Abstract
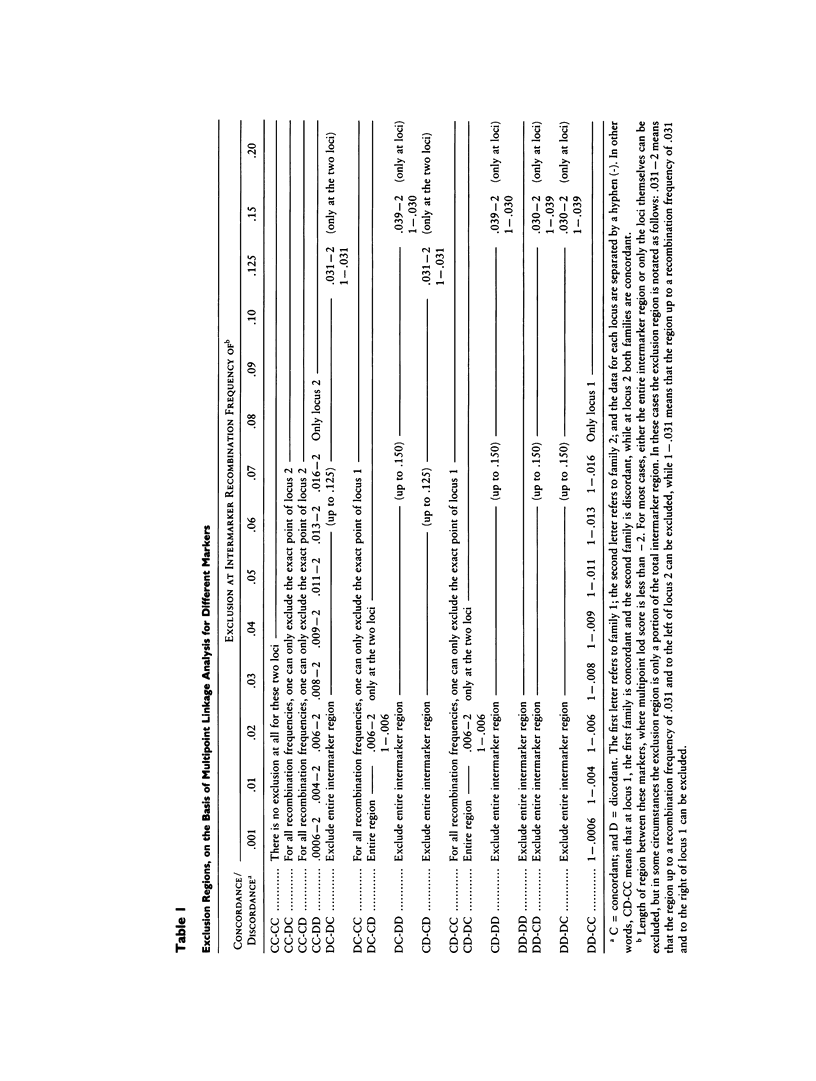
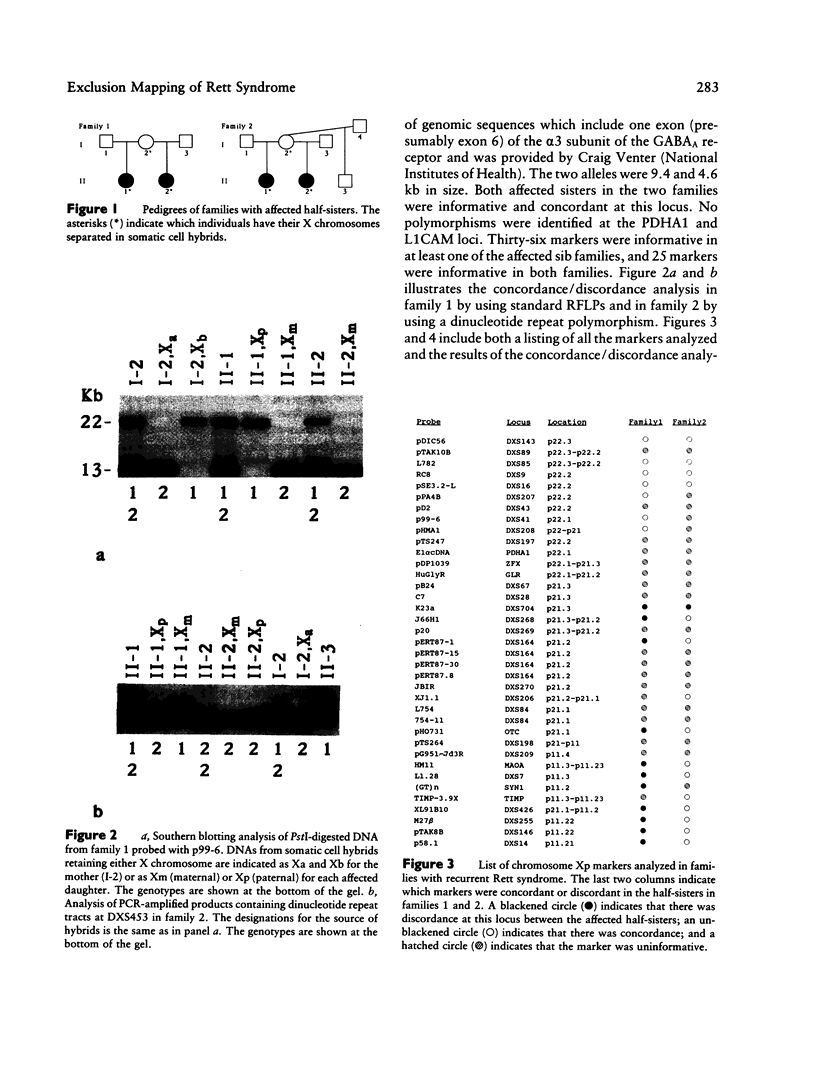
Rett syndrome is a neurologic disorder characterized by early normal development followed by regression, acquired deceleration of head growth, autism, ataxia, and stereotypic hand movements. The exclusive occurrence of the syndrome in females and the occurrence of a few familial cases with inheritance through maternal lines suggest that this disorder is most likely secondary to a mutation on the X chromosome. To address this hypothesis and to identify candidate regions for the Rett syndrome gene locus, genotypic analysis was performed in two families with maternally related affected half-sisters by using 63 DNA markers from the X chromosome. Maternal and paternal X chromosomes from the affected sisters were separated in somatic cell hybrids and were examined for concordance/discordance of maternal alleles at the tested loci. Thirty-six markers were informative in at least one of the two families, and 25 markers were informative in both families. Twenty loci were excluded as candidates for the Rett syndrome gene, on the basis of discordance for maternal alleles in the half-sisters. Nineteen of the loci studied were chosen for multipoint linkage analysis because they have been previously genetically mapped using a large number of meioses from reference families. Using the exclusion criterion of a lod score less than -2, we were able to exclude the region between the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus and the DXS456 locus. This region extends from Xp21.2 to Xq21-q23. The use of the multipoint linkage analysis approach outlined in this study should allow the exclusion of additional regions of the X chromosome as new markers are analyzed. This in turn will result in a defined region of the X chromosome that should be searched for candidate sequences for the Rett syndrome gene in both familial and sporadic cases.
