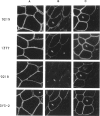
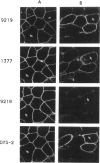
Abstract
Many Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients are known to have rare staining dystrophin-positive fibers, termed "revertants." The precise etiology of these rare fibers is unknown. The most likely explanation, however, is somatic mosaicism or somatic reversion/suppression. Immunocytochemistry was performed on serial sections from deleted and nondeleted patients, with a panel of antibodies--9219, 1377, 9218, and Dys-2--that span dystrophin. Both familial and nonfamilial patients possessed revertants. Either the same clusters or individual revertant fibers stained with amino- and carboxyl-terminal antibodies in all 14 DMD patients. In patients with deletions, revertants did not stain with antibodies raised to polypeptide sequences within the deletion. These results indicate that positively staining fibers are not the result of somatic mosaicism in deleted patients. Five of 10 patients without deletions had revertant fibers. In two of these patients, the revertant fibers did not stain with antibody 9218, which was generated against amino acids 2305-2554 and which corresponds to exons 48-52. The remaining antibodies from the panel stained the same fibers on separate serial sections in these two patients. The most likely mechanism giving rise to these positively staining fibers is a second site in-frame deletion. Antibodies generated to polypeptide sequences within deletions can be used to control for the natural occurrence of revertant fibers in myoblast transfer studies and may be useful in the detection of point mutations.
Full text
PDF



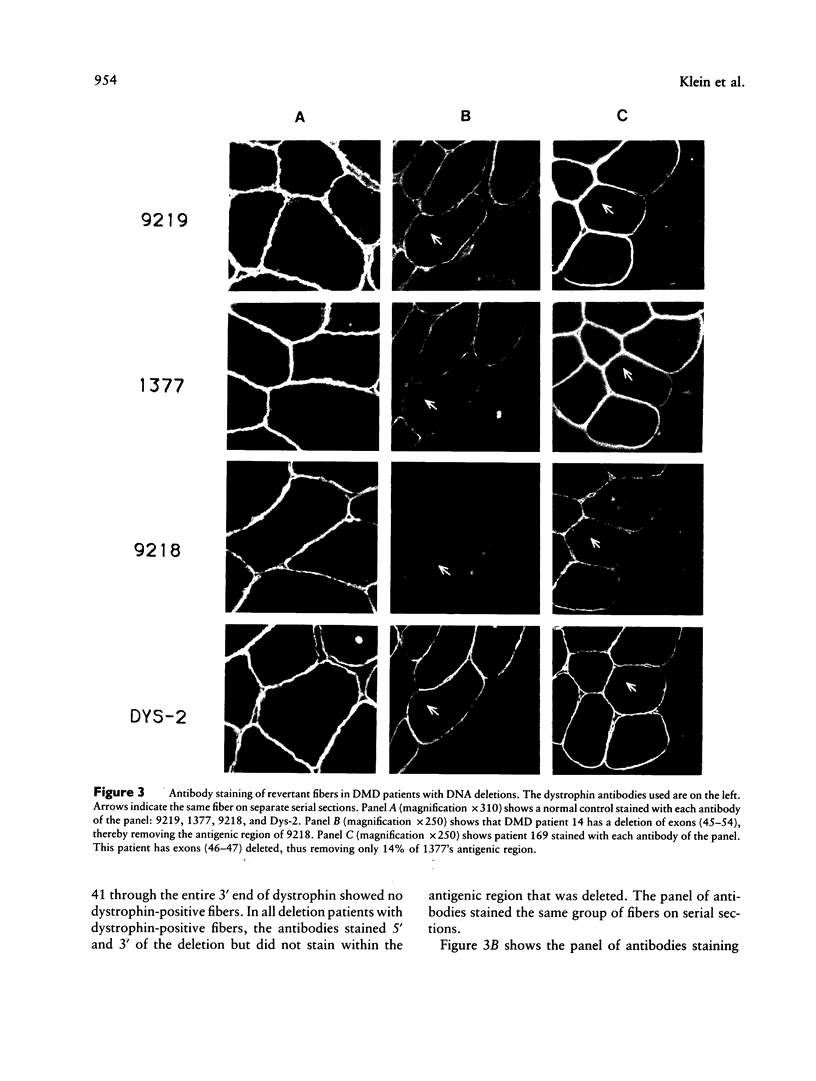
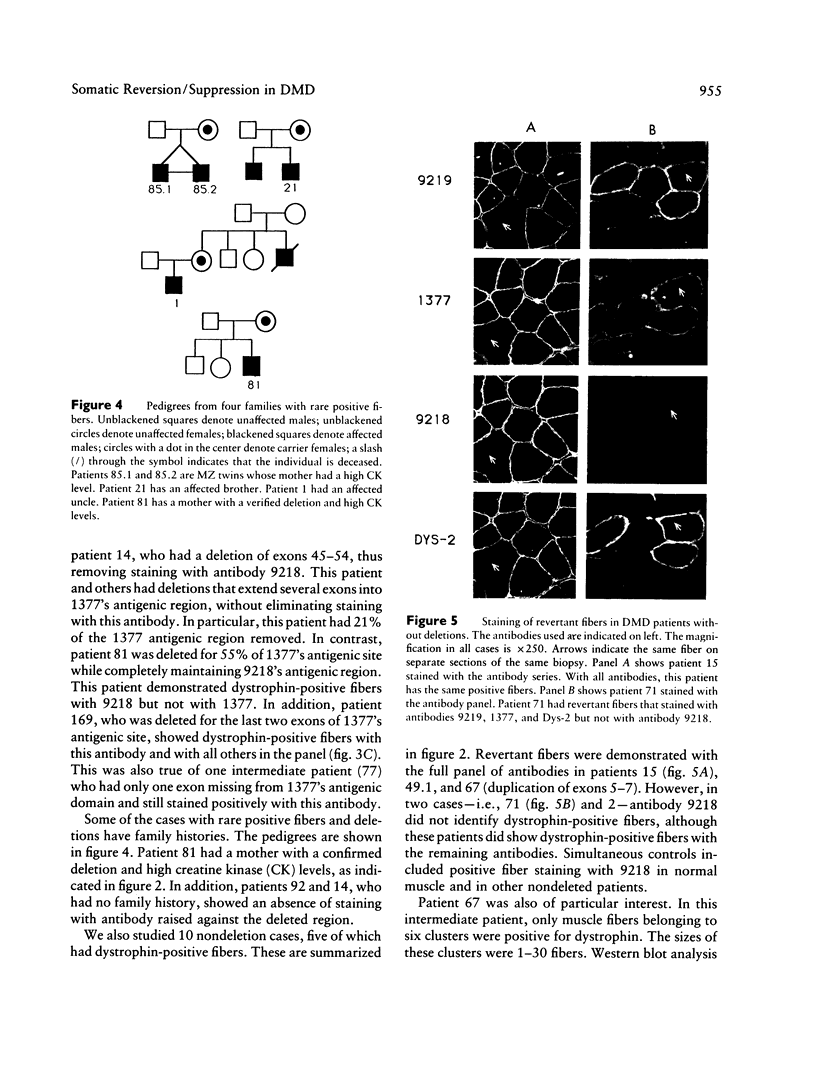




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E., Van Broeckhoven C., Bonten E. J., van de Vooren M. J., Veenema H., Van Hul W., Van Ommen G. J., Vandenberghe A., Pearson P. L. Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):554–556. doi: 10.1038/329554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Veenema H., Den Dunnen J. T., van Broeckhoven C., Grootscholten P. M., Bonten E. J., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Germinal mosaicism increases the recurrence risk for 'new' Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. J Med Genet. 1989 Sep;26(9):553–559. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.9.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce F. M., Beggs A. H., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin is transcribed in brain from a distant upstream promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Fenichel G. M., Griggs R. C., Mendell J. R., Moxley R., Miller J. P., Province M. A. Clinical investigation in Duchenne dystrophy: 2. Determination of the "power" of therapeutic trials based on the natural history. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):91–103. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulman D. E., Gangopadhyay S. B., Bebchuck K. G., Worton R. G., Ray P. N. Point mutation in the human dystrophin gene: identification through western blot analysis. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):457–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulman D. E., Murphy E. G., Zubrzycka-Gaarn E. E., Worton R. G., Ray P. N. Differentiation of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy phenotypes with amino- and carboxy-terminal antisera specific for dystrophin. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):295–304. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghes A. H., Logan C., Hu X., Belfall B., Worton R. G., Ray P. N. A cDNA clone from the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy gene. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):434–437. doi: 10.1038/328434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrow K. L., Coovert D. D., Klein C. J., Bulman D. E., Kissel J. T., Rammohan K. W., Burghes A. H., Mendell J. R. Dystrophin expression and somatic reversion in prednisone-treated and untreated Duchenne dystrophy. CIDD Study Group. Neurology. 1991 May;41(5):661–666. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.5.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Karpati G., Zubrzycka-Gaarn E., Bulman D. E., Ray P. N., Worton R. G. Dystrophin is localized to the plasma membrane of human skeletal muscle fibers by electron-microscopic cytochemical study. Muscle Nerve. 1990 May;13(5):376–380. doi: 10.1002/mus.880130503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Starman B. J., Blumberg B., Byers P. H. Recurrence of lethal osteogenesis imperfecta due to parental mosaicism for a dominant mutation in a human type I collagen gene (COL1A1). Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):591–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou C. D., Pack M., Young S. B., Prockop D. J. Phenotypic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta: the mildly affected mother of a proband with a lethal variant has the same mutation substituting cysteine for alpha 1-glycine 904 in a type I procollagen gene (COL1A1). Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Oct;47(4):670–679. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. J., Walsh J., Nicholson L. V., Harris J. B. Ultrastructural localization of dystrophin in human muscle by using gold immunolabelling. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 May 22;240(1297):197–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Francke U. A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):556–558. doi: 10.1038/329556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Alternative splicing of human dystrophin mRNA generates isoforms at the carboxy terminus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):509–511. doi: 10.1038/338509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Chamberlain J. S., Murphy E. G., Duff C. L., Smith B., Burghes A. H., Thompson M. W., Sutherland J., Oss I., Bodrug S. E. Molecular and phenotypic analysis of patients with deletions within the deletion-rich region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):507–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. A., Xu F. M., Davidson R. L. Molecular analysis of ethyl methanesulfonate-induced reversion of a chromosomally integrated mutant shuttle vector gene in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4185–4189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatlen L., Attardi G. Proportion of HeLa cell genome complementary to transfer RNA and 5 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):535–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Morgan J. E., Watkins S. C., Partridge T. A. Somatic reversion/suppression of the mouse mdx phenotype in vivo. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Oct;99(1):9–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90195-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Beggs A. H., Moyer M., Scherpf S., Heindrich K., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R., Lindlöf M., Kaariainen H. The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):498–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra S. B., Hart K. A., Klamut H. J., Thomas N. S., Bodrug S. E., Burghes A. H., Bobrow M., Harper P. S., Thompson M. W., Ray P. N. Frame-shift deletions in patients with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3055295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Liechti-Gallati S., Moser H., Kunkel L. M. An explanation for the phenotypic differences between patients bearing partial deletions of the DMD locus. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson L. V., Davison K., Johnson M. A., Slater C. R., Young C., Bhattacharya S., Gardner-Medwin D., Harris J. B. Dystrophin in skeletal muscle. II. Immunoreactivity in patients with Xp21 muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Dec;94(1-3):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge T. A., Morgan J. E., Coulton G. R., Hoffman E. P., Kunkel L. M. Conversion of mdx myofibres from dystrophin-negative to -positive by injection of normal myoblasts. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):176–179. doi: 10.1038/337176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R. Frameshift mutations. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:319–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicinski P., Geng Y., Ryder-Cook A. S., Barnard E. A., Darlison M. G., Barnard P. J. The molecular basis of muscular dystrophy in the mdx mouse: a point mutation. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1578–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2662404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. A., Deugau K. V., Lillicrap D. P. Somatic mosaicism and female-to-female transmission in a kindred with hemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):39–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis G. A., Starman B. J., Zinn A. B., Byers P. H. Variable expression of osteogenesis imperfecta in a nuclear family is explained by somatic mosaicism for a lethal point mutation in the alpha 1(I) gene (COL1A1) of type I collagen in a parent. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jun;46(6):1034–1040. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins S. C., Hoffman E. P., Slayter H. S., Kunkel L. M. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of dystrophin in myofibres. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):863–866. doi: 10.1038/333863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubrzycka-Gaarn E. E., Bulman D. E., Karpati G., Burghes A. H., Belfall B., Klamut H. J., Talbot J., Hodges R. S., Ray P. N., Worton R. G. The Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene product is localized in sarcolemma of human skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):466–469. doi: 10.1038/333466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Breteler E. G., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):640–642. doi: 10.1038/329640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]