Abstract
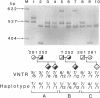
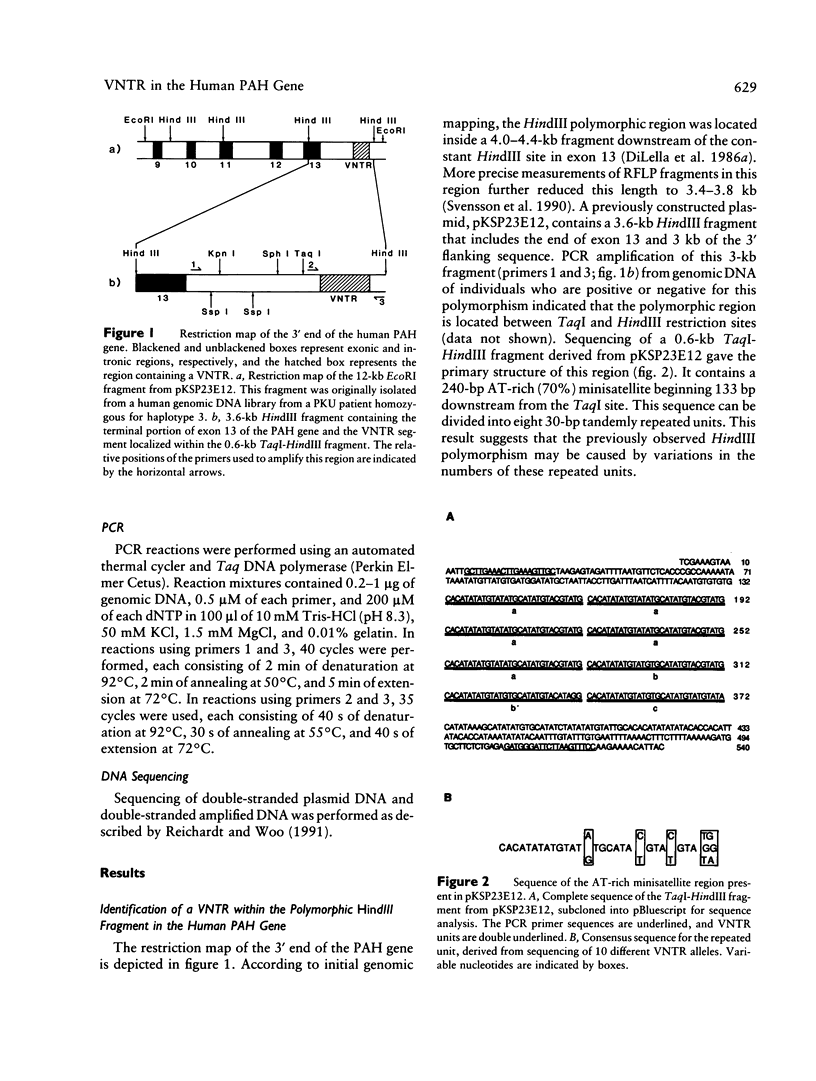
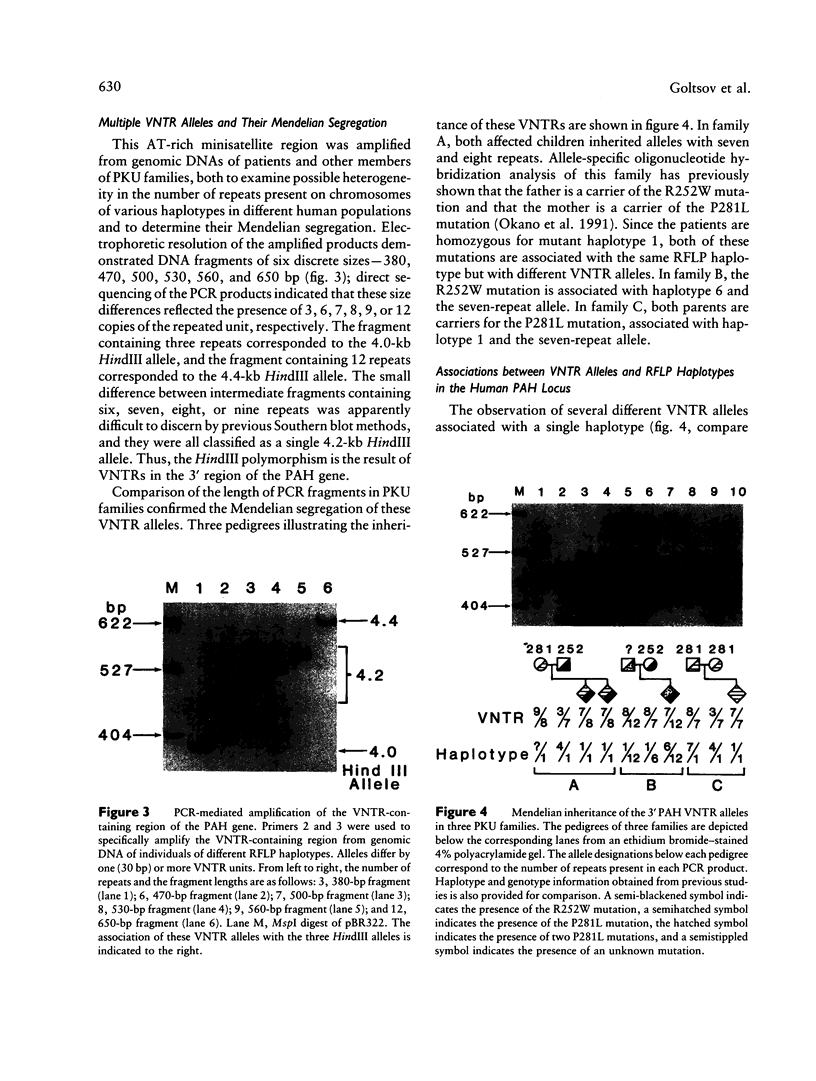
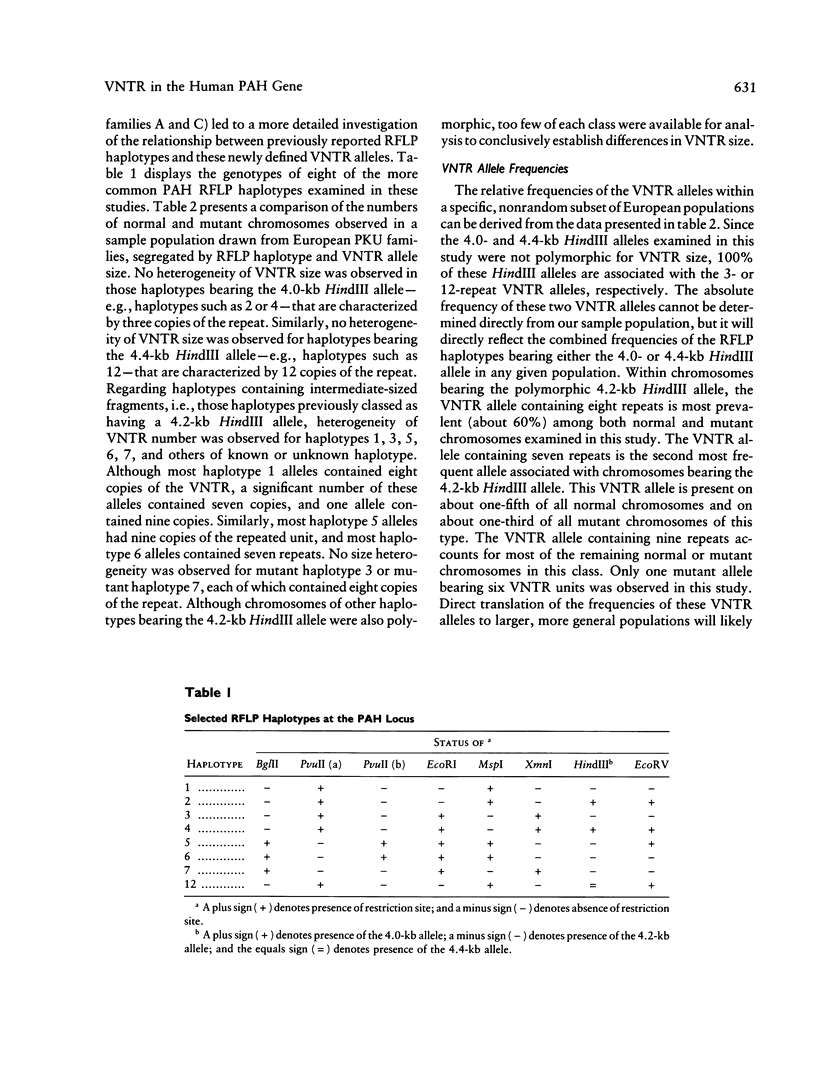
The HindIII RFLP in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene is caused by the presence of an AT-rich (70%) minisatellite region. This region contains various multiple of 30-bp tandem repeats and is located 3 kb downstream of the final exon of the gene. PCR-mediated amplification of this region from haplotyped PAH chromosomes indicates that the previously reported 4.0-kb HindIII allele contains three of these repeats, while the 4.4-kb HindIII allele contains 12 of these repeats. The 4.2-kb HindIII fragment can contain six, seven, eight, or nine copies of this repeat. These variations permit more detailed analysis of mutant haplotypes 1, 5, 6, and, possibly, others. Kindred analysis in phenylketonuria families demonstrates Mendelian segregation of these VNTR alleles, as well as associations between these alleles and certain PAH mutations. The R261Q mutation, associated with haplotype 1, is associated almost exclusively with an allele containing eight repeats; the R408W mutation, when occurring on a haplotype 1 background, may also be associated with the eight-repeat VNTR allele. Other PAH mutations associated with haplotype 1, R252W and P281L, do not appear to segregate with specific VNTR alleles. The IVS-10 mutation, when associated with haplotype 6, is associated exclusively with an allele containing seven repeats. The combined use of this VNTR system and the existing RFLP haplotype system will increase the performance of prenatal diagnostic tests based on haplotype analysis. In addition, this VNTR may prove useful in studies concerning the origins and distributions of PAH mutations in different human populations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
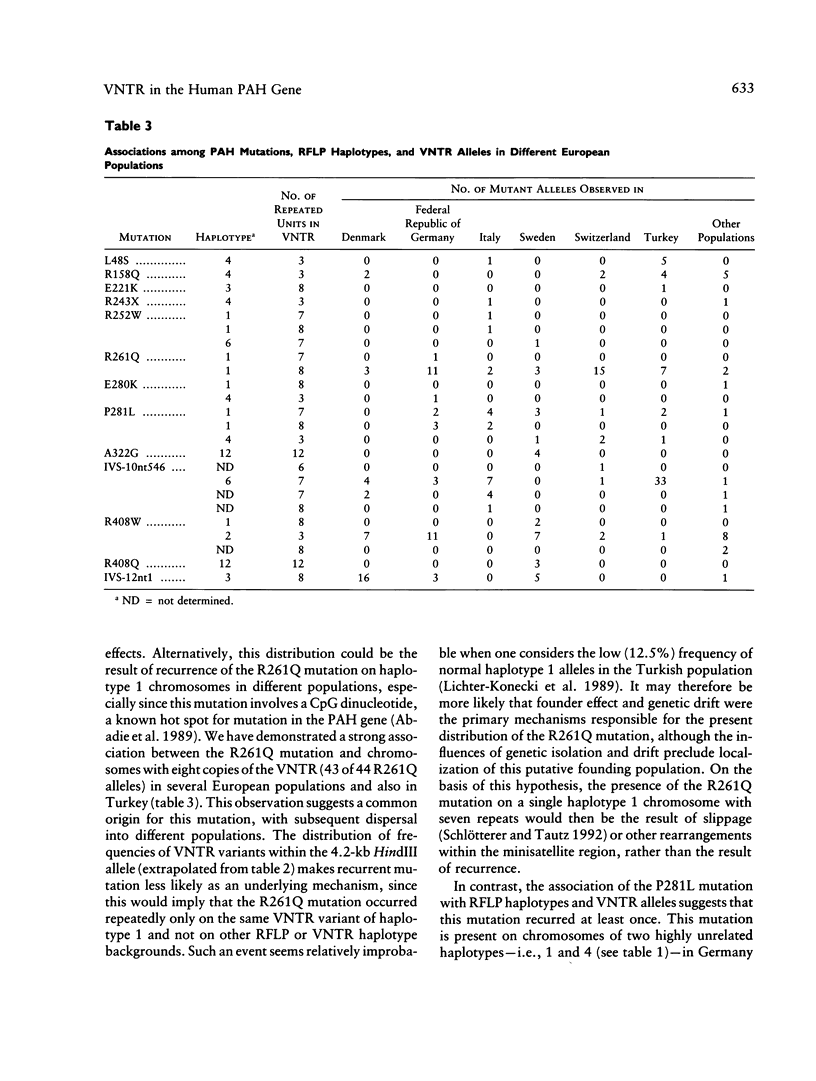
