Abstract
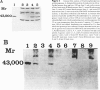
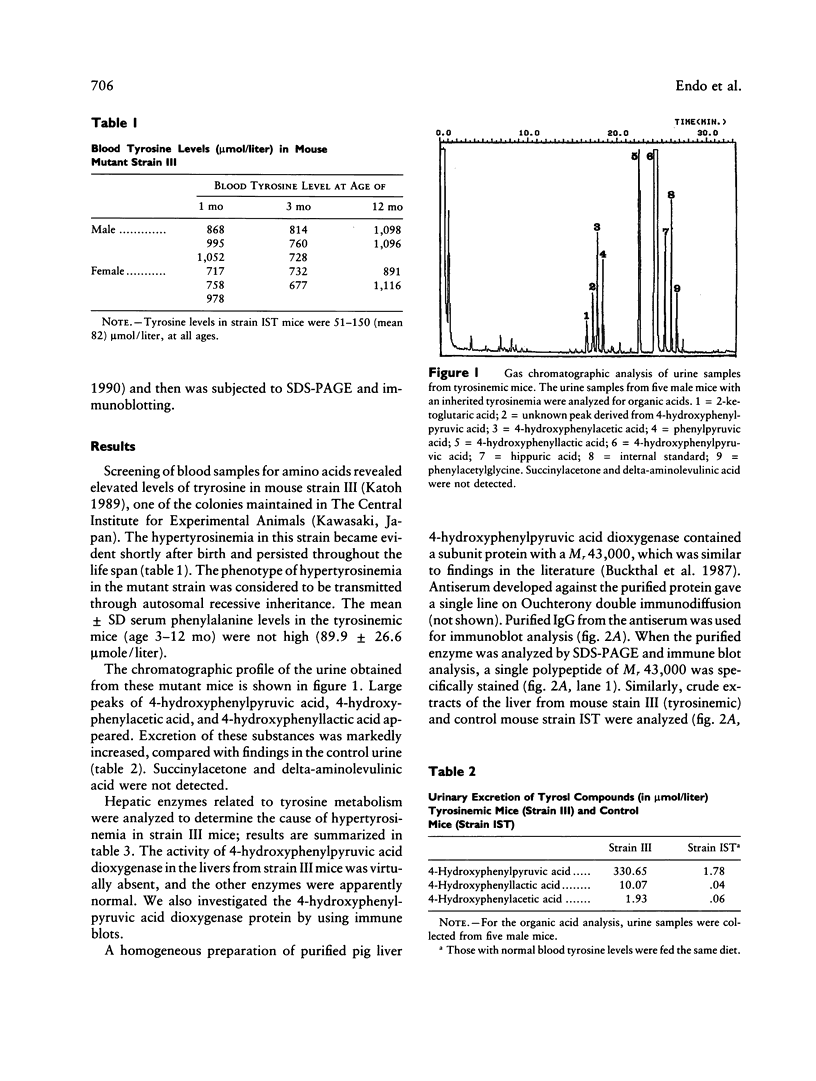
We have characterized a new mutant strain of mouse that has hypertyrosinemia. The blood tyrosine level was persistently high, and increased amounts of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid and its derivatives were excreted into the urine. Succinylacetone was not detected in urine samples from these mice. All the animals were apparently healthy, and there was no evidence of hepatorenal dysfunction. The hypertyrosinemia was transmitted through an autosomal recessive inheritance. Analyses of hepatic enzymes related to tyrosine metabolism revealed that 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase activity was virtually absent, while fumarylacetoacetase and tyrosine aminotransferases (cytosolic and mitochondrial forms) were normal in these mutant mice. Immunoblot analysis of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase protein in the liver indicated that the subunit protein of the enzyme was absent. It would appear that hypertyrosinemia in this mutant strain was caused by a genetic defect in 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase. These features are similar to type III tyrosinemia in humans. Analysis of this mutant strain of mouse is expected to provide valuable information on the pathogenesis of human type III tyrosinemia and can also serve as a useful system for studies on tyrosine metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger R., Smit G. P., Stoker-de Vries S. A., Duran M., Ketting D., Wadman S. K. Deficiency of fumarylacetoacetase in a patient with hereditary tyrosinemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Jul 18;114(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckthal D. J., Roche P. A., Moorehead T. J., Forbes B. J., Hamilton G. A. 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase from pig liver. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., LeVan S. L., Trend B. L., Russell L. B. Abnormal ornithine carbamoyltransferase in mice having the sparse-fur mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1693–1697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo F., Kitano A., Uehara I., Nagata N., Matsuda I., Shinka T., Kuhara T., Matsumoto I. Four-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid oxidase deficiency with normal fumarylacetoacetase: a new variant form of hereditary hypertyrosinemia. Pediatr Res. 1983 Feb;17(2):92–96. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198302000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo F., Tanoue A., Kitano A., Arata J., Danks D. M., Lapière C. M., Sei Y., Wadman S. K., Matsuda I. Biochemical basis of prolidase deficiency. Polypeptide and RNA phenotypes and the relation to clinical phenotypes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):162–169. doi: 10.1172/JCI114407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellman J. H., Vanbellinghen P. J., Jones R. T., Koler R. D. Soluble and mitochondrial forms of tyrosine aminotransferase. Relationship to human tyrosinemia. Biochemistry. 1969 Feb;8(2):615–622. doi: 10.1021/bi00830a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardini O., Cantani A., Kennaway N. G., D'Eufemia P. Chronic tyrosinemia associated with 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase deficiency with acute intermittent ataxia and without visceral and bone involvement. Pediatr Res. 1983 Jan;17(1):25–29. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198301000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvittingen E. A., Jellum E., Stokke O. Assay of fumarylacetoacetate fumarylhydrolase in human liver-deficient activity in a case of hereditary tyrosinemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Sep;115(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Du B. N. The enzymatic deficiency in tyrosinemia. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Jan;113(1):54–57. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090160104010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad B., Lindstedt G., Lindstedt S., Rundgren M. Purification and some properties of human 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (I). J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5073–5084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad B. Radiochemical assays for p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase activity in human liver. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Aug;34(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstedt S., Odelhög B. 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase from human liver. Methods Enzymol. 1987;142:139–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)42021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Moorehead T. J., Hamilton G. A. Purification and properties of hog liver 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jun;216(1):62–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Hine D. G., West-Dull A., Lynn T. B. Gas-chromatographic method of analysis for urinary organic acids. I. Retention indices of 155 metabolically important compounds. Clin Chem. 1980 Dec;26(13):1839–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada G. H., Fellman J. H., Fujita T. S., Roth E. S. Purification and properties of avian liver p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6720–6726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]