Abstract
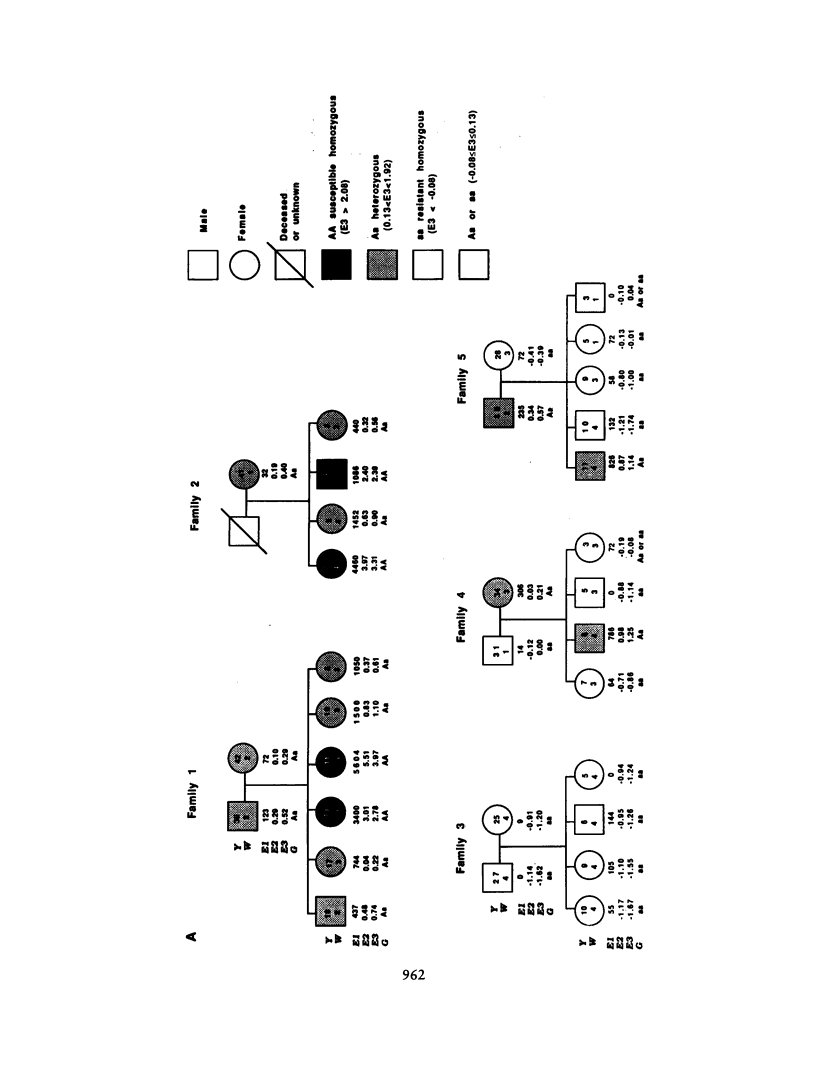
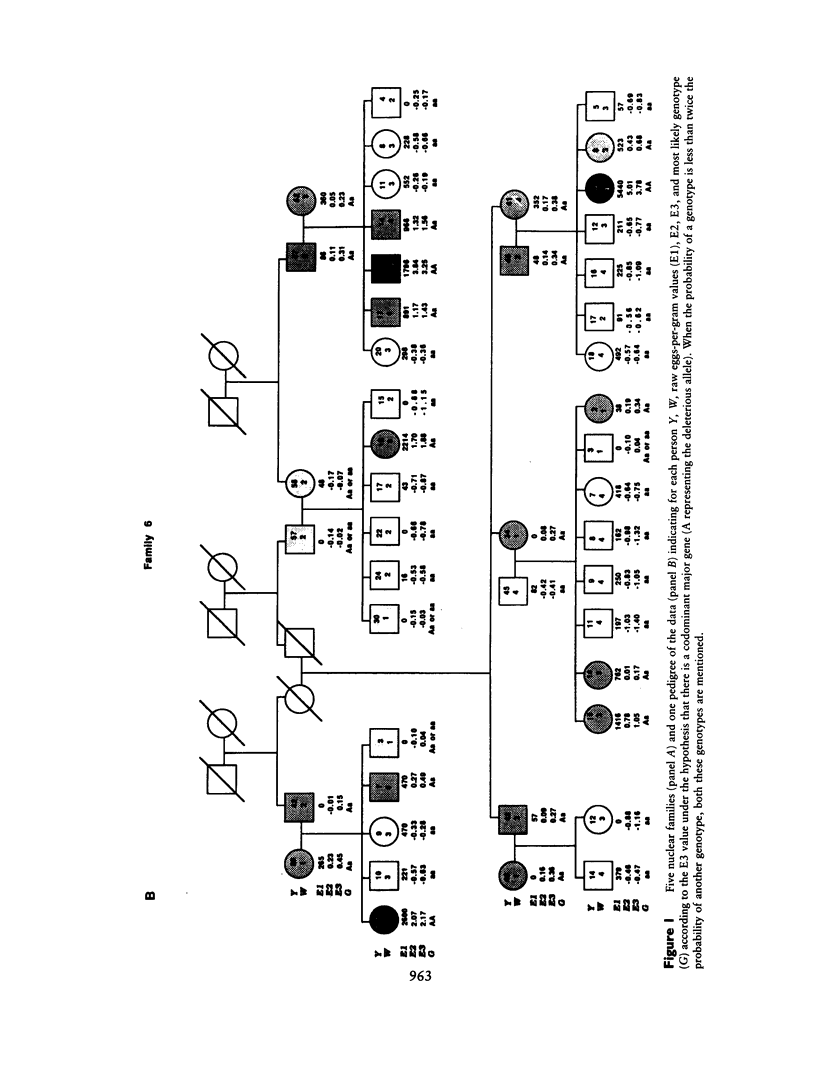
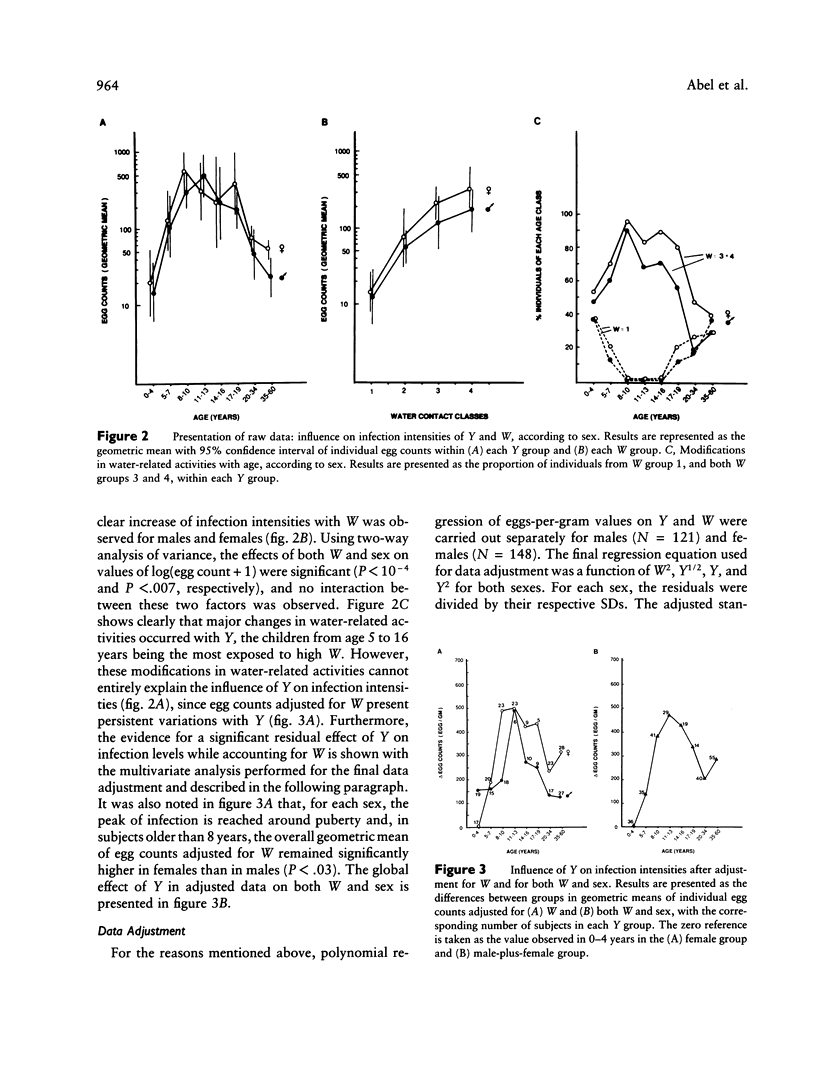
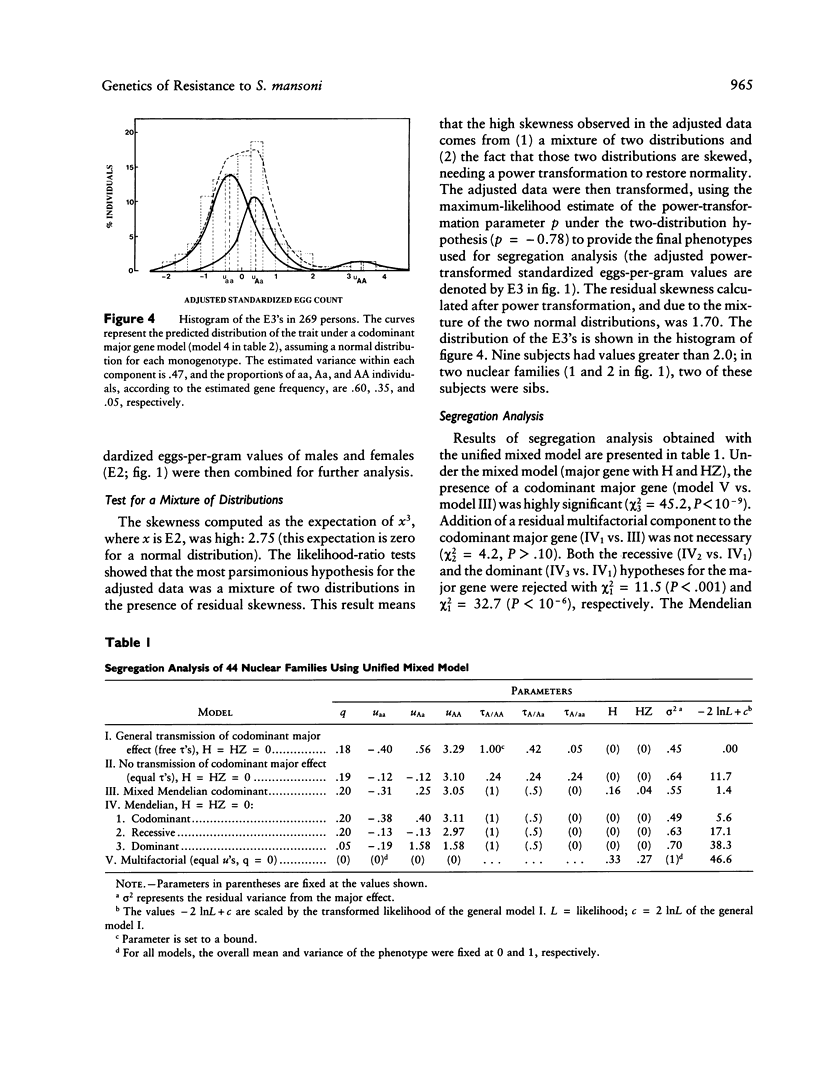
Severe clinical disease caused by the major human parasite Schistosoma mansoni is the consequence of high and prolonged infections. Epidemiological studies indicate that, for individuals having frequent contacts with cercaria-infested waters, both infection intensities and reinfection after treatment depend, in large part, on their intrinsic susceptibility/resistance to infection, suggesting the role of genetic factors in human resistance to S. mansoni. To investigate whether a major gene controls human susceptibility/resistance to infection by S. mansoni, segregation analysis of infection intensities, adjusted for the factors relevant in schistosomiasis (water contact, age, sex), was performed on 20 Brazilian pedigrees (269 individuals), using both the unified mixed model and the regressive model of analysis. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that there is a codominant major gene controlling human susceptibility/resistance to infection by S. mansoni. Parameter estimates indicate a frequency of .20-.25 for the deleterious allele; thus, about 5% of the population is predisposed to high infections, 60% is resistant, and 35% has an intermediate, although fairly good, level of resistance. These findings provide a genetic basis for earlier observations on the lower resistance and the predisposition to reinfection of certain individuals. In addition to the detection of a major gene effect, the data suggest that immunity to S. mansoni develops progressively during childhood to reach a maximum around the age of puberty. The implications of these results for the strategy to be used in endemic areas to reduce morbidity and to control parasite transmission are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abel L., Demenais F. Detection of major genes for susceptibility to leprosy and its subtypes in a Caribbean island: Desirade island. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):256–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney G. E. On the statistical determination of major gene mechanisms in continuous human traits: regressive models. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;18(4):731–749. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Bensted-Smith R., Capron A., Capron M., Dalton P. R., Dunne D. W., Grzych J. M., Kariuki H. C., Khalife J., Koech D. Immunity in human schistosomiasis mansoni: prevention by blocking antibodies of the expression of immunity in young children. Parasitology. 1987 Apr;94(Pt 2):281–300. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000053956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Capron M., Cordingley J. S., Dalton P. R., Dunne D. W., Kariuki H. C., Kimani G., Koech D., Mugambi M., Ouma J. H. Immunity after treatment of human schistosomiasis mansoni. II. Identification of resistant individuals, and analysis of their immune responses. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1985;79(3):393–408. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(85)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A., Dunne D., Fulford A., Capron M., Khalife J., Capron A., Koech D., Ouma J., Sturrock R. Immunity in human schistosomiasis mansoni: cross-reactive IgM and IgG2 anti-carbohydrate antibodies block the expression of immunity. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byram J. E., von Lichtenberg F. Altered schistosome granuloma formation in nude mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Sep;26(5 Pt 1):944–956. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L., David C. S. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. In vitro characterization of T lymphocyte subsets involved in the production and suppression of migration inhibition factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claas F. H., Deelder A. M. H-2 linked immune response to murine experimental Schistosoma mansoni infections. J Immunogenet. 1979 Jun;6(3):167–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1979.tb00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa-Oliveira R., James S. L., McCall D., Sher A. Identification of a genetic locus, Rsm-1, controlling protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):2014–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa-Oliveira R., James S. L., Sher A. Genetic complementation of defects in vaccine-induced immunity against Schistosoma mansoni in P- and A-strain inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):708–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.708-710.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crombie J. A., Anderson R. M. Population dynamics of Schistosoma mansoni in mice repeatedly exposed to infection. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):491–493. doi: 10.1038/315491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demenais F. M., Bonney G. E. Equivalence of the mixed and regressive models for genetic analysis. I. Continuous traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(5):597–617. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demenais F. M., Murigande C., Bonney G. E. Search for faster methods of fitting the regressive models to quantitative traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7(5):319–334. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370070503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demenais F., Lathrop M., Lalouel J. M. Robustness and power of the unified model in the analysis of quantitative measurements. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):228–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A. J., Begley M., Demeure C., Caillol D., Fueri J., dos Reis M. G., Andrade Z. A., Prata A., Bina J. C. Human resistance to Schistosoma mansoni is associated with IgG reactivity to a 37-kDa larval surface antigen. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2727–2736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessein A. J., Lenzi H. L., Bina J. C., Carvalho E. M., Weiser W. Y., Andrade Z. A., David J. R. Modulation of eosinophil cytotoxicity by blood mononuclear cells from healthy subjects and patients with chronic schistosomiasis mansoni. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 15;85(1):100–113. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning M. M., Peters P. A., Davis R. S., Kazura J. W., Mahmoud A. A. Immunopathology of murine infection with Schistosoma mansoni: relationship of genetic background to hepatosplenic disease and modulation. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):148–153. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudot-Crozel V., Caillol D., Djabali M., Dessein A. J. The major parasite surface antigen associated with human resistance to schistosomiasis is a 37-kD glyceraldehyde-3P-dehydrogenase. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2065–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Sher A. Mechanisms of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice vaccinated with irradiated cercariae III. Identification of a mouse strain, P/N, that fails to respond to vaccination. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Nov;5(6):567–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. T., McCaffery D. M., Kusel J. R. The influence of the H-2 complex on responses to infection by Schistosoma mansoni in mice. Parasitology. 1983 Feb;86(Pt 1):19–30. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000057139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- José M. V. On the solution of mathematical models of herd immunity in human helminth infections. J Math Biol. 1989;27(6):707–715. doi: 10.1007/BF00276952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N., Zicker F., Rocha R. S., Oliveira V. B. Re-infection of patients in schistosomiasis mansoni endemic areas after specific treatment. I--influence of age and worm burden. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1978 Sep-Oct;20(5):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E. Complex segregation analysis with pointers. Hum Hered. 