Abstract
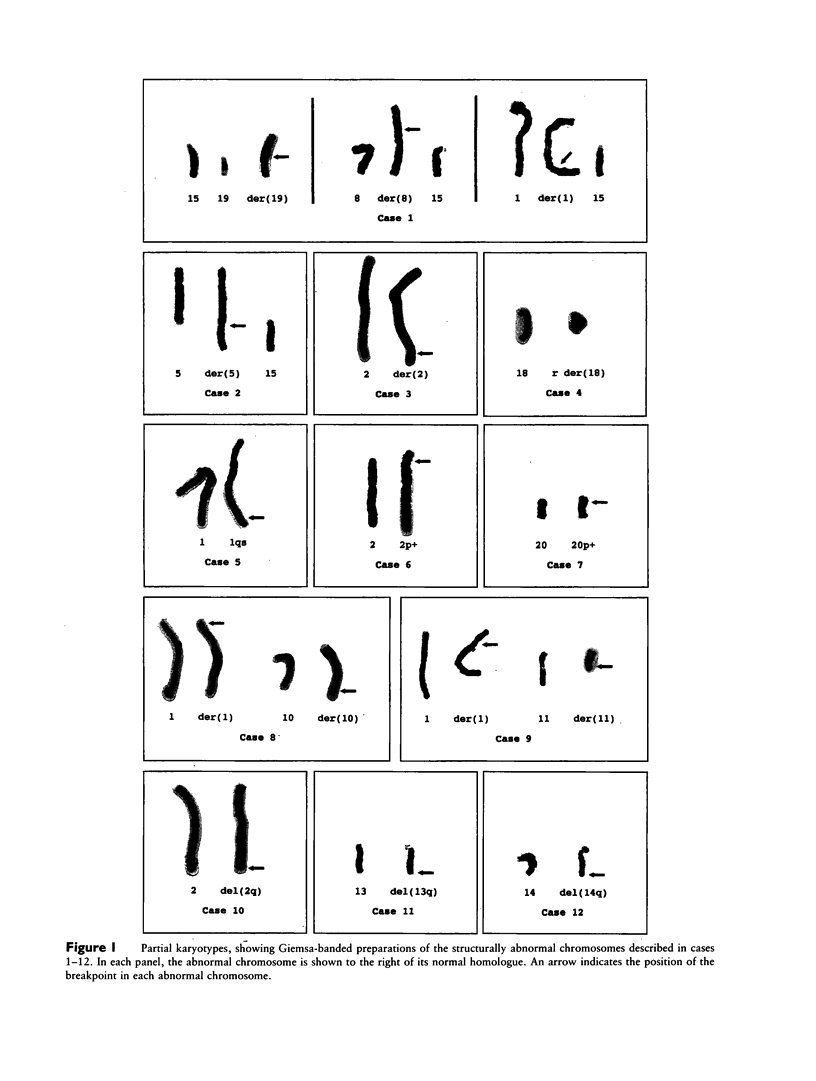
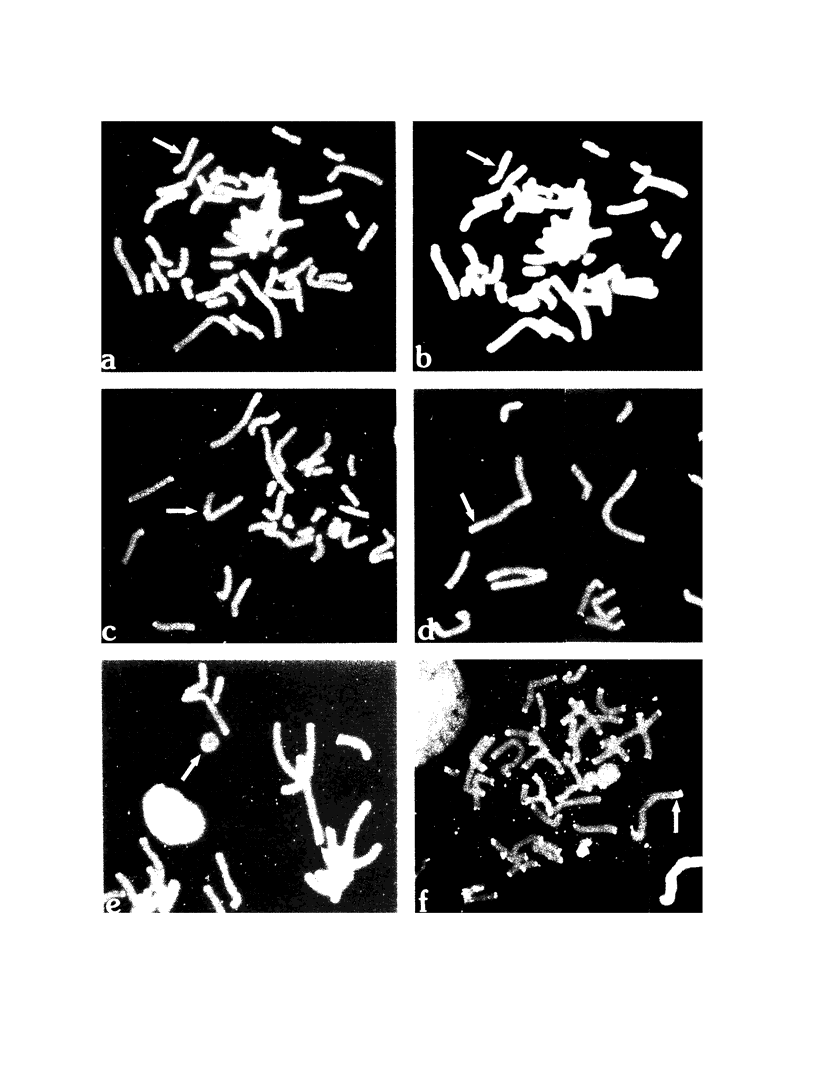
We describe a novel chromosome structure in which telomeric sequences are present interstitially, at the apparent breakpoint junctions of structurally abnormal chromosomes. In the linear chromosomes with interstitial telomeric sequences, there were three sites of hybridization of the telomere consensus sequence within each derived chromosome: one at each terminus and one at the breakpoint junction. Telomeric sequences also were observed within a ring chromosome. The rearrangements examined were constitutional chromosome abnormalities with a breakpoint assigned to a terminal band. In each case (with the exception of the ring chromosome), an acentric segment of one chromosome was joined to the terminus of an apparently intact recipient chromosome. One case exhibited apparent instability of the chromosome rearrangement, resulting in somatic mosaicism. The rearrangements described here differ from the telomeric associations observed in certain tumors, which appear to represent end-to-end fusion of two or more intact chromosomes. The observed interstitial telomeric sequences appear to represent nonfunctional chromosomal elements, analogous to the inactivated centromeres observed in dicentric chromosomes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth M. N., Meyne J., Littlefield L. G., Bailey S. M., Moyzis R. K. Telomere staining of human chromosomes and the mechanism of radiation-induced dicentric formation. Radiat Res. 1989 Nov;120(2):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. T., Celander D. W., Price C. M., Cech T. R. Cloning and expression of genes for the Oxytricha telomere-binding protein: specific subunit interactions in the telomeric complex. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90075-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P., Dancis B. Telomere replication, kinetochore organizers, and satellite DNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4566–4570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IJdo J. W., Baldini A., Ward D. C., Reeders S. T., Wells R. A. Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9051–9055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Baker R. J., Hobart H. H., Hsu T. C., Ryder O. A., Ward O. G., Wiley J. E., Wurster-Hill D. H., Yates T. L., Moyzis R. K. Distribution of non-telomeric sites of the (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequence in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(1):3–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01737283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Moyzis R. K. Conservation of the human telomere sequence (TTAGGG)n among vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7049–7053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera H., Zuffardi O., Gargantini L. Nonreciprocal and jumping translocations of 15q1----qter in Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Nov;37(3):311–317. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]