Full text
PDF







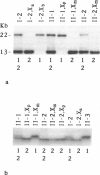
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo T., Kruse T. A., Ahrens P., Albertsen H. M., Eriksson A. W., de la Chapelle A. Genetic mapping of 12 marker loci in the Xp22.3-p21.2 region. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):599–603. doi: 10.1007/BF00201548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archidiacono N., Lerone M., Rocchi M., Anvret M., Ozcelik T., Francke U., Romeo G. Rett syndrome: exclusion mapping following the hypothesis of germinal mosaicism for new X-linked mutations. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):604–606. doi: 10.1007/BF00201549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan K. B., Ayres T. M., Popko B., Takahashi N., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Repetitive DNA (TGGA)n 5' to the human myelin basic protein gene: a new form of oligonucleotide repetitive sequence showing length polymorphism. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):16–22. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Monaco A. P., Nussbaum R. L., Willard H. F. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):254–313. doi: 10.1159/000133019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Civitello A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T. DNA typing and genetic mapping with trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeats. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):746–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison K. A., Fill C. P., Zoghbi H. Y. MspI and MboI polymorphisms at the DXS704 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5101–5101. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5101-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Deletion and amplification of the HGPRT locus in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1086–1096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B., Aicardi J., Dias K., Ramos O. A progressive syndrome of autism, dementia, ataxia, and loss of purposeful hand use in girls: Rett's syndrome: report of 35 cases. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):471–479. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B., Rasmussen P. "Forme fruste" of Rett syndrome--a case report. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;1:175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B. Rett syndrome: Swedish approach to analysis of prevalence and cause. Brain Dev. 1985;7(3):276–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho L., Wexler I. D., Liu T. C., Thekkumkara T. J., Patel M. S. Characterization of cDNAs encoding human pyruvate dehydrogenase alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5330–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Edwards A., Pettigrew A. L., Herrera C. A., Hammond H. A., Caskey C. T., Zoghbi H. Y., Ledbetter D. H. Linkage of the gene for an X-linked mental retardation disorder to a hypervariable (AGAT)n repeat motif within the human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) locus (Xq26). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1312–1319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journel H., Melki J., Turleau C., Munnich A., de Grouchy J. Rett phenotype with X/autosome translocation: possible mapping to the short arm of chromosome X. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):142–147. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B. J., Sherman S. L., Ott J. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):387–394. doi: 10.1159/000133023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner C. U., Trofatter J. A., Mahtani M. M., Willard H. F., DeGennaro L. J. A highly polymorphic dinucleotide repeat on the proximal short arm of the human X chromosome: linkage mapping of the synapsin I/A-raf-1 genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):184–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., de Martinville B., Horwich A. L., Rosenberg L. E., Francke U. Human ornithine transcarbamylase locus mapped to band Xp21.1 near the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.6494904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Luty J. A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):397–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luty J. A., Guo Z., Willard H. F., Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S., Litt M. Five polymorphic microsatellite VNTRs on the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):776–783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Tacke R., Scherer H., Teplow D., Früh K., Schachner M. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):701–703. doi: 10.1038/334701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. Expression of the fragile (X) chromosome in an interspecific somatic cell hybrid. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):148–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00327113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Hsu Y. P., Bruns G., Powell J. F., Chen S., Weyler W., Utterback M., Zucker D., Haines J., Trofatter J. A. Human monoamine oxidase gene (MAOA): chromosome position (Xp21-p11) and DNA polymorphism. Genomics. 1988 Jul;3(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Phillips K., Betz H., Grenningloh G., Warner K., Hung W. Y., Laing N., Roses A. D. RFLPs of the gene for the human glycine receptor on the X-chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1785–1785. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Ledbetter S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS453, DXS454 and DXS458 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4037–4037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., Daiger S. P., McCall A., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Extensive DNA polymorphism at the factor XIIIa (F13A) locus and linkage to HLA. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;42(6):877–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., Ledbetter D. H., Schultz R., Percy A. K., Glaze D. G. A de novo X;3 translocation in Rett syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):148–151. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Y., Percy A. K., Schultz R. J., Fill C. Patterns of X chromosome inactivation in the Rett syndrome. Brain Dev. 1990;12(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(12)80194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoghbi H. Genetic aspects of Rett syndrome. J Child Neurol. 1988;3 (Suppl):S76–S78. doi: 10.1177/0883073888003001s15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]