Abstract
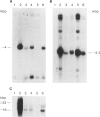
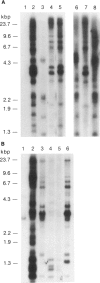
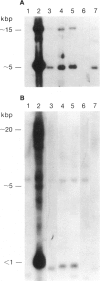
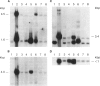
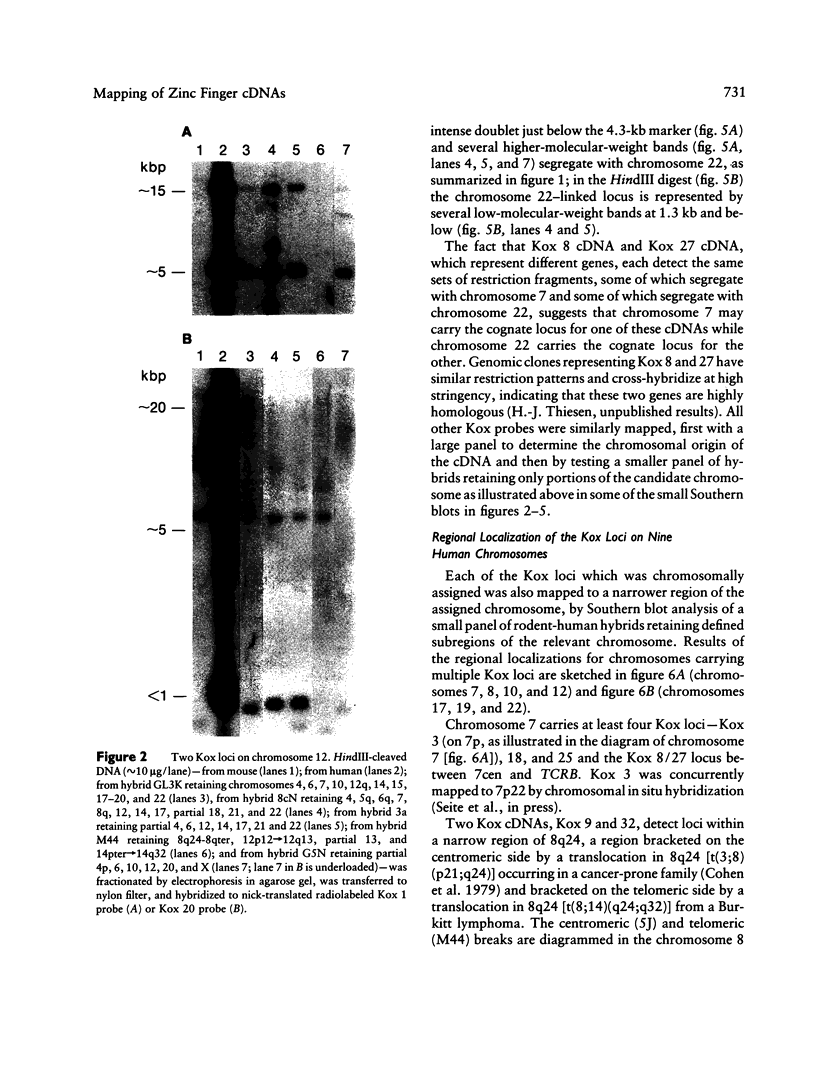
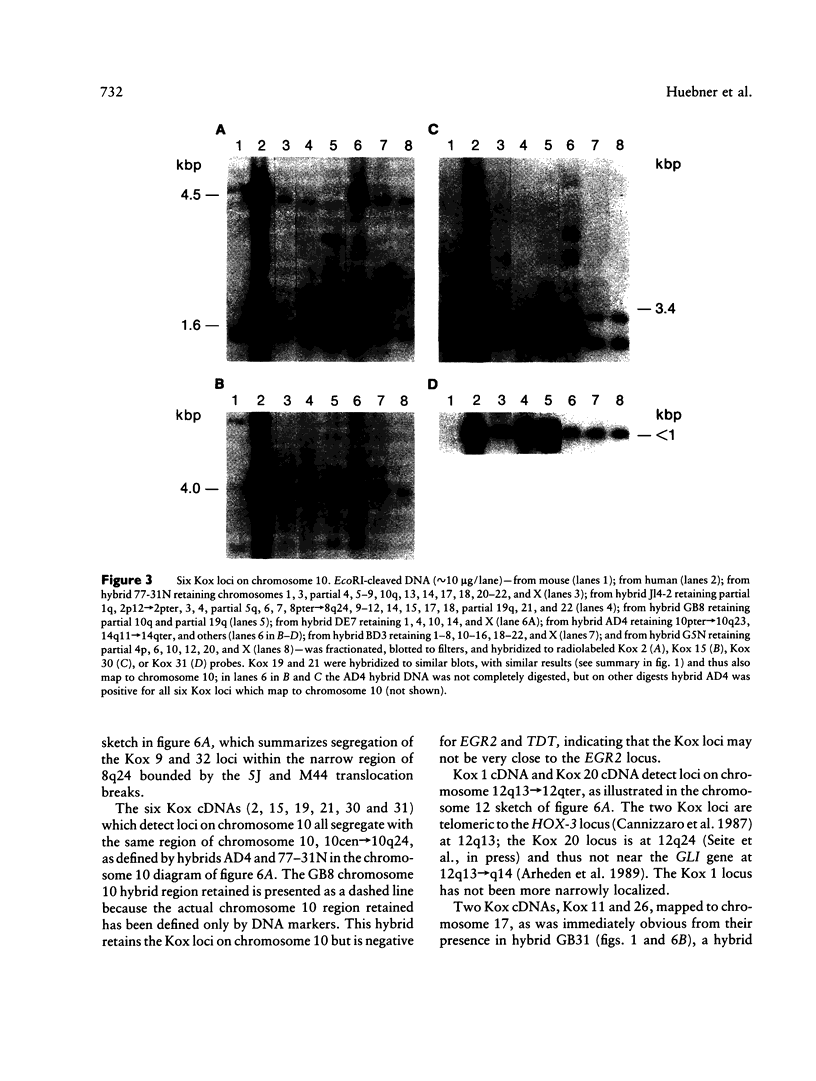
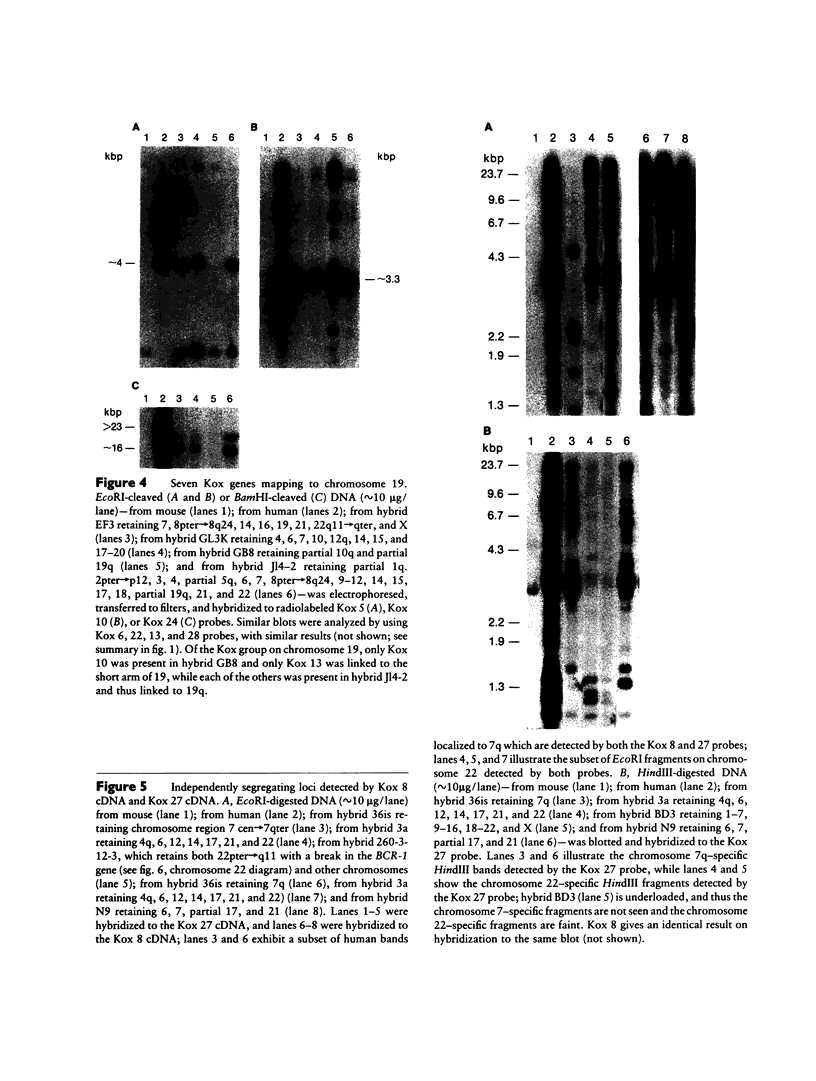
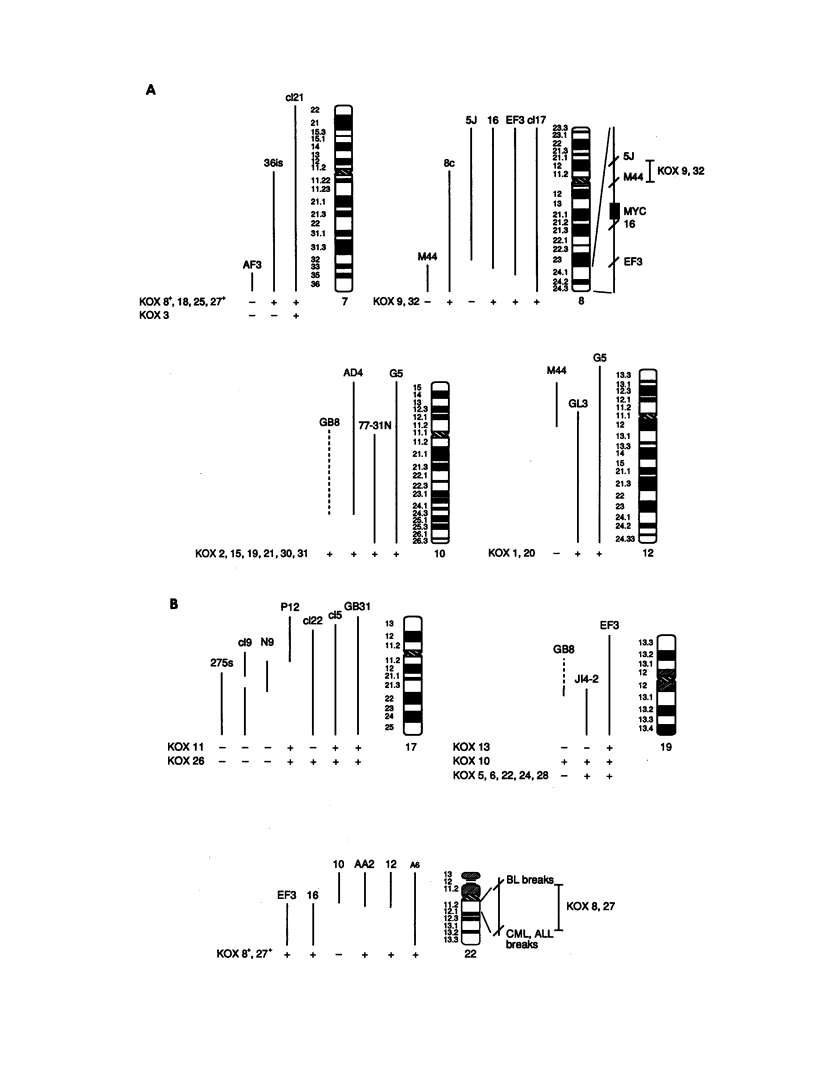
cDNA clones encoding zinc finger structures were isolated by screening Molt4 and Jurkat cDNA libraries with zinc finger consensus sequences. Candidate clones were partially sequenced to verify the presence of zinc finger-encoding regions; nonoverlapping cDNA clones were chosen on the basis of sequences and genomic hybridization pattern. Zinc finger structure-encoding clones, which were designated by the term "Kox" and a number from 1 to 32 and which were apparently unique (i.e., distinct from each other and distinct from those isolated by other laboratories), were chosen for mapping in the human genome. DNAs from rodent-human somatic cell hybrids retaining defined complements of human chromosomes were analyzed for the presence of each of the Kox genes. Correlation between the presence of specific human chromosome regions and specific Kox genes established the chromosomal locations. Multiple Kox loci were mapped to 7q (Kox 18 and 25 and a locus detected by both Kox 8 cDNA and Kox 27 cDNA), 8q24 5' to the myc locus (Kox 9 and 32), 10cen----q24 (Kox 2, 15, 19, 21, 30, and 31), 12q13-qter (Kox 1 and 20), 17p13 (Kox 11 and 26), and 19q (Kox 5, 6, 10, 22, 24, and 28). Single Kox loci were mapped to 7p22 (Kox 3), 18q12 (Kox 17), 19p (Kox 13), 22q11 between IG lambda and BCR-1 (locus detected by both Kox 8 cDNA and Kox 27 cDNA), and Xp (Kox 14). Several of the Kox loci map to regions in which other zinc finger structure-encoding loci have already been localized, indicating possible zinc finger gene clusters. In addition, Kox genes at 8q24, 17p13, and 22q11--and perhaps other Kox genes--are located near recurrent chromosomal translocation breakpoints. Others, such as those on 7p and 7q, may be near regions specifically active in T cells.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arheden K., Rønne M., Mandahl N., Heim S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Mitelman F. In situ hybridization localizes the human putative oncogene GLI to chromosome subbands 12q13.3-14.1. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):1–2. doi: 10.1007/BF00288260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashworth A., Williams B. P., Buchberg A. M., Goodfellow P. N., Solomon E., Potter J., Willison K. R. Chromosomal localization of zinc finger protein genes in man and mouse. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer S. R., Huebner K., Budarf M., Finan J., Erikson J., Emanuel B. S., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M., Melchers F. The human Vpre B gene is located on chromosome 22 near a cluster of V lambda gene segments. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(5):328–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00364231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid E. J., Lecocq P. J., Benhida A., Poncelet D. A., Belayew A., Martial J. A. The human genome contains hundreds of genes coding for finger proteins of the Krüppel type. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):377–387. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Thiesen H. J. Putting the finger on DNA. Zinc Finger Gene Meeting sponsored by the Imperical Cancer Research Fund, London, UK, February 15-16, 1990. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):325–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Croce C. M., Griffin C. A., Simeone A., Boncinelli E., Huebner K. Human homeo box-containing genes located at chromosome regions 2q31----2q37 and 12q12----12q13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;41(1):1–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. J., Li F. P., Berg S., Marchetto D. J., Tsai S., Jacobs S. C., Brown R. S. Hereditary renal-cell carcinoma associated with a chromosomal translocation. N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):592–595. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donti E., Lanfrancone L., Huebner K., Pascucci A., Venti G., Pengue G., Grignani F., Croce C. M., Lania L., Pelicci P. G. Localization of the human HF.10 finger gene on a chromosome region (3p21-22) frequently deleted in human cancers. Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;84(5):391–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00195806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in mesoderm-derived structures correlate with the linear gene order along the chromosome. Differentiation. 1989 Sep;41(3):193–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Croce C. M., Gissmann L., Schwarz E., Huebner K. Papillomavirus sequences integrate near cellular oncogenes in some cervical carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Cannizzaro L. A., Battini R., Huebner K., Baserga R. The gene encoding human vimentin is located on the short arm of chromosome 10. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;41(4):616–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco A., Ittmann M., Barletta C., Basilico C., Croce C. M., Cannizzaro L. A., Huebner K. Chromosomal localization of human genes required for G1 progression in mammalian cells. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):240–245. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haluska F. G., Finver S., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. The t(8; 14) chromosomal translocation occurring in B-cell malignancies results from mistakes in V-D-J joining. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):158–161. doi: 10.1038/324158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Frézal J., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Schinzel A. Report of the committee on clinical disorders and chromosomal deletion syndromes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):563–611. doi: 10.1159/000132808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Cannizzaro L. A., Frey A. Z., Hecht B. K., Hecht F., Croce C. M., Wallner B. P. Chromosomal localization of the human genes for lipocortin I and lipocortin II. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):299–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Cannizzaro L. A., Nakamura T., Hillova J., Mariage-Samson R., Hecht F., Hill M., Croce C. M. A rearranged transforming gene, tre, is made up of human sequences derived from chromosome regions 5q, 17q and 18q. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):449–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Isobe M., Gasson J. C., Golde D. W., Croce C. M. Localization of the gene encoding human erythroid-potentiating activity to chromosome region Xp11.1----Xp11.4. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):819–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Nagarajan L., Besa E., Angert E., Lange B. J., Cannizzaro L. A., van den Berghe H., Santoli D., Finan J., Croce C. M. Order of genes on human chromosome 5q with respect to 5q interstitial deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):26–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho K. E., Darby M. K., Crawford E. T., Brown D. D. A finger protein structurally similar to TFIIIA that binds exclusively to 5S RNA in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90809-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph L. J., Le Beau M. M., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Acharya S., Shows T. B., Rowley J. D., Sukhatme V. P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and mapping of EGR2, a human early growth response gene encoding a protein with "zinc-binding finger" structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan J., Finger L. R., Letofsky J., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Clustering of breakpoints on chromosome 10 in acute T-cell leukemias with the t(10;14) chromosome translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4161–4165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Ruppert J. M., Bigner S. H., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene is a member of the Kruppel family of zinc finger proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):371–374. doi: 10.1038/332371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene encodes a nuclear protein which binds specific sequences in the human genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):634–642. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lania L., Donti E., Pannuti A., Pascucci A., Pengue G., Feliciello I., La Mantia G., Lanfrancone L., Pelicci P. G. cDNA isolation, expression analysis, and chromosomal localization of two human zinc finger genes. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90574-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessin S. R., Huebner K., Isobe M., Croce C. M., Steinert P. M. Chromosomal mapping of human keratin genes: evidence of non-linkage. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Dec;91(6):572–578. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12477087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinerie C., Cannizzaro L. A., Croce C. M., Huebner K., Katzav S., Barbacid M. The human VAV proto-oncogene maps to chromosome region 19p12----19p13.2. Hum Genet. 1990 Nov;86(1):65–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00205175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Schempp W. Mapping the human ZFX locus to Xp21.3 by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):82–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00288279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Birkenmeier C. S., Chowdhury K., Crosby J. L., Lalley P. A. Zinc finger protein gene complexes on mouse chromosomes 8 and 11. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90033-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Disteche C. M., Simpson E. M., de la Chapelle A., Andersson M., Alitalo T., Brown L. G., Green P., Akots G. Chromosomal localization of ZFX--a human gene that escapes X inactivation--and its murine homologs. Genomics. 1990 May;7(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90516-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Mosher R., Simpson E. M., Fisher E. M., Mardon G., Pollack J., McGillivray B., de la Chapelle A., Brown L. G. The sex-determining region of the human Y chromosome encodes a finger protein. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1091–1104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannuti A., Lanfrancone L., Pascucci A., Pelicci P. G., La Mantia G., Lania L. Isolation of cDNAs encoding finger proteins and measurement of the corresponding mRNA levels during myeloid terminal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4227–4237. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss A., Rosenberg U. B., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Jäckle H. Molecular genetics of Krüppel, a gene required for segmentation of the Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):27–32. doi: 10.1038/313027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter G., Giarre M., Farah J., Gausz J., Spierer A., Spierer P. Dependence of position-effect variegation in Drosophila on dose of a gene encoding an unusual zinc-finger protein. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):219–223. doi: 10.1038/344219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Merck M. F., Huebner K., Berger R., Thiesen H. J. Chromosomal localization of two human zinc finger protein genes, ZNF24 (KOX17) and ZNF29 (KOX26), to 18q12 and 17p13-p12, respectively. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J. M., Kinzler K. W., Wong A. J., Bigner S. H., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Seuanez H. N., O'Brien S. J., Vogelstein B. The GLI-Kruppel family of human genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3104–3113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo G., Isobe M., Pegoraro L., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Molecular analysis of a t(7;14)(q35;q32) chromosome translocation in a T cell leukemia of a patient with ataxia telangiectasia. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90495-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanojević D., Hoey T., Levine M. Sequence-specific DNA-binding activities of the gap proteins encoded by hunchback and Krüppel in Drosophila. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):331–335. doi: 10.1038/341331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Cao X. M., Chang L. C., Tsai-Morris C. H., Stamenkovich D., Ferreira P. C., Cohen D. R., Edwards S. A., Shows T. B., Curran T. A zinc finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J. Multiple genes encoding zinc finger domains are expressed in human T cells. New Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):363–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Kaneko Y., Mitelman F. Report of the committee on structural chromosome changes in neoplasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):533–562. doi: 10.1159/000132807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Lee J. S., Bear S. E., Lazo P. A., Patriotis C., Gustafson E., Shinton S., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Huebner K. Activation of multiple genes by provirus integration in the Mlvi-4 locus in T-cell lymphomas induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2236–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2236-2244.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vingron M., Nordheim A., Müller R. Anatomy of fos proteins. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tuinen P., Rich D. C., Summers K. M., Ledbetter D. H. Regional mapping panel for human chromosome 17: application to neurofibromatosis type 1. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):374–381. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]