Abstract
The ubiquitousness of RFLPs in the human genome has greatly helped the mapping of human disease genes, and it has been suggested that population measures of association between disease and marker loci could help with this mapping. For rare diseases, random samples are taken from within disease genotypes in order to obtain reasonable sample sizes, but this sampling strategy requires a modification of the usual measures of association. We present theoretical predictions for the mean and variance of such a modified measure, under the assumption that the disease gene is maintained at a constant low frequency in the population. The coefficient of variation of this modified measure is large enough that caution is needed in using the measure to locate disease genes, and, furthermore, the coefficient of variation cannot be made arbitrarily small by increasing sample size. The modified association measure is calculated for recently published data on cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF


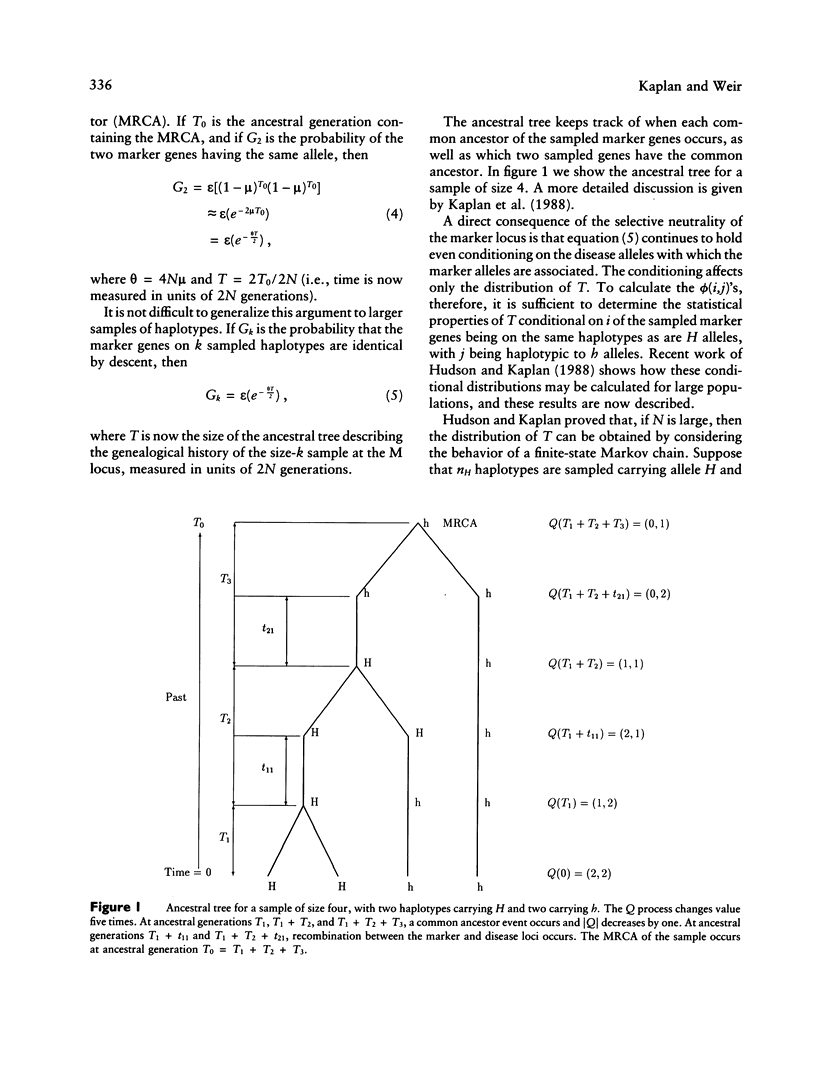

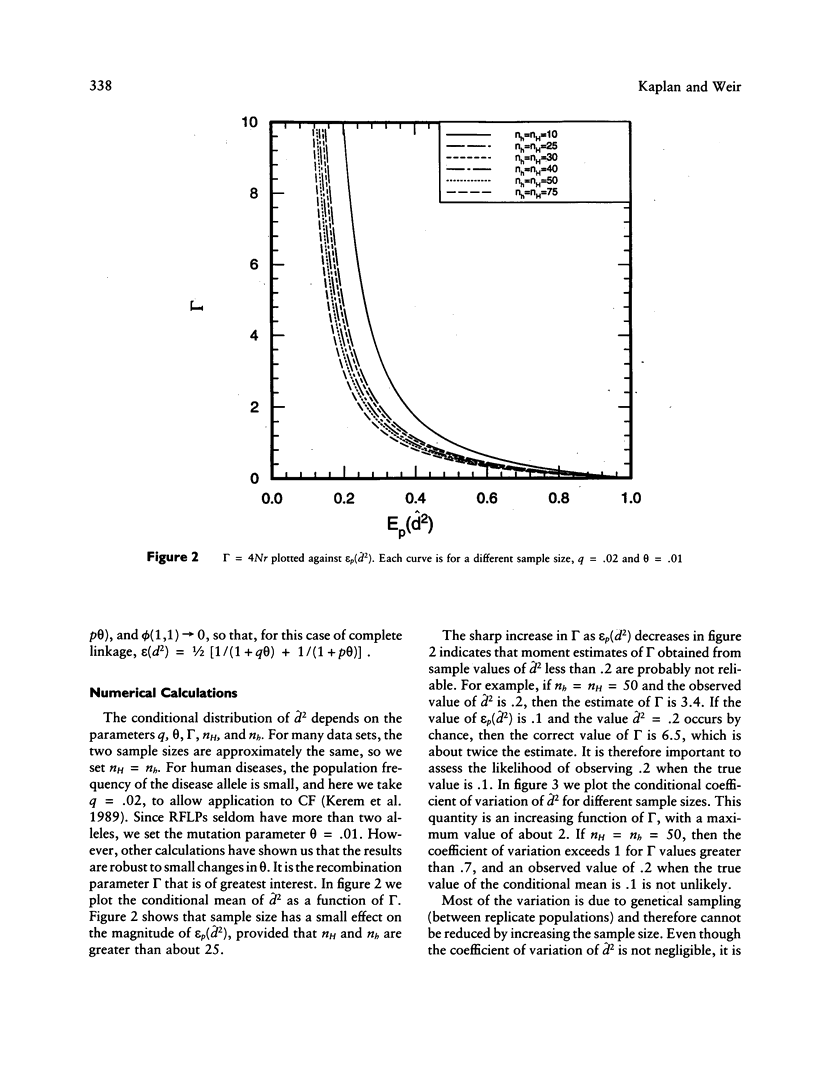
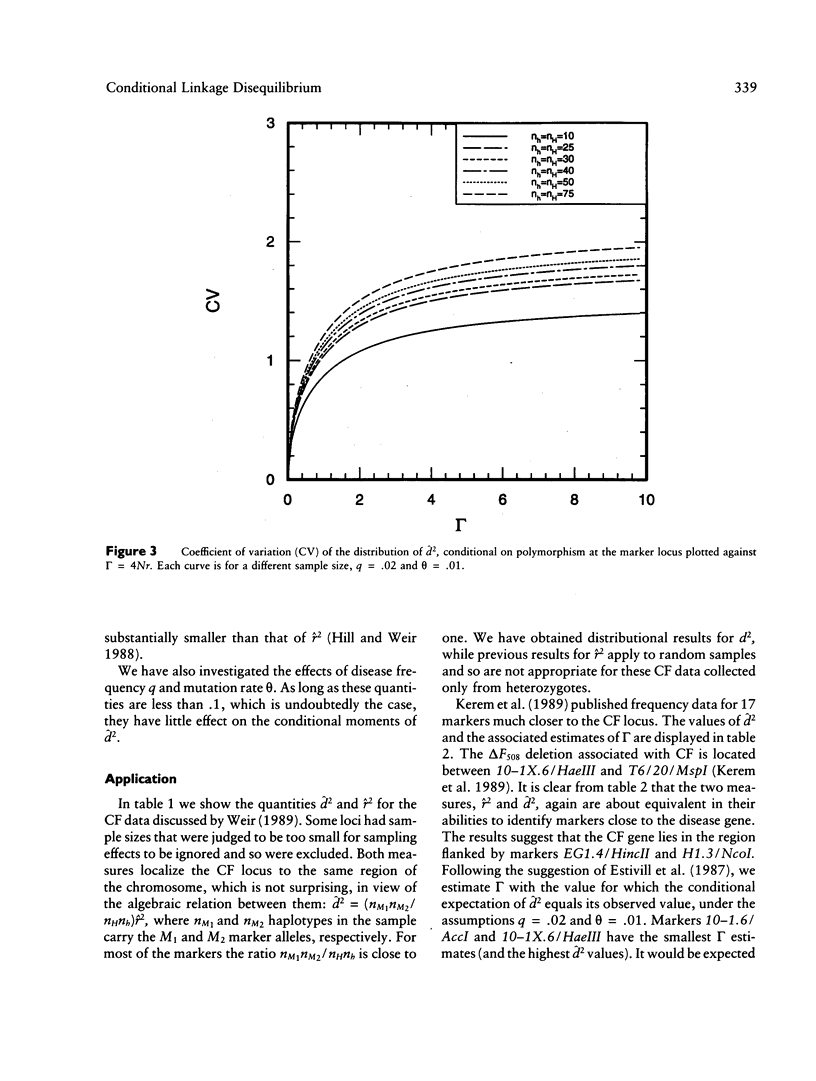
