Abstract
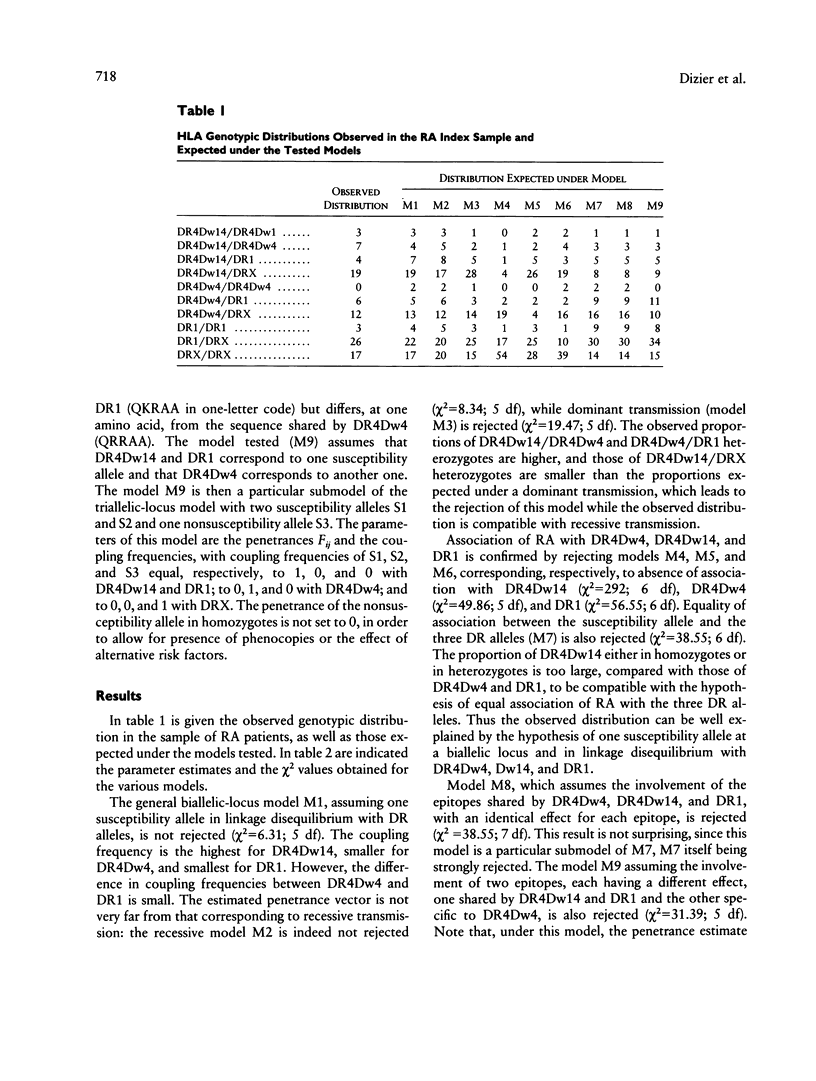
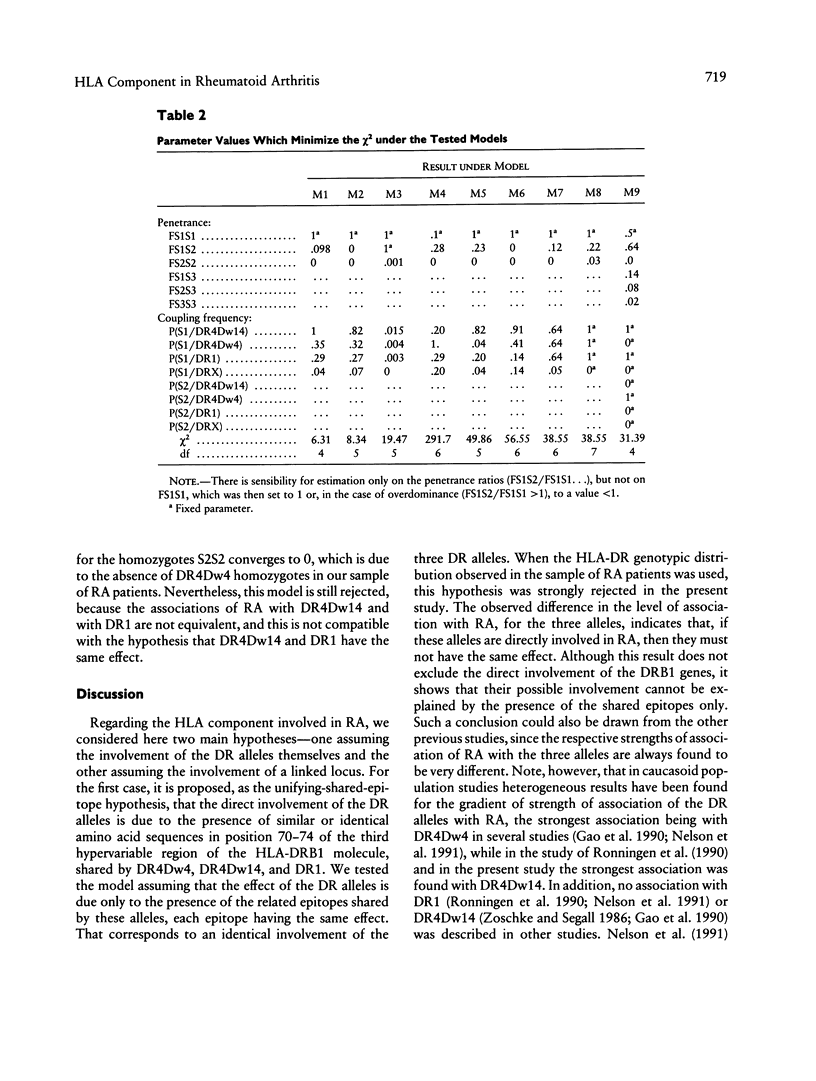
In order to investigate the HLA component involved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we tested genetic models by the marker association-segregation chi 2 (MASC) method, using the HLA genotypic distribution observed in a sample of 97 RA patients. First we tested models assuming the involvement of a susceptibility gene linked to the DR locus. We showed that the present data are compatible with a simple model assuming the effect of a recessive allele of a biallelic locus linked to the DR locus and without any assumption of synergistic effect. Then we considered models assuming the direct involvement of the DR allele products, and we tested the unifying-shared-epitope hypothesis, which has been proposed. Under this hypothesis the DR alleles are assumed to be directly involved in the susceptibility to the disease because of the presence of similar or identical amino acid sequences in position 70-74 of the third hypervariable region of the DRBI molecules, shared by the RA-associated DR alleles DR4Dw4, DR4Dw14, and DR1. This hypothesis was strongly rejected with the present data. In the case of the direct involvement of the DR alleles, hypotheses more complex than the unifying-shared-epitope hypothesis would have to be considered.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerget-Darpoux F., Babron M. C., Prum B., Lathrop G. M., Deschamps I., Hors J. A new method to test genetic models in HLA associated diseases: the MASC method. Ann Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;52(Pt 3):247–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1988.tb01102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. L. Genes predisposing to IDDM in multiplex families. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(1):101–106. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. J., Olsen N. J., Pincus T., Stastny P. HLA-DR alleles with naturally occurring amino acid substitutions and risk for development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jul;33(7):939–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimberg J., Nawoschik S., Belluscio L., McKee R., Turck A., Eisenberg A. A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8390–8390. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaraquemada D., Ollier W., Awad J., Young A., Silman A., Roitt I. M., Corbett M., Hay F., Cosh J. A., Maini R. N. HLA and rheumatoid arthritis: a combined analysis of 440 British patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Aug;45(8):627–636. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.8.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Khan M. K. Analysis of genetic susceptibility to familial rheumatoid arthritis. Dis Markers. 1986 Jun;4(1-2):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Juji T., Mitsui H., Sonozaki H., Okitsu K. HLA DR4 and rheumatoid arthritis in Japanese people. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):299–302. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. L., Mickelson E., Masewicz S., Barrington R., Dugowson C., Koepsell T., Hansen J. A. Dw14(DRB1*0404) is a Dw4-dependent risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Rethinking the "shared epitope" hypothesis. Tissue Antigens. 