1981;31(5):312–321. doi: 10.1159/000153231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Elston R. C. A unified model for complex segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):816–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean C. J., Morton N. E., Elston R. C., Yee S. Skewness in commingled distributions. Biometrics. 1976 Sep;32(3):695–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. K., Beaver P. C. Evaluation of Kato thick-smear technique for quantitative diagnosis of helminth infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 May;17(3):382–391. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salam E. A., Ishaac S., Mahmoud A. A. Histocompatibilty-linked susceptibility for hepatospleenomegaly in human schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1829–1831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Skamene E., Forget A., Gros P. Linkage analysis of the Bcg gene on mouse chromosome 1. Identification of a tightly linked marker. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4507–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Hieny S., James S. Mechanisms of protective immunity against S. mansoni infection in mice vaccinated with irradiated cercariae. VI. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Jul;6(4):319–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingley G. A., Butterworth A. E., Anderson R. M., Kariuki H. C., Koech D., Mugambi M., Ouma J. H., Arap Siongok T. K., Sturrock R. F. Predisposition of humans to infection with Schistosoma mansoni: evidence from the reinfection of individuals following chemotherapy. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(3):448–452. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin D. Genetic control of immunity to helminth infections. Parasitol Today. 1985 Jul;1(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(85)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Domingo E. O., Cowan R. B. Granuloma formation around schistosome eggs as a manifestation of delayed hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):735–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. Schistosomiasis: a multiplicity of immunopathology. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Sep;67(3):464–469. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12514738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M. D., Tiu W. U., Wood S. M., Walker J. C., Garcia E. G., Mitchell G. F. Schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum worm numbers in 129/J mice of two types and dominance of susceptibility in F1 hybrids. J Parasitol. 1988 Aug;74(4):618–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


