Abstract
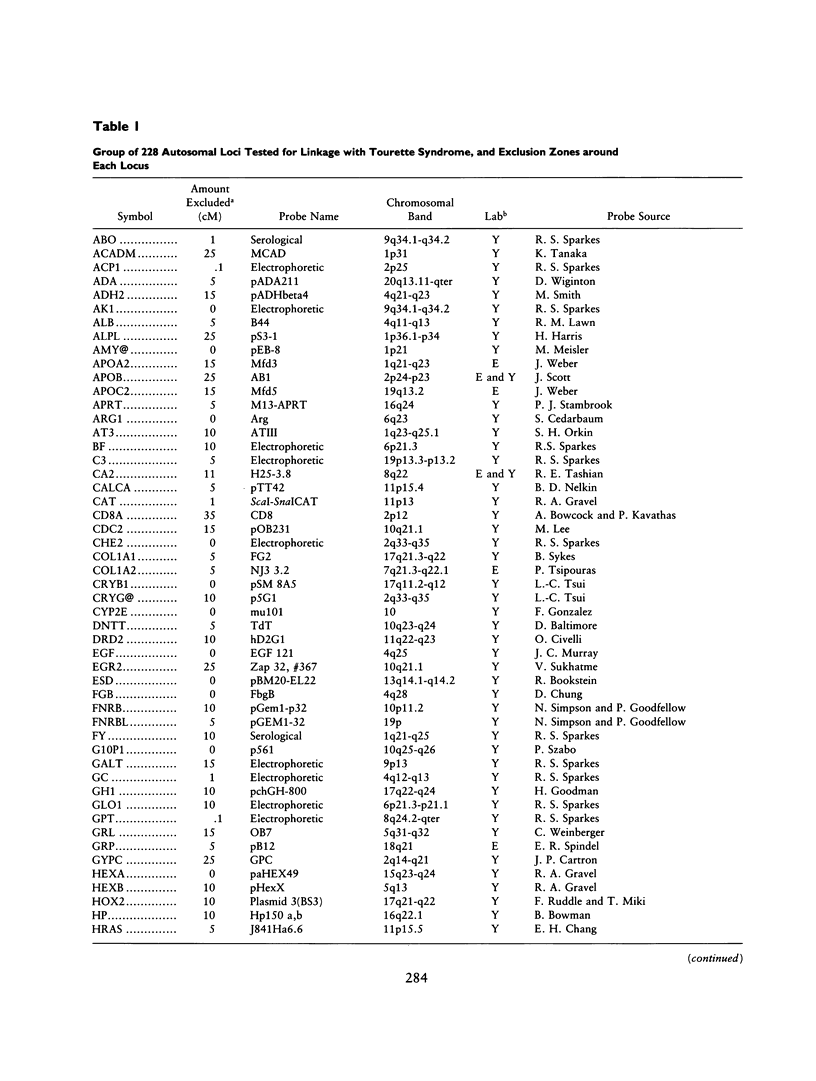
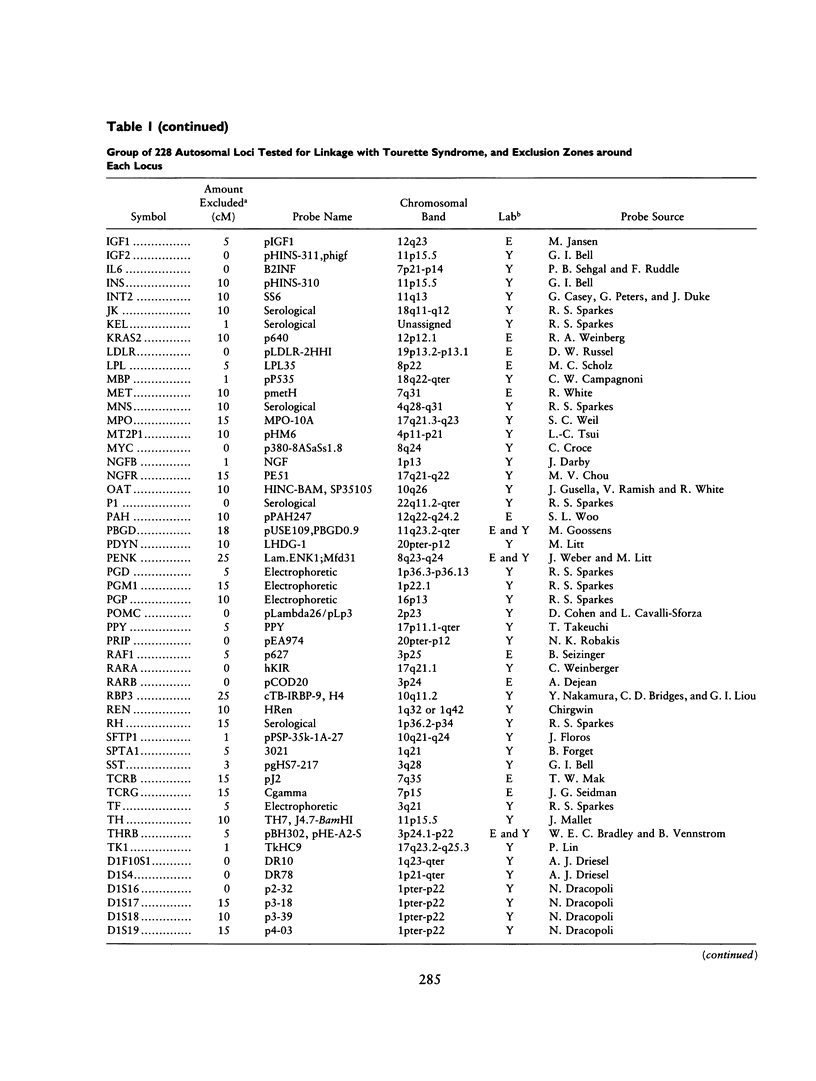
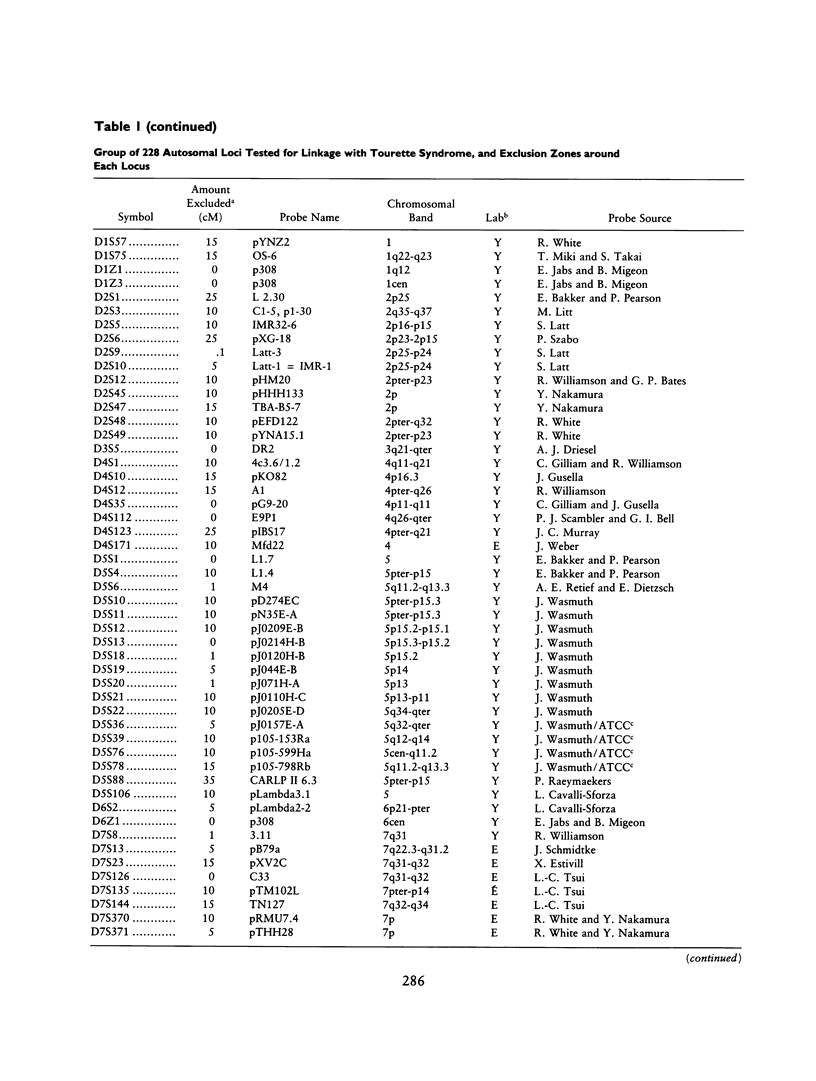
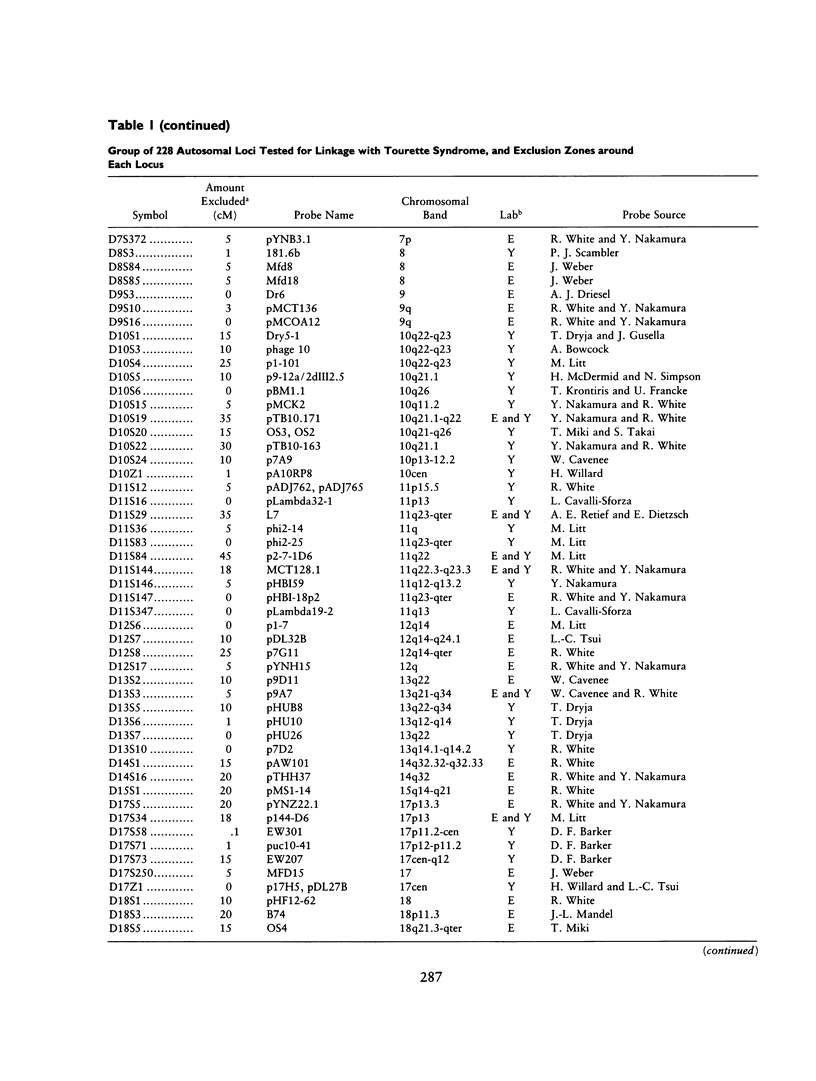
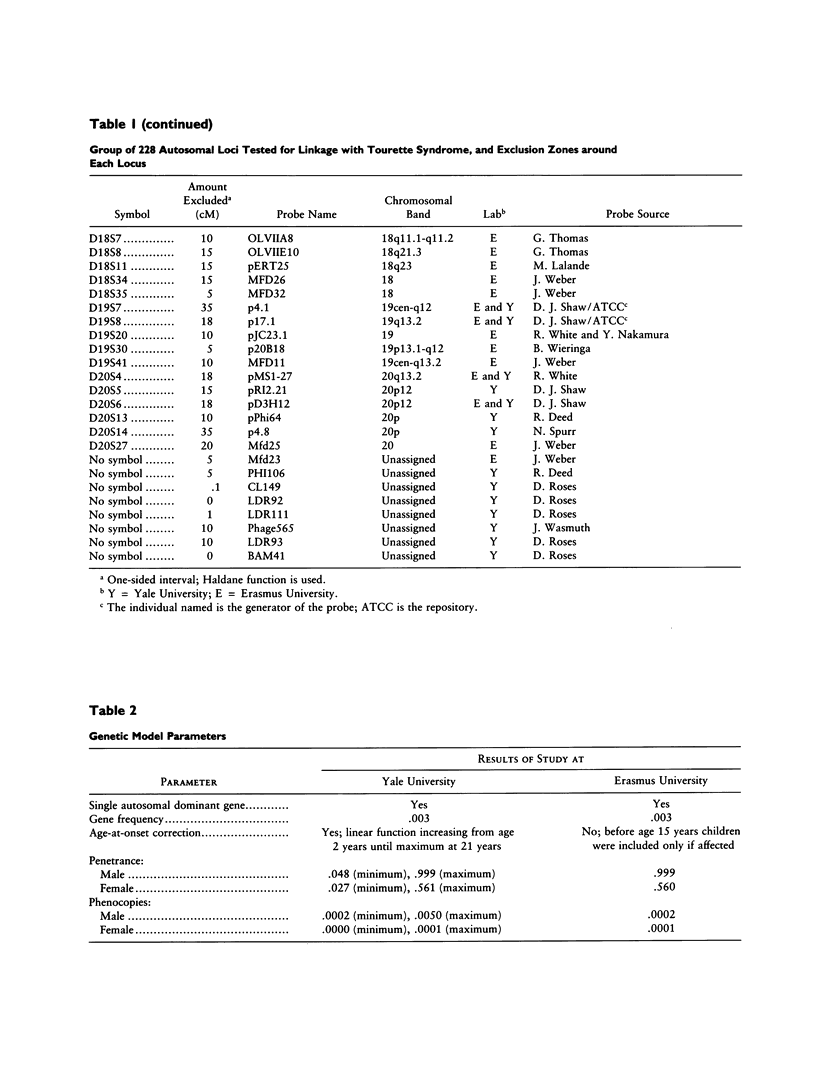
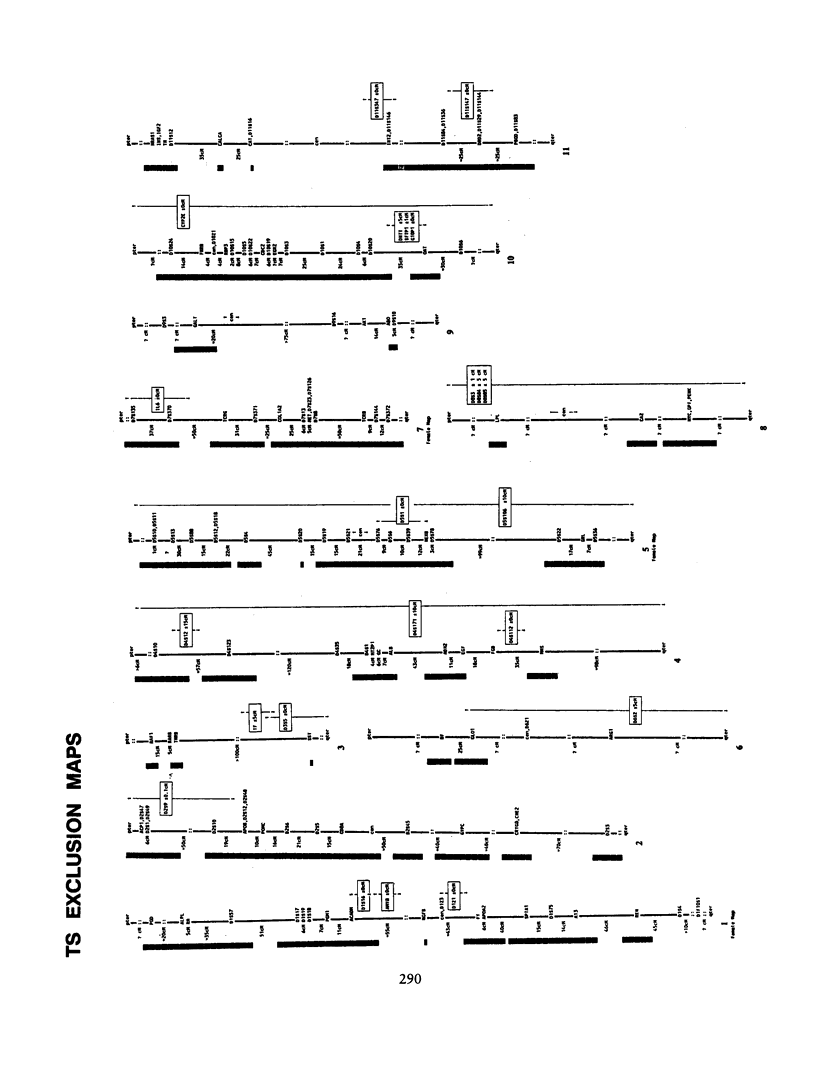
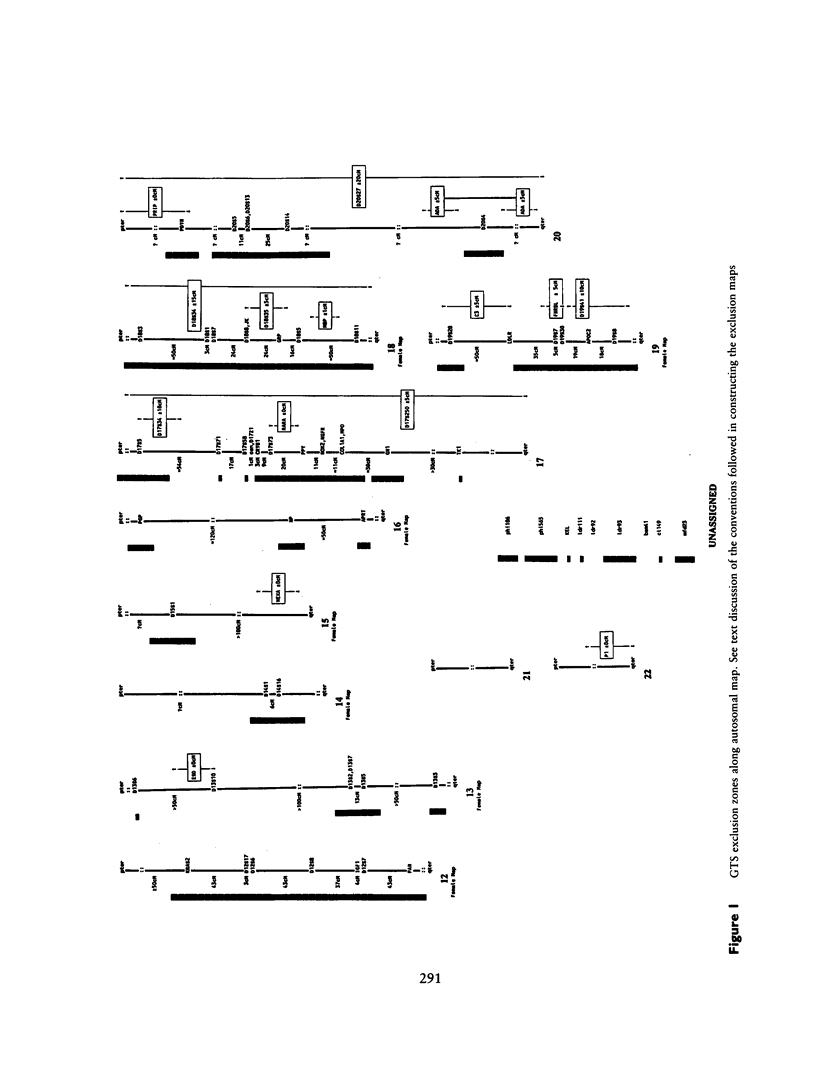
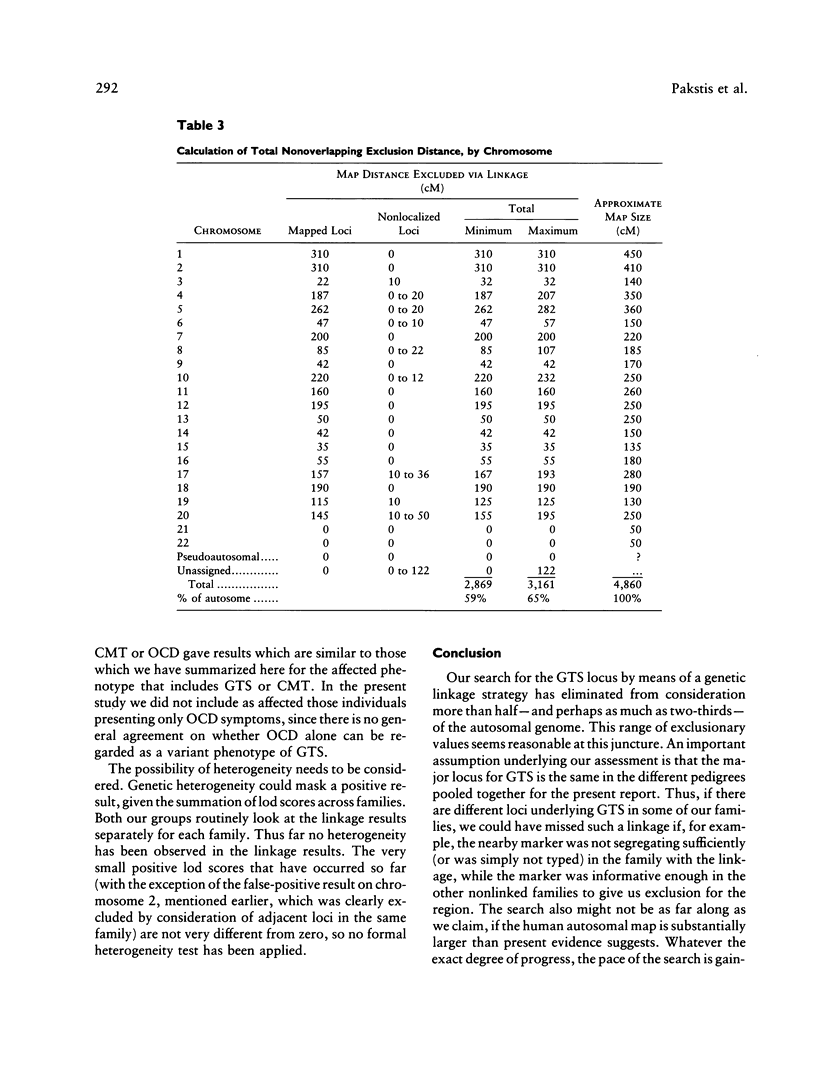
Gilles de la Tourette syndrome is a neuropsychiatric disorder with an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance and reduced penetrance at a single genetic locus. Several research groups have genetic linkage studies underway to detect the chromosomal location of the gene that predisposes for this disorder. Strong and clear evidence of linkage has not yet been produced for Tourette syndrome. This paper presents an overview of the methods and progress of the groups centered at Yale University and Erasmus University in excluding linkage from a large portion of the genome. Our labs have screened 228 genetic marker loci for linkage with a gene for this disorder in a series of affected families in the United