Abstract
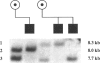
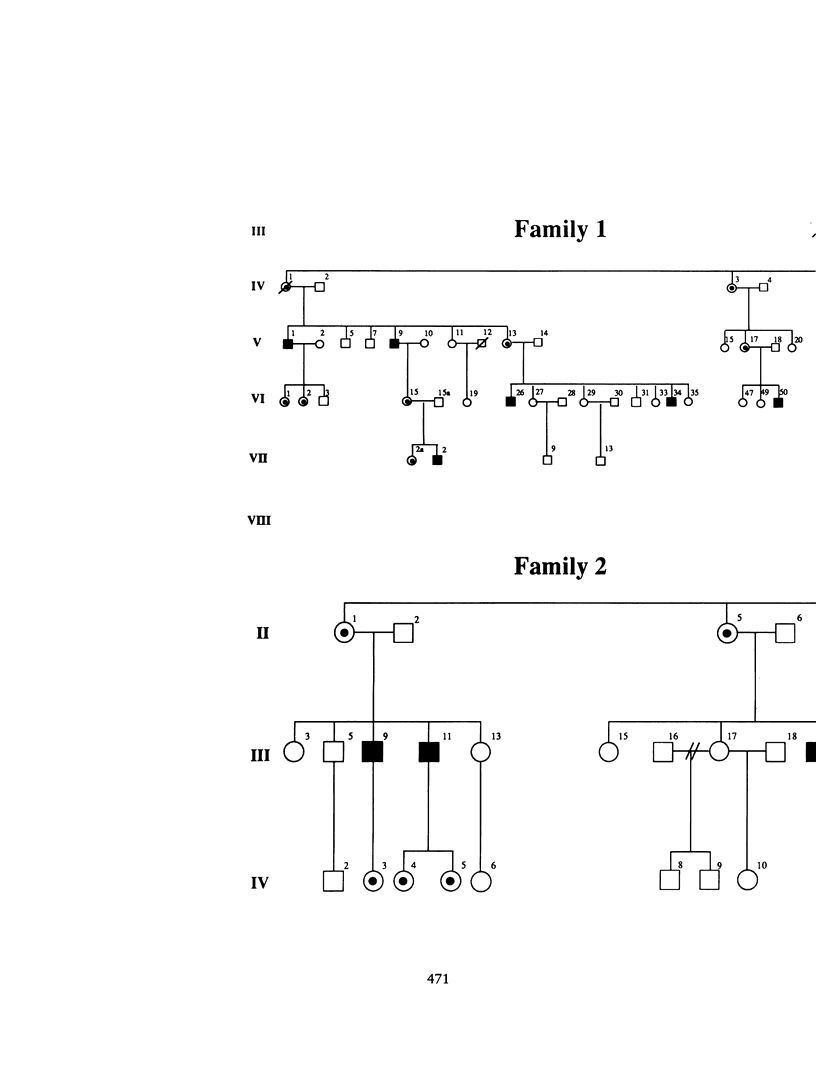
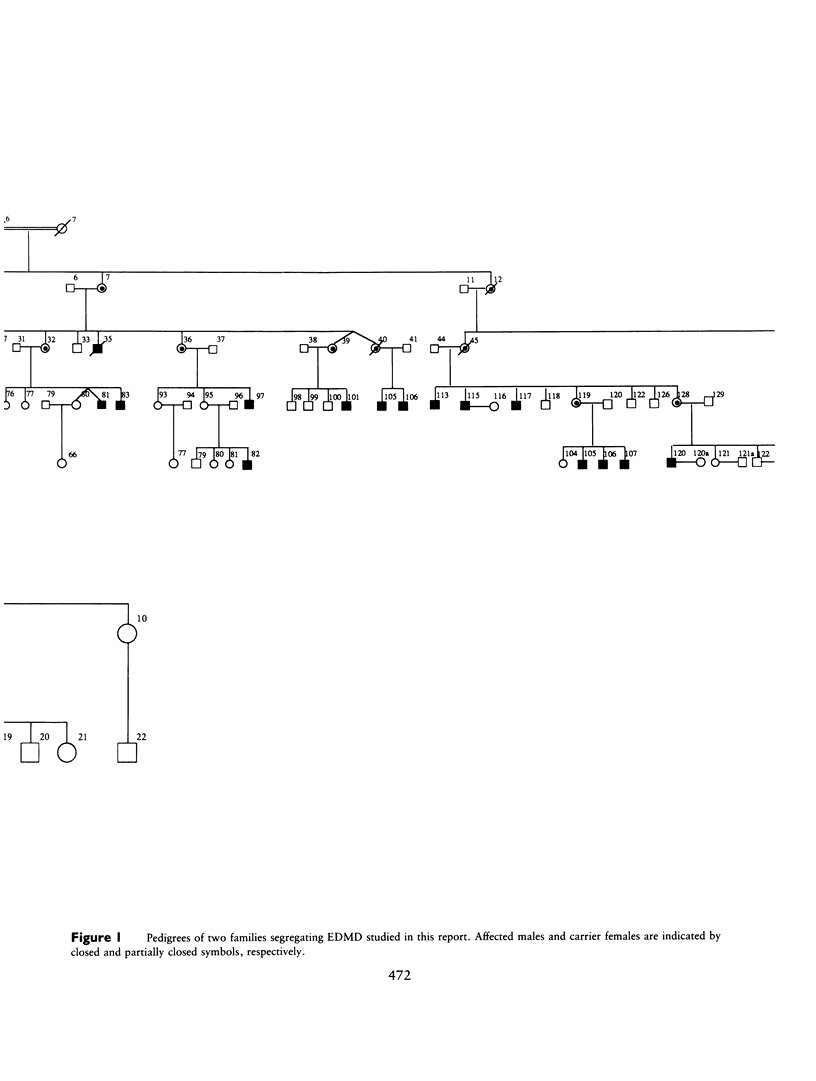
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) is an X-linked humeroperoneal dystrophy associated with cardiomyopathy that is distinct from the Duchenne and Becker forms of X-linked muscular dystrophy. Linkage analysis has assigned EDMD to the terminal region of the human X chromosome long arm. We report here further linkage analysis in two multigenerational EDMD families using seven Xq28 marker loci. Cumulative lod scores suggest that EDMD is approximately 2 cM from DXS52 (lod = 15.67) and very close to the factor VIII (F8C) and the red/green color pigment (R/GCP) loci, with respective lod scores of 9.62 and 10.77, without a single recombinant. Several recombinations between EDMD and three proximal Xq28 markers suggest that the EDMD gene is located in distal Xq28. Multipoint linkage analysis indicates that the odds are 2,000:1 that EDMD lies distal to DXS305. These data substantially refine the ability to perform accurate carrier detection, prenatal diagnosis, and the presymptomatic diagnosis of at-risk males for EDMD by linkage analysis. The positioning of the EDMD locus close to the loci for F8C and R/GCP will assist in future efforts to identify and isolate the disease gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arveiler B., Vincent A., Mandel J. L. Toward a physical map of the Xq28 region in man: linking color vision, G6PD, and coagulation factor VIII genes to an X-Y homology region. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):460–471. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood J., Bryant S. A computer program to make linkage analysis with LIPED and LINKAGE easier to perform and less prone to input errors. Ann Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;52(Pt 3):259–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1988.tb01103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREIFUSS F. E., HOGAN G. R. Survival in x-chromosomal muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 1961 Aug;11:734–737. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.8.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Goonewardena P., Malmgren H., Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Seemanova E., Annerén G., Flood A., Pettersson U. Linkage analysis of families with fragile-X mental retardation, using a novel RFLP marker (DXS 304). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):304–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E., Dreifuss F. E. Unusual type of benign x-linked muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Aug;29(4):338–342. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Emery-Dreifuss syndrome. J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;26(10):637–641. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.10.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. X-linked muscular dystrophy with early contractures and cardiomyopathy (Emery-Dreifuss type). Clin Genet. 1987 Nov;32(5):360–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil R., Palmieri G., d'Urso M., Heilig R., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Physical and genetic mapping of polymorphic loci in Xq28 (DXS15, DXS52, and DXS134): analysis of a cosmid clone and a yeast artificial chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):720–728. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Schram L. J., Wallis G., Oswald A., Beighton P. Emery-Dreifuss syndrome and X-linked muscular dystrophy with contractures: evidence for homogeneity. Clin Genet. 