Abstract
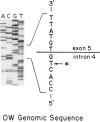
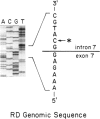
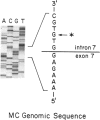
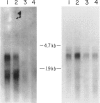
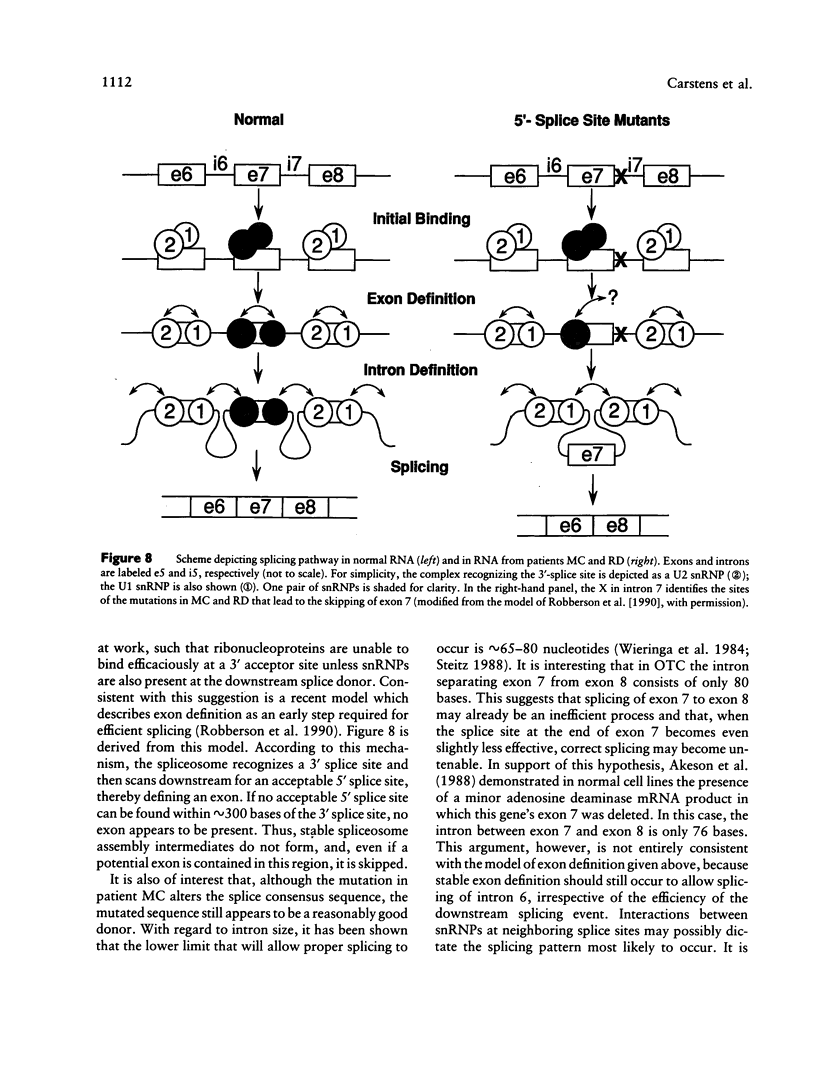
Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) is an X-linked, liver-specific enzyme that catalyzes the second step of the urea cycle. In humans, inherited deficiency of OTC in hemizygous affected males usually results in severe ammonia intoxication and early death. To characterize mutations responsible for OTC deficiency, we used the PCR to amplify cDNAs prepared from patient livers which demonstrated no OTC enzyme activity and no OTC cross-reacting material on western blots. In three of seven cases, smaller than normal products were observed. Sequencing of these cDNAs revealed that two were missing exon 7 of the OTC gene and that the other was missing the first 12 bp of exon 5. Sequencing of genomic DNA from these three patients revealed that one mutant missing exon 7 had a T-to-C substitution in the 5' splice donor site of intron 7. The other mutant missing exon 7 had an A-to-G change in the third position of intron 7. It is interesting that both of these mutations resulted in skipping the preceding exon rather than in inclusion of some or all of the affected intron. In the third mutant, an A-to-T substitution was found in the 3' splice acceptor site at the end of intron 4. Here, a cryptic splice acceptor site within exon 5 was used. Northern blotting of liver RNA from these patients demonstrated (a) reduced, but significant, amounts of OTC mRNA in one of the patients who had a deleted exon 7 but (b) very little OTC mRNA in the other two patients. We propose that these point mutations, which result in aberrant splicing of the OTC pre-mRNAs, lead to OTC deficiency through either decreased efficiency of mRNA export from the nucleus to the cytosol or synthesis of enzyme subunits that are unstable and rapidly degraded. We speculate that abnormal mRNA splicing may represent a relatively common mechanism in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Wong C., Reed R., Antonarakis S. E., Zhu D., Ghosh P. K., Maniatis T., Forget B. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr A new mutation in IVS-1 of the human beta globin gene causing beta thalassemia due to abnormal splicing. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. G., Rosenberg L. E., Snodgrass P. J., Nuzum C. T. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: a cause of lethal neonatal hyperammonemia in males. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Hack A. M., Fenton W. A., Rosenberg L. E. Identification and application of additional restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the human ornithine transcarbamylase locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):841–847. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandchamp B., Picat C., de Rooij F., Beaumont C., Wilson P., Deybach J. C., Nordmann Y. A point mutation G----A in exon 12 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6637–6649. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grompe M., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Scanning detection of mutations in human ornithine transcarbamoylase by chemical mismatch cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5888–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata A., Setoyama C., Shimada K., Takeda E., Kuroda Y., Akaboshi I., Matsuda I. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency resulting from a C-to-T substitution in exon 5 of the ornithine transcarbamylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):123–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata A., Tsuzuki T., Shimada K., Takiguchi M., Mori M., Matsuda I. Isolation and characterization of the human ornithine transcarbamylase gene: structure of the 5'-end region. J Biochem. 1986 Sep;100(3):717–725. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Fenton W. A., Williams K. R., Kalousek F., Kraus J. P., Doolittle R. F., Konigsberg W., Rosenberg L. E. Structure and expression of a complementary DNA for the nuclear coded precursor of human mitochondrial ornithine transcarbamylase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1068–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.6372096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Conner K., Springer T. A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Aberrant splicing of a conserved integrin sequence causes a moderate deficiency phenotype. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3588–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. RNA splice site selection: evidence for a 5' leads to 3' scanning model. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.6304877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddalena A., Spence J. E., O'Brien W. E., Nussbaum R. L. Characterization of point mutations in the same arginine codon in three unrelated patients with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1353–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI113738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. Spontaneous splicing mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Boggs B. A., Beaudet A. L., Doyle S., Potter J. L., O'Brien W. E. New mutation and prenatal diagnosis in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):149–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Gotoh Y. Signals for the selection of a splice site in pre-mRNA. Computer analysis of splice junction sequences and like sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Fenton W. A., Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Kraus J. P. Targeting of nuclear-encoded proteins to the mitochondrial matrix: implications for human genetic defects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:99–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen R., Fox J., Fenton W. A., Horwich A. L., Rosenberg L. E. Gene deletion and restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the human ornithine transcarbamylase locus. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):815–817. doi: 10.1038/313815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short E. M., Conn H. O., Snodgrass P. J., Campbell A. G., Rosenberg L. E. Evidence for x-linked dominant inheritance of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):7–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. "Snurps". Sci Am. 1988 Jun;258(6):56-60, 63. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0688-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Combates N., Wirtz M. K., Hollister D. W., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. Identification of a mutation that causes exon skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]