Abstract
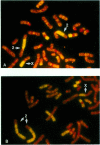
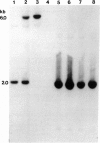
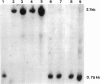
Menkes syndrome is a rare X-linked recessive disorder characterized by an inability to metabolize copper. A female patient with both this disease and an X; autosome translocation with karyotype 46,X,t(X;2)(q13;q32.2) has previously been described. The translocation breakpoint in Xq13 coincides with a previous assignment of the Menkes gene at Xq13 by linkage data in humans and by analogy to the mottled mutations which are models for Menkes disease in the mouse. Therefore, this translocation probably interrupts the gene for Menkes syndrome in band Xq13. We describe here experiments to precisely map the translocation breakpoint within this chromosomal band. We have established a lymphoblastoid cell line from this patient and have used it to isolate the der(2) translocation chromosome (2pter----2q32::Xq13----Xqter) in human/hamster somatic cell hybrids. Southern blot analyses using a number of probes specific for chromosomes X and 2 have been studied to define precisely the location of the translocation breakpoint. Our results show that the breakpoint in this patient--and, therefore, likely the Menkes gene--maps to a small subregion of band Xq13.2-q13.3 proximal to the PGK1 locus and distal to all other Xq13 loci tested.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown C. J., Lafreniere R. G., Powers V. E., Sebastio G., Ballabio A., Pettigrew A. L., Ledbetter D. H., Levy E., Craig I. W., Willard H. F. Localization of the X inactivation centre on the human X chromosome in Xq13. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):82–84. doi: 10.1038/349082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danks D. M., Campbell P. E., Walker-Smith J., Stevens B. J., Gillespie J. M., Blomfield J., Turner B. Menkes' kinky-hair syndrome. Lancet. 1972 May 20;1(7760):1100–1102. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Oliver N. Quantitative analysis of high-resolution trypsin-giemsa bands on human prometaphase chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 18;45(2):137–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00286957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N. Menkes' X-linked disease: prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1983;6 (Suppl 1):59–62. doi: 10.1007/BF01811325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Mooy P., McGuire V. M. Menkes X linked disease: two clonal cell populations in heterozygotes. J Med Genet. 1980 Aug;17(4):262–266. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Stene J., Møllekaer A. M., Friedrich U. Linkage studies in Menkes' disease. The Xg blood group system and C-banding of the X chromosome. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 May;48(Pt 2):161–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M. Primary defect in copper transport underlies mottled mutants in the mouse. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):852–854. doi: 10.1038/249852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutz M. H., Michelson A. M., Antonarakis S. E., Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Restriction site polymorphism in the phosphoglycerate kinase gene on the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):217–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00286604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur S., Higgins J. V., Delp K., Rogers B. Menkes syndrome in a girl with X-autosome translocation. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Feb;26(2):503–510. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keer J. T., Hamvas R. M., Brockdorff N., Page D., Rastan S., Brown S. D. Genetic mapping in the region of the mouse X-inactivation center. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):566–572. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90200-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith D. H., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Active X chromosome DNA is unmethylated at eight CCGG sites clustered in a guanine-plus-cytosine-rich island at the 5' end of the gene for phosphoglycerate kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4122–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Nelson D. L., Warren S. T., Ledbetter D. H. Rapid isolation of DNA probes within specific chromosome regions by interspersed repetitive sequence polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90477-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H., Ward D. C. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with Alu and L1 polymerase chain reaction probes for rapid characterization of human chromosomes in hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6634–6638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H., ALTER M., STEIGLEDER G. K., WEAKLEY D. R., SUNG J. H. A sex-linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, peculiar hair, and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration. Pediatrics. 1962 May;29:764–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. T., Chapman V. M. Electrophoretic variation for x-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase (pgk-1) in the mouse. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):319–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropers H. H., Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Davies K., Williamson R. On the genetic length of the short arm of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;65(1):53–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00285028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Horn N., Pearson P., Wienker T. F., McKay E., Ropers H. H. Menkes kinky hair disease: a search for closely linked restriction fragment length polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):139–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00327110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyandt H. E., Wysham D. G., Minden S. K., Anderson R. S., Hecht F. Mechanisms of giemsa banding of chromosomes. I. Giemsa-11 banding with azure and eosin. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]