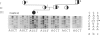Abstract
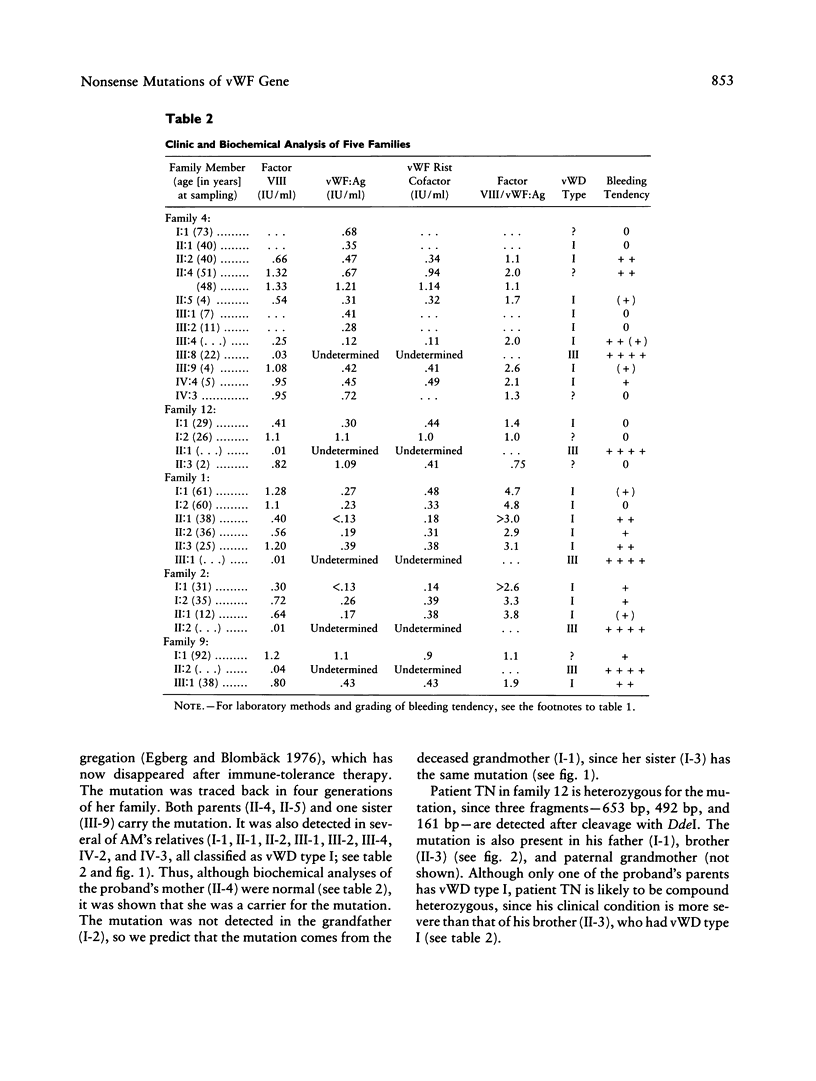
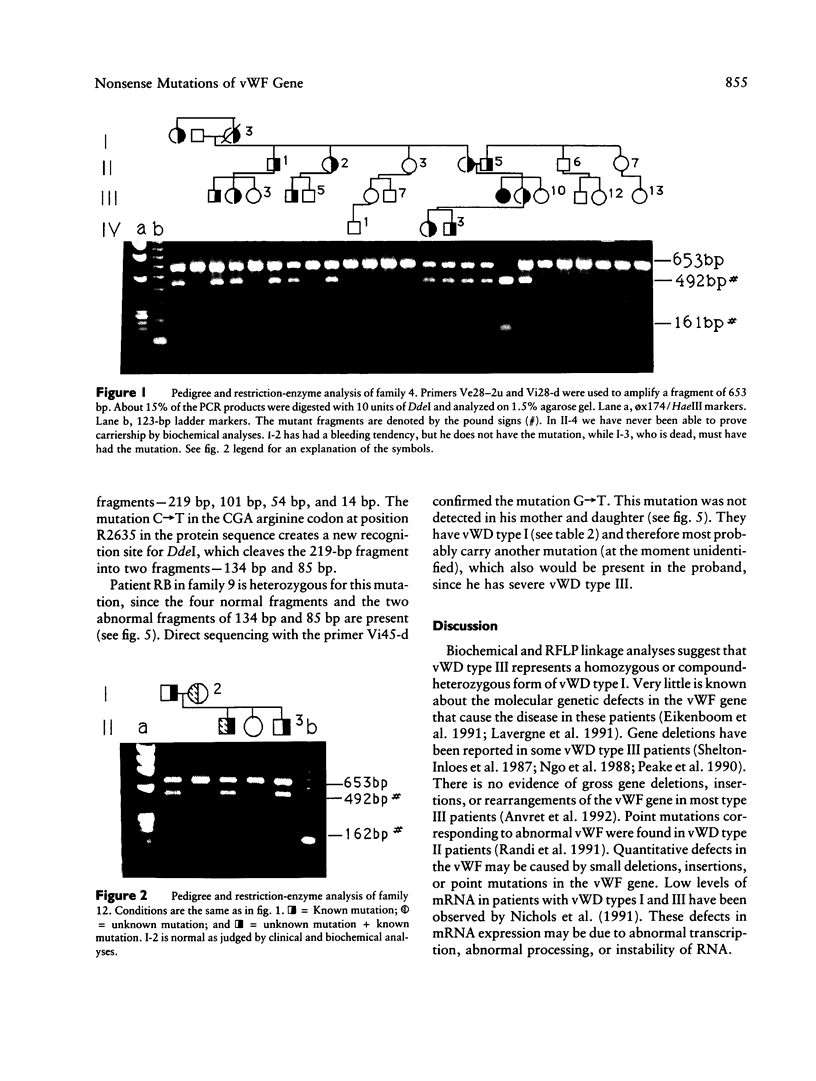
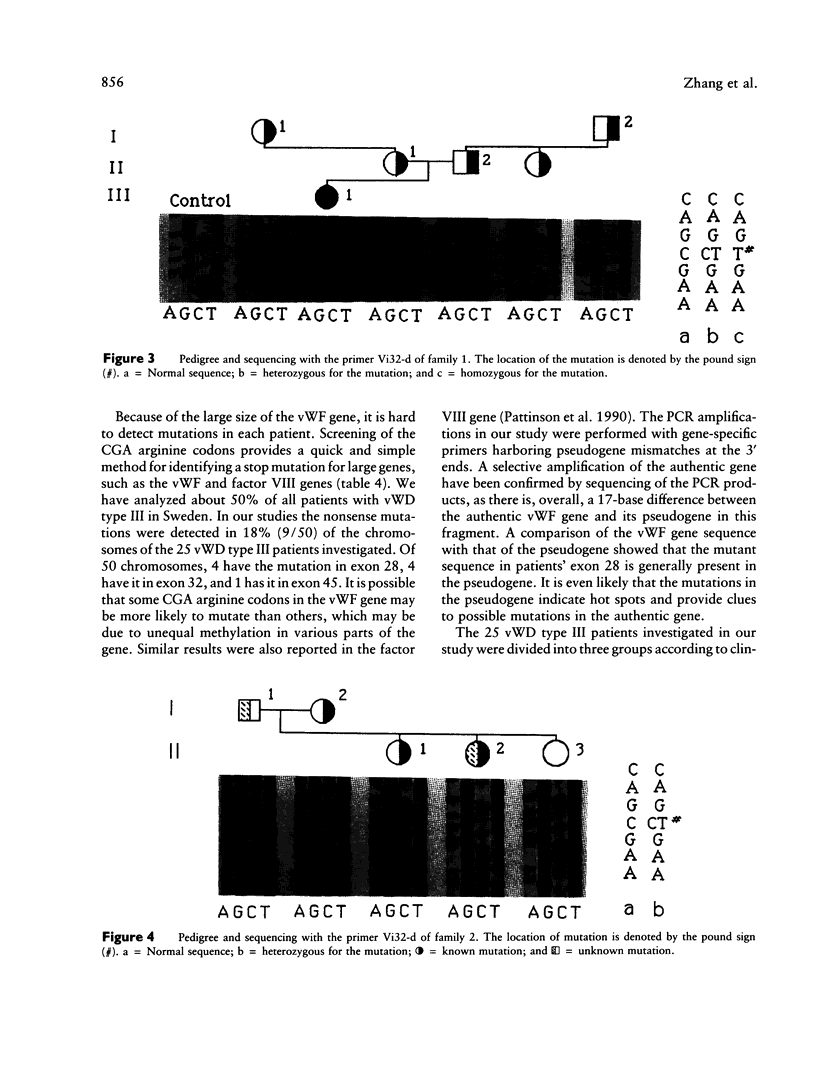
von Willebrand disease (vWD) is the most common inherited bleeding disorder in humans. The disease is caused by qualitative and quantitative abnormalities of the von Willebrand factor (vWF). Genomic DNA from 25 patients with vWD type III, the most severe form of the disease, was studied using PCR followed by restriction-enzyme analysis and direct sequencing of the products. Nonsense mutations (CGA----TGA) were detected in exons 28, 32, and 45 by screening of all the 11 CGA arginine codons of the vWF gene. Two patients were found to be homozygous and five heterozygous for the mutation. Both parents and some of the relatives of the homozygous patients carry the mutation. These are the first reported examples of homozygous point mutations associated with the severe form of vWD. In the three heterozygous probands, one of the parents carried the mutation and had vWD type I. Family studies including parents and family members with or without vWD type I indicated that these three heterozygous patients are likely to be compound heterozygous. Twenty-one individuals from these seven families with vWD type I were found to be heterozygous for the mutation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anvret M., Blombäck M., Lindstedt M., Söderlind E., Tapper-Persson M., Thelander A. C. Genetic and blood coagulation characterization of "Swedish" families with von Willebrand's disease types I and III: new aspects of heredity. Hum Genet. 1992 May;89(2):147–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00217114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck M., Eneroth P., Andersson O., Anvret M. On laboratory problems in diagnosing mild von Willebrand's disease. Am J Hematol. 1992 Jun;40(2):117–120. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830400208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D. Rapid isolation of eukaryotic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):463–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Miller J. H. Mutagenic deamination of cytosine residues in DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):560–561. doi: 10.1038/287560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egberg N., Blombäck M. On the characterization of acquired inhibitors to ristocetin induced platelet aggregation found in patients with von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Res. 1976 Nov;9(5):527–531. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S. Alternative dideoxy sequencing of double-stranded DNA by cyclic reactions using Taq polymerase. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):67–73. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Lester-Mancuso T. L., Le Beau M. M., Sorace J. M., Sadler J. E. Human von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene: structural analysis and differentiation by polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):253–269. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo K. Y., Glotz V. T., Koziol J. A., Lynch D. C., Gitschier J., Ranieri P., Ciavarella N., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Homozygous and heterozygous deletions of the von Willebrand factor gene in patients and carriers of severe von Willebrand disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2753–2757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Lyons S. E., Harrison J. S., Cody R. L., Ginsburg D. Severe von Willebrand disease due to a defect at the level of von Willebrand factor mRNA expression: detection by exonic PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3857–3861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattinson J. K., Millar D. S., McVey J. H., Grundy C. B., Wieland K., Mibashan R. S., Martinowitz U., Tan-Un K., Vidaud M., Goossens M. The molecular genetic analysis of hemophilia A: a directed search strategy for the detection of point mutations in the human factor VIII gene. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2242–2248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Liddell M. B., Moodie P., Standen G., Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Sorace J. M., Sadler J. E., Verweij C. L. Severe type III von Willebrand's disease caused by deletion of exon 42 of the von Willebrand factor gene: family studies that identify carriers of the condition and a compound heterozygous individual. Blood. 1990 Feb 1;75(3):654–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randi A. M., Rabinowitz I., Mancuso D. J., Mannucci P. M., Sadler J. E. Molecular basis of von Willebrand disease type IIB. Candidate mutations cluster in one disulfide loop between proposed platelet glycoprotein Ib binding sequences. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1220–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI115122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton-Inloes B. B., Chehab F. F., Mannucci P. M., Federici A. B., Sadler J. E. Gene deletions correlate with the development of alloantibodies in von Willebrand disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI112974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G., Cooper D. N., Gitschier J., Higuchi M., Hoyer L. W., Yoshioka A., Peake I. R., Schwaab R., Olek K., Kazazian H. H. Haemophilia A: database of nucleotide substitutions, deletions, insertions and rearrangements of the factor VIII gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4821–4833. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G. The varieties of von Willebrand's disease. Clin Lab Haematol. 1984;6(4):307–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1984.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
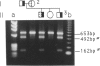
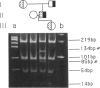
- Zhang Z. P., Falk G., Blombäck M., Egberg N., Anvret M. Identification of a new nonsense mutation in the von Willebrand factor gene in patients with von Willebrand disease type III. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):61–62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]