Abstract
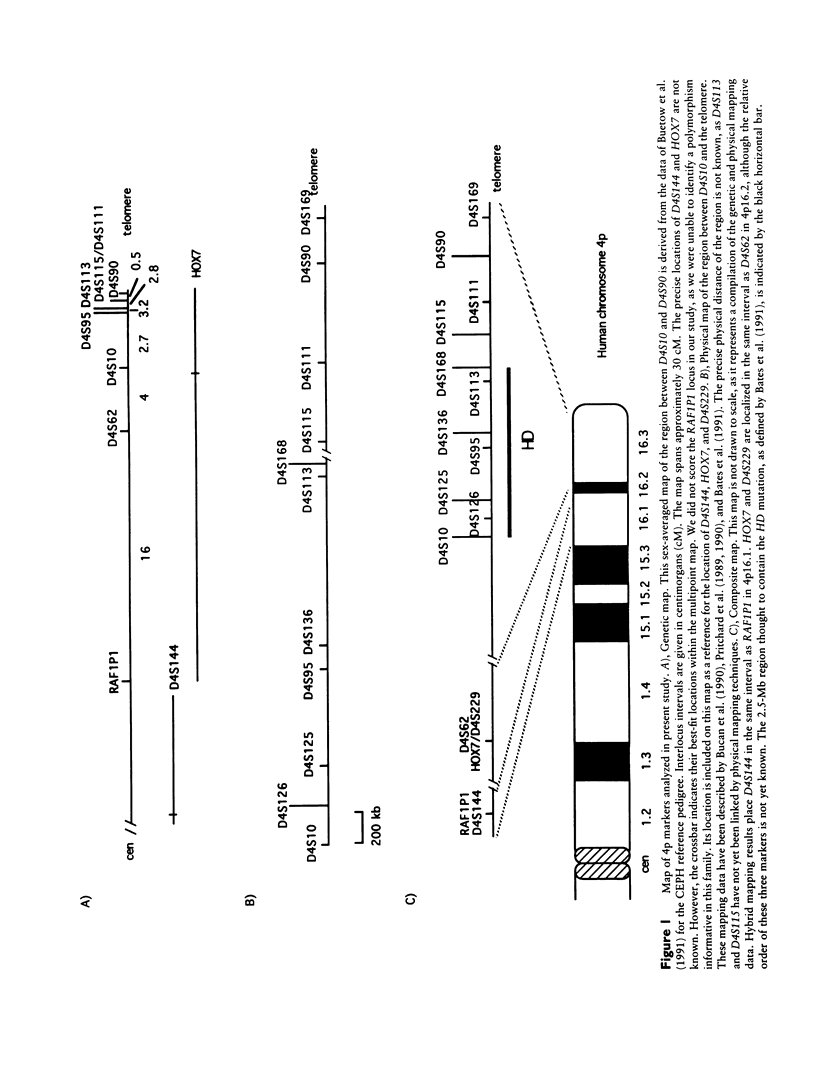
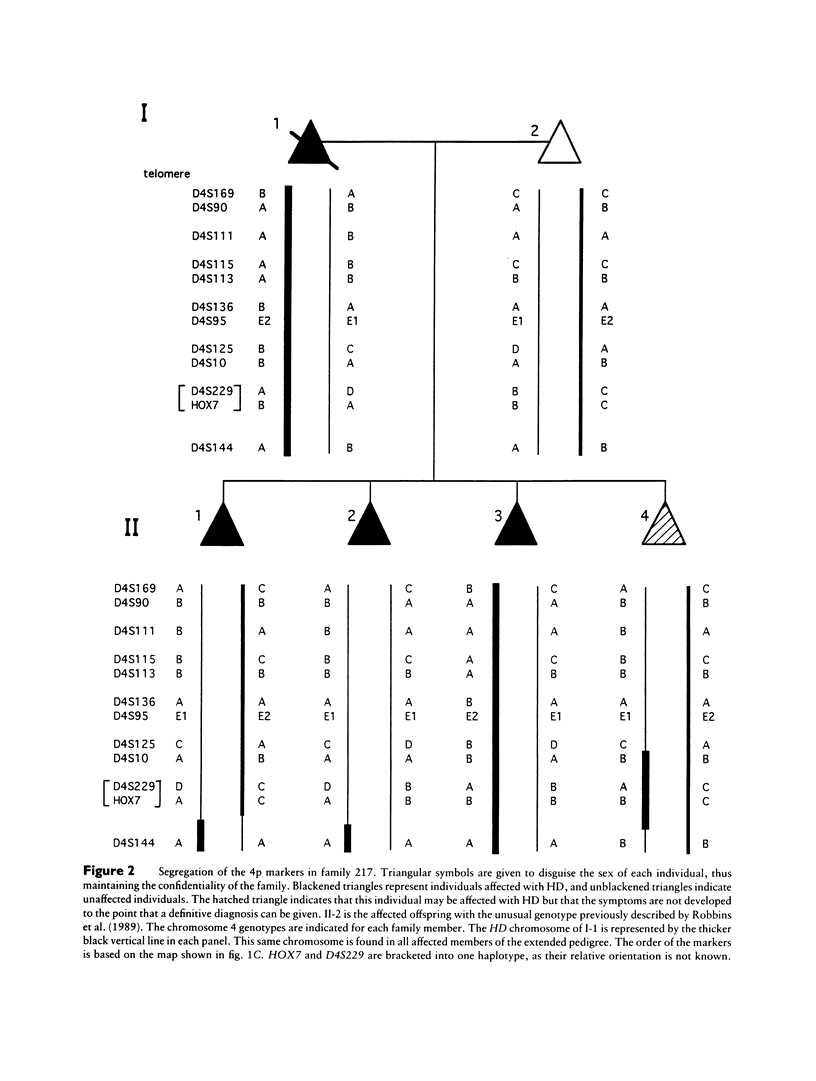
The Huntington disease (HD) mutation has been localized to human chromosome 4p16, in a 6-Mb region between the D4S10 locus and the 4p telomere. In a report by Robbins et al., a family was identified in which an affected individual failed to inherit three alleles within the 6-Mb region originating from the parental HD chromosome. To explain these results, it was suggested that the HD locus (HD) lies close to the telomere and that a recombination event took place between HD and the most telomeric marker examined, D4S90. As a test of this telomere hypothesis, we examined six members of this family, five of whom are affected with HD, for the segregation of 12 polymorphic markers from 4p16, including D4S169, which lies within 80 kb of the 4p telomere. We separated, in somatic cell hybrids, the chromosomes 4 from each family member, to determine the phase of marker alleles on each chromosome. We excluded nonpaternity by performing DNA fingerprint analyses on all six family members, and we found no evidence for chromosomal rearrangements when we used high-resolution karyotype analysis. We found that two affected siblings, including one of the patients originally described by Robbins et al., inherited alleles from the non-HD chromosome 4 of their affected parents, throughout the 6-Mb region. We found that a third affected sibling, also studied by Robbins et al., inherited alleles from the HD chromosome 4 of the affected parent, throughout the 6-Mb region. Finally, we found that a fourth sibling, who is likely affected with HD, has both a recombination event within the 6-Mb region and an additional recombination event in a more centromeric region of the short arm of chromosome 4. Our results argue against a telomeric location for HD and suggest that the HD mutation in this family is either associated with DNA predisposed to double recombination and/or gene conversion within the 6-Mb region or is in a gene that is outside this region and that is different from that mutated in most other families with HD.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S., Theilmann J., Buetow K., Hedrick A., Collins C., Weber B., Huggins M., Hayden M. Linkage disequilibrium and modification of risk for Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):595–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour J. A., Patel I., Thein S. L., Fey M. F., Jeffreys A. J. Analysis of somatic mutations at human minisatellite loci in tumors and cell lines. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron L., Curtis A., Shrimpton A. E., Holloway S., May H., Snell R. G., Brock D. J. Linkage disequilibrium and recombination make a telomeric site for the Huntington's disease gene unlikely. J Med Genet. 1991 Aug;28(8):520–522. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.8.