- Abadie V., Lyonnet S., Maurin N., Berthelon M., Caillaud C., Giraud F., Mattei J. F., Rey J., Rey F., Munnich A. CpG dinucleotides are mutation hot spots in phenylketonuria. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):936–939. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki K., Wada Y. Outcome of the patients detected by newborn screening in Japan. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1988 Aug;30(4):429–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1988.tb02533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Xiong W. J., Fourest E., Chan L. Rapid typing of tandemly repeated hypervariable loci by the polymerase chain reaction: application to the apolipoprotein B 3' hypervariable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):212–216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Lidsky A. S., Daiger S. P., Güttler F., Sullivan S., Dilella A. G., Woo S. L. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and their relationship with phenylketonuria. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00283048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Chakraborty R., Reed L., Fekete G., Schuler D., Berenssi G., Nasz I., Brdicka R., Kamarýt J., Pijácková A. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in European families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):310–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasovich M., Konecki D., Lichter-Konecki U., Eisensmith R. C., Güttler F., Naughton E., Mullins C., Giovannini M., Riva E., Woo S. L. Molecular characterization of PKU allele prevalent in southern Europe and Ireland. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 May;17(3):303–309. doi: 10.1007/BF01232824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., Marvit J., Woo S. L. Molecular structure and polymorphic map of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):743–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworniczak B., Grudda K., Stümper J., Bartholomé K., Aulehla-Scholz C., Horst J. Phenylalanine hydroxylase gene: novel missense mutation in exon 7 causing severe phenylketonuria. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90238-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. S., Breslow J. L. A unique AT-rich hypervariable minisatellite 3' to the ApoB gene defines a high information restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):8952–8955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Rozen R., Scriver C. R., Laframboise R., Laberge C. Recurrent mutation, gene conversion, or recombination at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus: evidence in French-Canadians and a catalog of mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):970–974. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaydjieva L., Dworniczak B., Aulehla-Scholz C., Devoto M., Romeo G., Stuhrmann M., Horst J. Phenylketonuria mutation in southern Europeans. Lancet. 1991 Apr 6;337(8745):865–865. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92584-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Lichter-Konecki U. The phenylketonuria locus: current knowledge about alleles and mutations of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene in various populations. Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;87(4):377–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00197152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter-Konecki U., Schlotter M., Yaylak C., Ozgü M., Coskun T., Ozalp I., Wendel U., Batzler U., Trefz F. K., Konecki D. DNA haplotype analysis at the phenylalanine hydroxylase locus in the Turkish population. Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;81(4):373–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00283695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Daiger S. P., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):619–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig E. H., Friedl W., McCarthy B. J. High-resolution analysis of a hypervariable region in the human apolipoprotein B gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):458–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Wang T., Eisensmith R. C., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Recurrent mutation in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):919–924. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Wang T., Eisensmith R. C., Longhi R., Riva E., Giovannini M., Cerone R., Romano C., Woo S. L. Phenylketonuria missense mutations in the Mediterranean. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Wang T., Eisensmith R. C., Steinmann B., Gitzelmann R., Woo S. L. Missense mutations associated with RFLP haplotypes 1 and 4 of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):18–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Gil A., Maniatis T. The structure of the human zeta-globin gene and a closely linked, nearly identical pseudogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt J. K., Woo S. L. Molecular basis of galactosemia: mutations and polymorphisms in the gene encoding human galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2633–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlötterer C., Tautz D. Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):211–215. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson E., Andersson B., Hagenfeldt L. Two mutations within the coding sequence of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;85(3):300–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00206750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Nakamura Y., White R. Molecular characterization of a spontaneously generated new allele at a VNTR locus: no exchange of flanking DNA sequence. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Chandra T., Robson K. J. Cloned human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene allows prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of classical phenylketonuria. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):151–155. doi: 10.1038/306151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]