1989 Jan;35(1):1–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins L. C., Jackson J. A., Elsas L. J. Emery-dreifuss humeroperoneal muscular dystrophy: an x-linked myopathy with unusual contractures and bradycardia. Ann Neurol. 1981 Sep;10(3):230–237. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Sankila E. M., Miao J., Somer M., Salonen R., Rapola J., de la Chapelle A. X linked neonatal myotubular myopathy: one recombination detected with four polymorphic DNA markers from Xq28. J Med Genet. 1990 May;27(5):288–291. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.5.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M. N., Bell M. V., Bloomfield J., Flint T., Dorkins H., Thibodeau S. N., Schaid D., Bren G., Schwartz C. E., Wieringa B. Genetic and physical mapping of a novel region close to the fragile X site on the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):570–578. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., Roncuzzi L., Sangiorgi S., Giacanelli M., Liguori M., Tessarolo D., Rocchi M. Mapping of the Emery-Dreifuss gene through reconstruction of crossover points in two Italian pedigrees. Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;80(1):59–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00451457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saviranta P., Lindlöf M., Lehesjoki A. E., Kalimo H., Lang H., Sonninen V., Savontaus M. L., de la Chapelle A. Linkage studies in a new X-linked myopathy, suggesting exclusion of DMD locus and tentative assignment to distal Xq. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):84–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Williams H., Elsas L. J., Hopkins L. C., Sarfarazi M., Harper P. S. Localisation of the gene for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy to the distal long arm of the X chromosome. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):596–598. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Calne D. B., Elliott C. F. X-linked scapuloperoneal syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Apr;35(2):208–215. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Dahl N., Oberlé I., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L., Malmgren H., Pettersson U. The polymorphic marker DXS304 is within 5 centimorgans of the fragile X locus. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):797–801. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. A new polymorphic marker very closely linked to DXS52 in the q28 region of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00288280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters D. D., Nutter D. O., Hopkins L. C., Dorney E. R. Cardiac features of an unusual X-linked humeroperoneal neuromuscular disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 13;293(20):1017–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511132932004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M. L., Elsas L. J., 2nd Application of benefit-to-cost analysis to an X-linked recessive cardiac and humeroperoneal neuromuscular disease. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(4):315–329. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Affara N. A., Jamieson D. M., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Zaremba J., Borkowska J., Johnston A. W., Kelly K. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: localisation to Xq27.3----qter confirmed by linkage to the factor VIII gene. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):587–590. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]