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. P., MacDonald M. E., Baxendale S., Sedlacek Z., Youngman S., Romano D., Whaley W. L., Allitto B. A., Poustka A., Gusella J. F. A yeast artificial chromosome telomere clone spanning a possible location of the Huntington disease gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):762–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. P., MacDonald M. E., Baxendale S., Youngman S., Lin C., Whaley W. L., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F., Lehrach H. Defined physical limits of the Huntington disease gene candidate region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):7–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow K. H., Shiang R., Yang P., Nakamura Y., Lathrop G. M., White R., Wasmuth J. J., Wood S., Berdahl L. D., Leysens N. J. A detailed multipoint map of human chromosome 4 provides evidence for linkage heterogeneity and position-specific recombination rates. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):911–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmelster M., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism located at D21S120. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4969–4969. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bućan M., Zimmer M., Whaley W. L., Poustka A., Youngman S., Allitto B. A., Ormondroyd E., Smith B., Pohl T. M., MacDonald M. Physical maps of 4p16.3, the area expected to contain the Huntington disease mutation. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90442-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Haines J. L., Tanzi R. E., Wexler N. S., Penchaszadeh G. K., Harper P. S., Folstein S. E., Cassiman J. J., Myers R. H., Young A. B. Huntington disease: no evidence for locus heterogeneity. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Pritchard C. A., Uglum E., Casher D., Kobori J., Myers R. M. Segregation of the Huntington disease region of human chromosome 4 in a somatic cell hybrid. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Bonner T. I., Faryniarz A. G., Hobbs W. J., MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Folstein S. E., Conneally P. M. Localization of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Haines J. L., Zimmer M., Cheng S. V., Youngman S., Whaley W. L., Wexler N., Bucan M., Allitto B. A., Smith B. Recombination events suggest potential sites for the Huntington's disease gene. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelberg S. J., Plaetke R., Eldridge J. R., Ballard L., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Leppert M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Characterization of eight VNTR loci by agarose gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90134-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. A., Casher D., Uglum E., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Isolation and field-inversion gel electrophoresis analysis of DNA markers located close to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C., Casher D., Bull L., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. A cloned DNA segment from the telomeric region of human chromosome 4p is not detectably rearranged in Huntington disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7309–7313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism located at D4S169. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6347–6347. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6347-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Smead D. L., Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: localization within the region Xq13.1-q21.1 by linkage and deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):724–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B., Horn G. T., Merrill J. J., Klinger K. W. Characterization and rapid analysis of the highly polymorphic VNTR locus D4S125 (YNZ32), closely linked to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1991 Feb;9(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90247-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C., Theilmann J., Youngman S., Haines J., Altherr M. J., Harper P. S., Payne C., Junker A., Wasmuth J., Hayden M. R. Evidence from family studies that the gene causing Huntington disease is telomeric to D4S95 and D4S90. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):422–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M., Caro A. The mutation rate to Huntington's chorea. J Med Genet. 1982 Jun;19(3):161–167. doi: 10.1136/jmg.19.3.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Skarecky D., Bengtsson U., Magenis R. E., Carpenter N., Wasmuth J. J. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington disease gene from the G8 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassart G., Georges M., Monsieur R., Brocas H., Lequarre A. S., Christophe D. A sequence in M13 phage detects hypervariable minisatellites in human and animal DNA. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):683–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2880398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley W. L., Bates G. P., Novelletto A., Sedlacek Z., Cheng S., Romano D., Ormondroyd E., Allitto B., Lin C., Youngman S. Mapping of cosmid clones in Huntington's disease region of chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 Jan;17(1):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01233207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley W. L., Michiels F., MacDonald M. E., Romano D., Zimmer M., Smith B., Leavitt J., Bucan M., Haines J. L., Gilliam T. C. Mapping of D4S98/S114/S113 confines the Huntington's defect to a reduced physical region at the telomere of chromosome 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11769–11780. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman S., Shaw D. J., Gusella J. F., MacDonald M., Stanbridge E. J., Wasmuth J., Harper P. S. A DNA probe, D5 [D4S90] mapping to human chromosome 4p16.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1648–1648. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]