1991 Oct;38(4):145–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1991.tb01888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Nishimura Y. K., Tanimoto K., Horiuchi Y., Abe C., Shiokawa Y., Abe T., Katagiri M., Yoshiki T., Sasazuki T. Association between HLA and Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1982 Oct;5(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Thomson G., Khan M. A., Grennan D. M., Sanders P., Dyer P., Dostal C. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Feb;27(2):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb01499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pile K. D., Tikly M., Bell J. I., Wordsworth B. P. HLA-DR antigens and rheumatoid arthritis in black South Africans: a study of ethnic groups. Tissue Antigens. 1992 Mar;39(3):138–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1992.tb01924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby A. S., Silman A. J., Voelm L., Gregory J. C., Ollier W. E., Khan M. A., Nepom G. T., Thomson G. Investigating the HLA component in rheumatoid arthritis: an additive (dominant) mode of inheritance is rejected, a recessive mode is preferred. Genet Epidemiol. 1991;8(3):153–175. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370080303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønningen K. S., Spurkland A., Egeland T., Iwe T., Munthe E., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Rheumatoid arthritis may be primarily associated with HLA-DR4 molecules sharing a particular sequence at residues 67-74. Tissue Antigens. 1990 Nov;36(5):235–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1990.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):869–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. Investigation of the mode of inheritance of the HLA associated diseases by the method of antigen genotype frequencies among diseased individuals. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Feb;21(2):81–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G., Robinson W. P., Kuhner M. K., Joe S., Klitz W. HLA and insulin gene associations with IDDM. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(1):155–160. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. The affected-pedigree-member method of linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):315–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willkens R. F., Nepom G. T., Marks C. R., Nettles J. W., Nepom B. S. Association of HLA-Dw16 with rheumatoid arthritis in Yakima Indians. Further evidence for the "shared epitope" hypothesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jan;34(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth B. P., Lanchbury J. S., Sakkas L. I., Welsh K. I., Panayi G. S., Bell J. I. HLA-DR4 subtype frequencies in rheumatoid arthritis indicate that DRB1 is the major susceptibility locus within the HLA class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth P., Pile K. D., Buckely J. D., Lanchbury J. S., Ollier B., Lathrop M., Bell J. I. HLA heterozygosity contributes to susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):585–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoschke D., Segall M. Dw subtypes of DR4 in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for a preferential association with Dw4. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jan;15(1):118–124. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