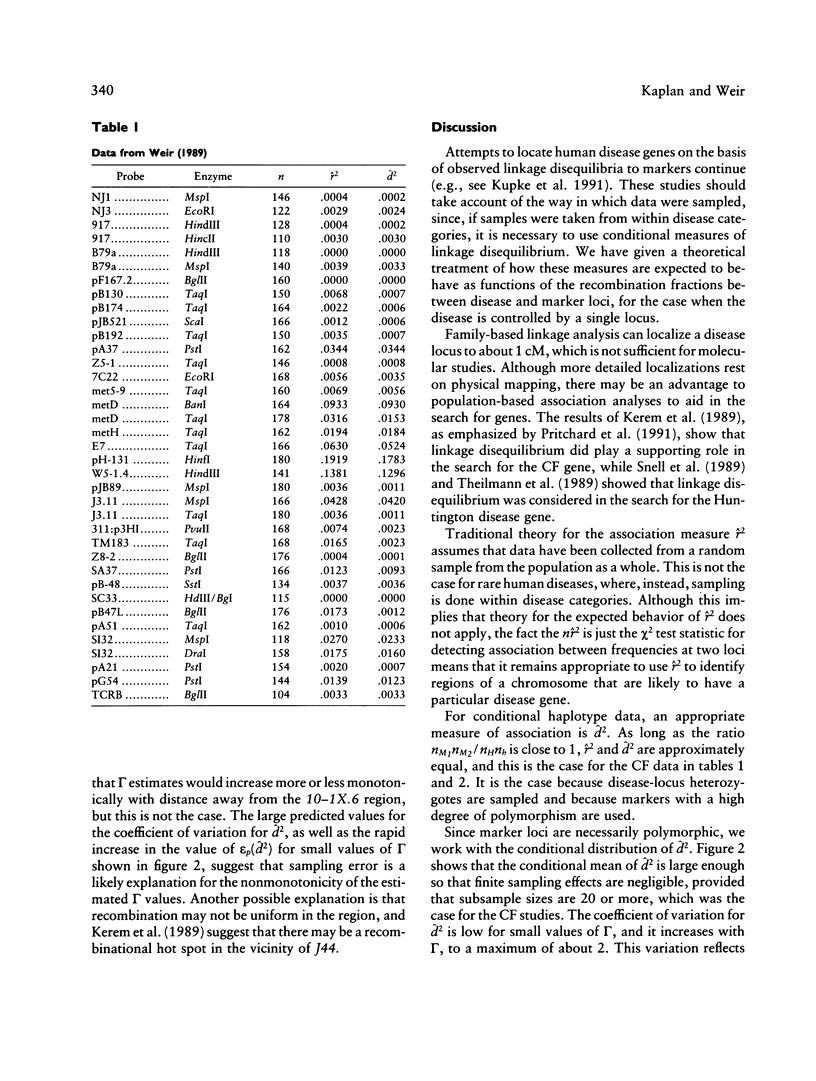


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R. Estimation of linkage disequilibrium from conditional haplotype data: application to beta-globin gene cluster in American blacks. Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(5):323–333. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Li C. C., Buetow K. H. Estimation of the marker gene frequency and linkage disequilibrium from conditional marker data. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):177–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Mohr J., Schmiegelow K., Nielsen L. S., Williamson R. Linkage relationships of paraoxonase (PON) with other markers: indication of PON-cystic fibrosis synteny. Clin Genet. 1985 Oct;28(4):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Farrall M., Scambler P. J., Bell G. M., Hawley K. M., Lench N. J., Bates G. P., Kruyer H. C., Frederick P. A., Stanier P. A candidate for the cystic fibrosis locus isolated by selection for methylation-free islands. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):840–845. doi: 10.1038/326840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Variances and covariances of squared linkage disequilibria in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol. 1988 Feb;33(1):54–78. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. R., Kaplan N. L. The coalescent process in models with selection and recombination. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):831–840. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. R. The sampling distribution of linkage disequilibrium under an infinite allele model without selection. Genetics. 1985 Mar;109(3):611–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Darden T., Hudson R. R. The coalescent process in models with selection. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):819–829. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
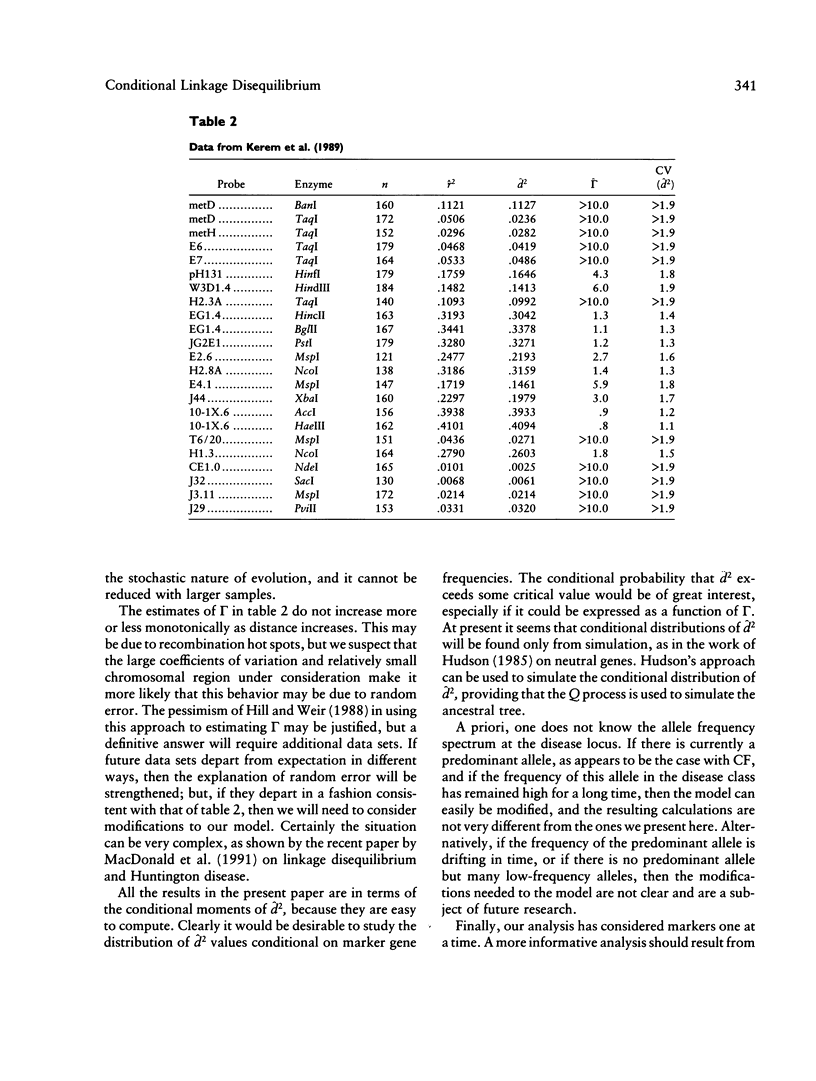
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. The number of heterozygous nucleotide sites maintained in a finite population due to steady flux of mutations. Genetics. 1969 Apr;61(4):893–903. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiste P. J., Weir B. S. Estimating linkage disequilibrium from conditional data. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1139–1140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Non-random association between electromorphs and inversion chromosomes in finite populations. Genet Res. 1980 Feb;35(1):65–83. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001394x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C., Cox D. R., Myers R. M. The end in sight for Huntington disease? Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Buchwald M. Biochemical and molecular genetics of cystic fibrosis. Adv Hum Genet. 1991;20:153-266, 311-2. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5958-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson G. A. On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theor Popul Biol. 1975 Apr;7(2):256–276. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(75)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S., Hill W. G. Effect of mating structure on variation in linkage disequilibrium. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):477–488. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


