Abstract
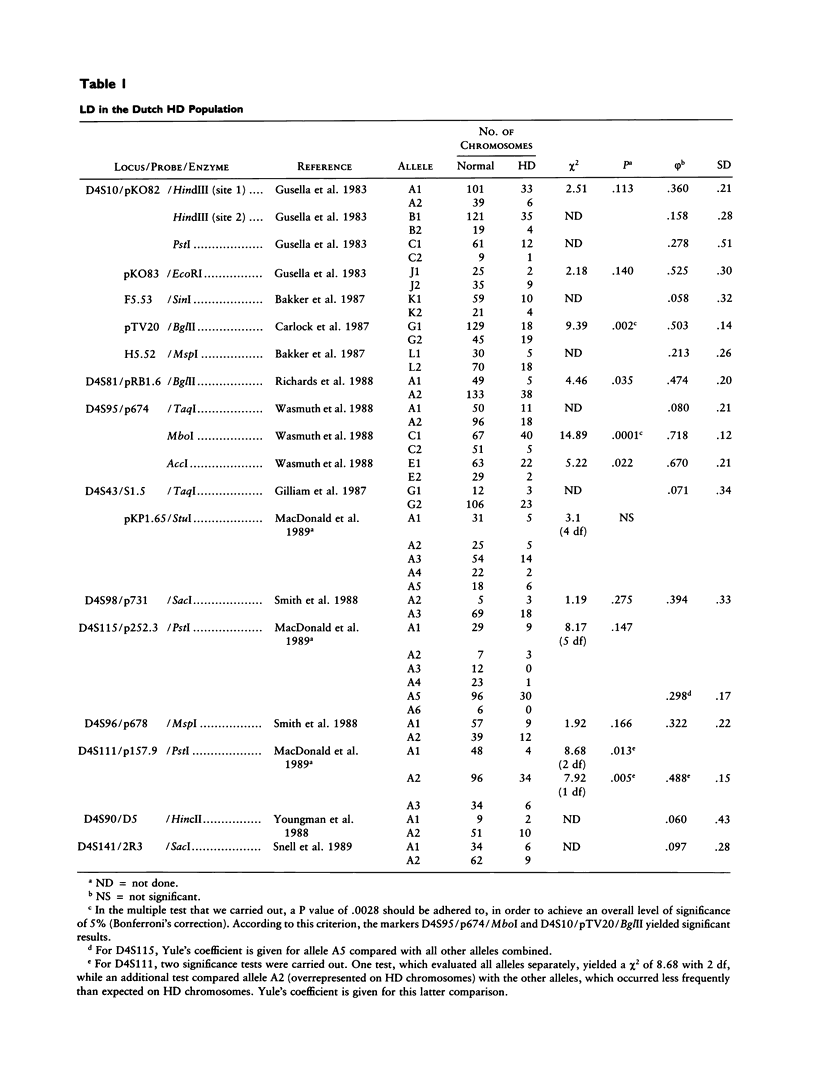
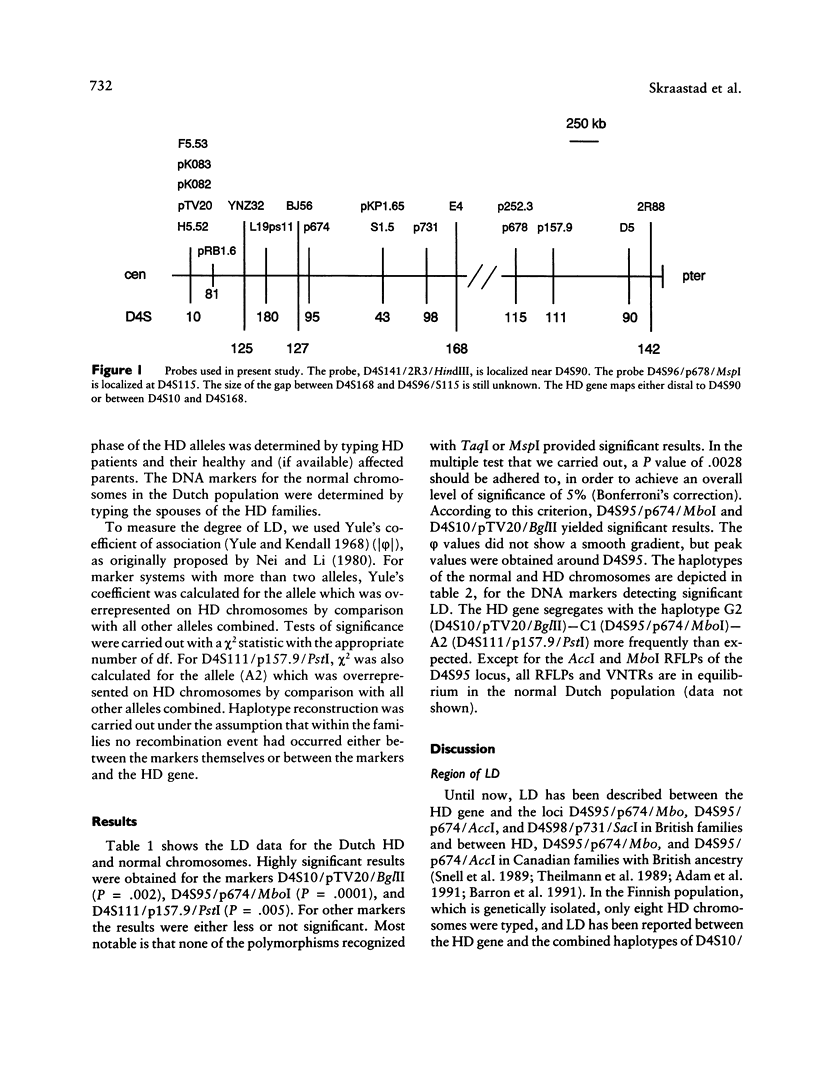
Significant linkage disequilibrium has been found between the Huntington disease (HD) gene and DNA markers located around D4S95 and D4S98. The linkage-disequilibrium studies favor the proximal location of the HD gene, in contrast to the conflicting results of recombination analyses. We have analyzed 45 Dutch HD families with 19 DNA markers and have calculated the strength of linkage disequilibrium. Highly significant linkage disequilibrium has been detected with D4S95, consistent with the studies in other populations. In contrast with most other studies, however, the area of linkage disequilibrium extends from D4S10 proximally to D4S95, covering 1,100 kb. These results confirm that the HD gene most likely maps near D4S95.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S., Theilmann J., Buetow K., Hedrick A., Collins C., Weber B., Huggins M., Hayden M. Linkage disequilibrium and modification of risk for Huntington disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):595–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Skraastad M. I., Fisser-Groen Y. M., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Two additional RFLPs at the D4S10 locus, useful for Huntington's disease (HD)-family studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9100–9100. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron L., Curtis A., Shrimpton A. E., Holloway S., May H., Snell R. G., Brock D. J. Linkage disequilibrium and recombination make a telomeric site for the Huntington's disease gene unlikely. J Med Genet. 1991 Aug;28(8):520–522. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.8.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. P., MacDonald M. E., Baxendale S., Youngman S., Lin C., Whaley W. L., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F., Lehrach H. Defined physical limits of the Huntington disease gene candidate region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):7–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Vo T. D., DeHaven C. R., Murray J. C. An anonymous genomic clone that detects a frequent RFLP adjacent to the D4S10 (G8) marker and Huntington's disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):377–377. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam T. C., Bucan M., MacDonald M. E., Zimmer M., Haines J. L., Cheng S. V., Pohl T. M., Meyers R. H., Whaley W. L., Allitto B. A. A DNA segment encoding two genes very tightly linked to Huntington's disease. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.2890209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonen E., Palo J., Ott J., Gusella J., Somer H., Karila L., Palotie A., Peltonen L. Huntington disease in Finland: linkage disequilibrium of chromosome 4 RFLP haplotypes and exclusion of a tight linkage between the disease and D4S43 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):5–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Cheng S. V., Zimmer M., Haines J. L., Poustka A., Allitto B., Smith B., Whaley W. L., Romano D. M., Jagadeesh J. Clustering of multiallele DNA markers near the Huntington's disease gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):1013–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI114222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Haines J. L., Zimmer M., Cheng S. V., Youngman S., Whaley W. L., Wexler N., Bucan M., Allitto B. A., Smith B. Recombination events suggest potential sites for the Huntington's disease gene. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Non-random association between electromorphs and inversion chromosomes in finite populations. Genet Res. 1980 Feb;35(1):65–83. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001394x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelletto A., Mandich P., Bellone E., Malaspina P., Vivona G., Ajmar F., Frontali M. Non-random association between DNA markers and Huntington disease locus in the Italian population. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Sep 1;40(3):374–376. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320400326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam T. C., Cole J. L., Drumm M. L., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F., Collins F. S. Chromosome jumping from D4S10 (G8) toward the Huntington disease gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6437–6441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C., Theilmann J., Youngman S., Haines J., Altherr M. J., Harper P. S., Payne C., Junker A., Wasmuth J., Hayden M. R. Evidence from family studies that the gene causing Huntington disease is telomeric to D4S95 and D4S90. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):422–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skraastad M. I., Bakker E., de Lange L. F., Vegter-van der Vlis M., Klein-Breteler E. G., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Mapping of recombinants near the Huntington disease locus by using G8 (D4S10) and newly isolated markers in the D4S10 region. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):560–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skraastad M. I., Verwest A., Bakker E., Vegter-van der Vlis M., van Leeuwen-Cornelisse I., Roos R. A., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Presymptomatic, prenatal, and exclusion testing for Huntington disease using seven closely linked DNA markers. Am J Med Genet. 1991 May 1;39(2):217–222. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320390221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Skarecky D., Bengtsson U., Magenis R. E., Carpenter N., Wasmuth J. J. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington disease gene from the G8 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Lazarou L. P., Youngman S., Quarrell O. W., Wasmuth J. J., Shaw D. J., Harper P. S. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: an improved localisation for the gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):673–675. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hewitt J., Smith B., Allard D., Haines J. L., Skarecky D., Partlow E., Hayden M. R. A highly polymorphic locus very tightly linked to the Huntington's disease gene. Nature. 1988 Apr 21;332(6166):734–736. doi: 10.1038/332734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley W. L., Bates G. P., Novelletto A., Sedlacek Z., Cheng S., Romano D., Ormondroyd E., Allitto B., Lin C., Youngman S. Mapping of cosmid clones in Huntington's disease region of chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1991 Jan;17(1):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01233207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman S., Sarfarazi M., Bucan M., MacDonald M., Smith B., Zimmer M., Gilliam C., Frischauf A. M., Wasmuth J. J., Gusella J. F. A new DNA marker (D4S90) is located terminally on the short arm of chromosome 4, close to the Huntington disease gene. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):802–809. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


