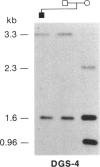
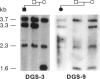
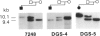Abstract
DiGeorge syndrome (DGS), a developmental field defect of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, is characterized by aplasia or hypoplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands and by conotruncal cardiac malformations. Cytogenetic studies support the presence of a DGS critical region in band 22q11. In the present study, we report the results of clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular studies of 14 patients with DGS. Chromosome analysis, utilizing high-resolution banding techniques, detected interstitial deletions in five probands and was inconclusive for a deletion in three probands. The remaining six patients had normal karyotypes. In contrast, molecular analysis detected DNA deletions in all 14 probands. Two of 10 loci tested, D22S75 and D22S259, are deleted in all 14 patients. A third locus, D22S66, is deleted in the eight DGS probands tested. Physical mapping using somatic cell hybrids places D22S66 between D22S75 and D22S259, suggesting that it should be deleted in the remaining six cases. Parent-of-origin studies were performed in five families. Four probands failed to inherit a maternal allele, and one failed to inherit a paternal allele. On the basis of these families, and of six maternally and five paternally derived unbalanced-translocation DGS probands in the literature, parent of origin or imprinting does not appear to play an important role in the pathogenesis of DGS. Deletion of the same three loci in all 14 DGS probands begins to delineate the region of chromosome 22 critical for DGS and confirms the hypothesis that submicroscopic deletions of 22q11 are etiologic in the vast majority of cases.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augusseau S., Jouk S., Jalbert P., Prieur M. DiGeorge syndrome and 22q11 rearrangements. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):206–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00282098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Stier R., Böhm N., Adlung A., Hameister H. Partial monosomy 22pter leads to q11 in a newborn with the clinical features of trisomy 13 syndrome. Ann Genet. 1980;23(4):244–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen P., Pabst H., Berry D., Collins-Nakai R., Hoo J. J. Thymus deficiency in an infant with a chromosome t(18;22)(q12.2;p11.2)pat rearrangement. Clin Genet. 1986 Feb;29(2):174–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M. L., McDermid H. E., Sellinger B., Emanuel B. S. Isolation and regional localization of 35 unique anonymous DNA markers for human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):996–1002. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90190-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M., Canaani E., Emanuel B. S. Linear order of the four BCR-related loci in 22q11. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):168–171. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Huebner K., Isobe M., Fainstain E., Lifshitz B., Shtivelman E., Canaani E. Mapping of four distinct BCR-related loci to chromosome region 22q11: order of BCR loci relative to chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia breakpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7174–7178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S. Antenatal diagnosis of DiGeorge syndrome. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1390–1391. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed M. J., Robertson J., Beck J. S., Cater J. I., Bose B., Madlom M. M. Features of di George syndrome in a child with 45,XX,-3,-22,+der(3),t(3;22)(p25;q11). J Med Genet. 1987 Apr;24(4):225–227. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.4.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibison W. J., Budarf M., McDermid H., Greenberg F., Emanuel B. S. Molecular studies of DiGeorge syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):888–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Crowder W. E., Paschall V., Colon-Linares J., Lubianski B., Ledbetter D. H. Familial DiGeorge syndrome and associated partial monosomy of chromosome 22. Hum Genet. 1984;65(4):317–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00291554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Elder F. F., Haffner P., Northrup H., Ledbetter D. H. Cytogenetic findings in a prospective series of patients with DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):605–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human gene mapping 11. London Conference (1991). Eleventh International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. London, UK, August 18-22, 1991. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;58(1-2):1–984. doi: 10.1159/000133157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W. The William Allan Memorial Award address: Thalassemia: molecular mechanism and detection. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;38(1):4–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I., Zackai E. H., Emanuel B. S., Kistenmacher M., Greenberg F., Punnett H. H. The association of the DiGeorge anomalad with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Graham J. M., Jr, Lalande M., Latt S. A. Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes share a common chromosome 15 deletion but differ in parental origin of the deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):285–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Ledbetter S. A., Dobyns W. B., Emanuel B. S., Ledbetter D. H. Detection of deletions and cryptic translocations in Miller-Dieker syndrome by in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):707–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Opitz J. M. The DiGeorge anomaly as a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;2:113–127. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., White R. L. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA revealed by cosmid-derived probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello J. T., Bastian J. F., Jones M. C. Interstitial deletion of chromosome 22 in a patient with the DiGeorge malformation sequence. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Jan;32(1):112–114. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid H. E., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S. Toward a long-range map of human chromosomal band 22q11. Genomics. 1989 Jul;5(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid H. E., Duncan A. M., Brasch K. R., Holden J. J., Magenis E., Sheehy R., Burn J., Kardon N., Noel B., Schinzel A. Characterization of the supernumerary chromosome in cat eye syndrome. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.3961499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pivnick E. K., Wilroy R. S., Summitt J. B., Tucker B., Herrod H. G., Tharapel A. T. Adjacent-2 disjunction of a maternal t(9;22) leading to duplication 9pter----q22 and deficiency of 22pter----q11.2. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):92–96. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Haines J. L., Bazanowski A., Colella-Crowley A., Trofatter J. A., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of the long arm of human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., Carey A. H., Wyse R. K., Roach S., Dumanski J. P., Nordenskjold M., Williamson R. Microdeletions within 22q11 associated with sporadic and familial DiGeorge syndrome. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. A., Carey J. C., Shigeoka A. O. Di George anomaly and velocardiofacial syndrome. Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Herva R., Koivisto M., Aula P. A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Fouly M. H., Higgins J. V., Kapur S., Sankey B. J., Matisoff D. N., Costa-Fox M. DiGeorge anomaly in an infant with deletion of chromosome 22 and dup(9p) due to adjacent type II disjunction. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Mar 15;38(4):569–573. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]