J., Jongbloed R. J., Vaes-Peeters G. P., van der Hulst R. R., Geraedts J. P. Distribution of meiotic recombination along nondisjunction chromosomes 21 in Down syndrome determined using cytogenetics and RFLP haplotyping. Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;83(3):280–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00285173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Schinzel A. A., Binkert F., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Collins F. A., Economou E. P., Antonarakis S. E. Use of short sequence repeat DNA polymorphisms after PCR amplification to detect the parental origin of the additional chromosome 21 in Down syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. B., Frantzen M., Antonarakis S. E., Warren A. C., Van Broeckhoven C., Chakravarti A., Cox T. K., Lund C., Olsen B., Poulsen H. Comparative study of microsatellite and cytogenetic markers for detecting the origin of the nondisjoined chromosome 21 in Down syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):516–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Rath D. S., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human liver-type 6-phosphofructokinase (PFKL) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2517–2517. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Takaesu N., Freeman S. B., Grantham M., Phillips C., Blackston R. D., Jacobs P. A., Cockwell A. E., Freeman V., Uchida I. Trisomy 21: association between reduced recombination and nondisjunction. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Sep;49(3):608–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. Correction of the evaluation of recombination in meiosis I and II nondisjunction in trisomy 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1137–1138. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wexler N. S., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21: analysis of recombination as a function of sex and age. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):551–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Wong C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Halloran S. L., Watkins P. C., Metaxotou C., Antonarakis S. E. Evidence for reduced recombination on the nondisjoined chromosomes 21 in Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.2955519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Petersen M. B., Van Hul W., McInnis M. G., Van Broeckhoven C., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. D21S215 is a (GT)n polymorphic marker close to centromeric alphoid sequences on chromosome 21. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1365–1367. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90072-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