States, Canada, The Netherlands, and Norway. More than 50% (and perhaps as much as 66%) of the autosomal genome has now been excluded on the assumption that genetic heterogeneity is not an important factor in the Tourette syndrome pedigrees pooled for this summary.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Devor E. J., Grandy D. K., Civelli O., Litt M., Burgess A. K., Isenberg K. E., van de Wetering B. J., Oostra B. Genetic linkage is excluded for the D2-dopamine receptor lambda HD2G1 and flanking loci on chromosome 11q22-q23 in Tourette syndrome. Hum Hered. 1990;40(2):105–108. doi: 10.1159/000153914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelernter J., Pakstis A. J., Pauls D. L., Kurlan R., Gancher S. T., Civelli O., Grandy D., Kidd K. K. Gilles de la Tourette syndrome is not linked to D2-dopamine receptor. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990 Nov;47(11):1073–1077. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1990.01810230089014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heutink P., van de Wetering B. J., Breedveld G. J., Weber J., Sandkuyl L. A., Devor E. J., Heiberg A., Niermeijer M. F., Oostra B. A. No evidence for genetic linkage of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome on chromosomes 7 and 18. J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;27(7):433–436. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.7.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Kidd J. R., Castiglione C. M., Genel M., Darby J., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Gusella J. F. Linkage analyses of multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 2A (MEN-2A) with 20 DNA polymorphisms: 5% of the genome excluded. Hum Hered. 1986;36(4):243–249. doi: 10.1159/000153634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Prusoff B. A., Cohen D. J. Familial pattern of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Dec;37(12):1336–1339. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780250022001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan R., Behr J., Medved L., Shoulson I., Pauls D., Kidd J. R., Kidd K. K. Familial Tourette's syndrome: report of a large pedigree and potential for linkage analysis. Neurology. 1986 Jun;36(6):772–776. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan R., Behr J., Medved L., Shoulson I., Pauls D., Kidd K. K. Severity of Tourette's syndrome in one large kindred. Implication for determination of disease prevalence rate. Arch Neurol. 1987 Mar;44(3):268–269. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520150024013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan R. Tourette's syndrome: current concepts. Neurology. 1989 Dec;39(12):1625–1630. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.12.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., Farrall M., Tsui L. C., Lalouel J. M., White R. Twenty-five loci form a continuous linkage map of markers for human chromosome 7. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):866–873. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop M., Nakamura Y., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Woodward S., Lalouel J. M., White R. A mapped set of genetic markers for human chromosome 9. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine P. J., Shows T. B., Boucheix C., Stranc L. C., Berent T. G., Pakstis A. J., Douté R. C. Report of the nomenclature committee and the 1989 catalog of mapped genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):13–66. doi: 10.1159/000132780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lalouel J. M., White R. A mapped set of DNA markers for human chromosome 15. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Law M., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., Hoff M., Kumlin E., Thomas W., Elsner T., Ballard L. A primary genetic linkage map for human chromosome 12. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., Müller U., Lalouel J. M., White R. Twelve loci form a continuous linkage map for human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Cohen D. J., Heimbuch R., Detlor J., Kidd K. K. Familial pattern and transmission of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome and multiple tics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Oct;38(10):1091–1093. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780350025002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Kruger S. D., Leckman J. F., Cohen D. J., Kidd K. K. The risk of Tourette's syndrome and chronic multiple tics among relatives of Tourette's syndrome patients obtained by direct interview. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1984 Mar;23(2):134–137. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198403000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Leckman J. F. The inheritance of Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome and associated behaviors. Evidence for autosomal dominant transmission. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 16;315(16):993–997. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610163151604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls D. L., Pakstis A. J., Kurlan R., Kidd K. K., Leckman J. F., Cohen D. J., Kidd J. R., Como P., Sparkes R. Segregation and linkage analyses of Tourette's syndrome and related disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1990 Mar;29(2):195–203. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. A., Pauls D. L., Kruger S. D., Caine E. D. Family data support a dominant major gene for Tourette syndrome. Psychiatry Res. 1988 Jun;24(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence M. A., Sparkes R. S., Heckenlively J. R., Pearlman J. T., Zedalis D., Sparkes M., Crist M., Tideman S. Probable genetic linkage between autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and amylase (AMY2): evidence of an RP locus on chromosome 1. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Jul;29(4):397–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavodny P. J., Petro M. E., Kumar C. C., Dailey S. H., Lonial H. K., Narula S. K., Leibowitz P. J. The nucleotide sequence of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain two. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1214–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


