Abstract
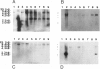
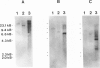
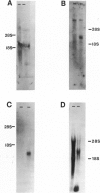
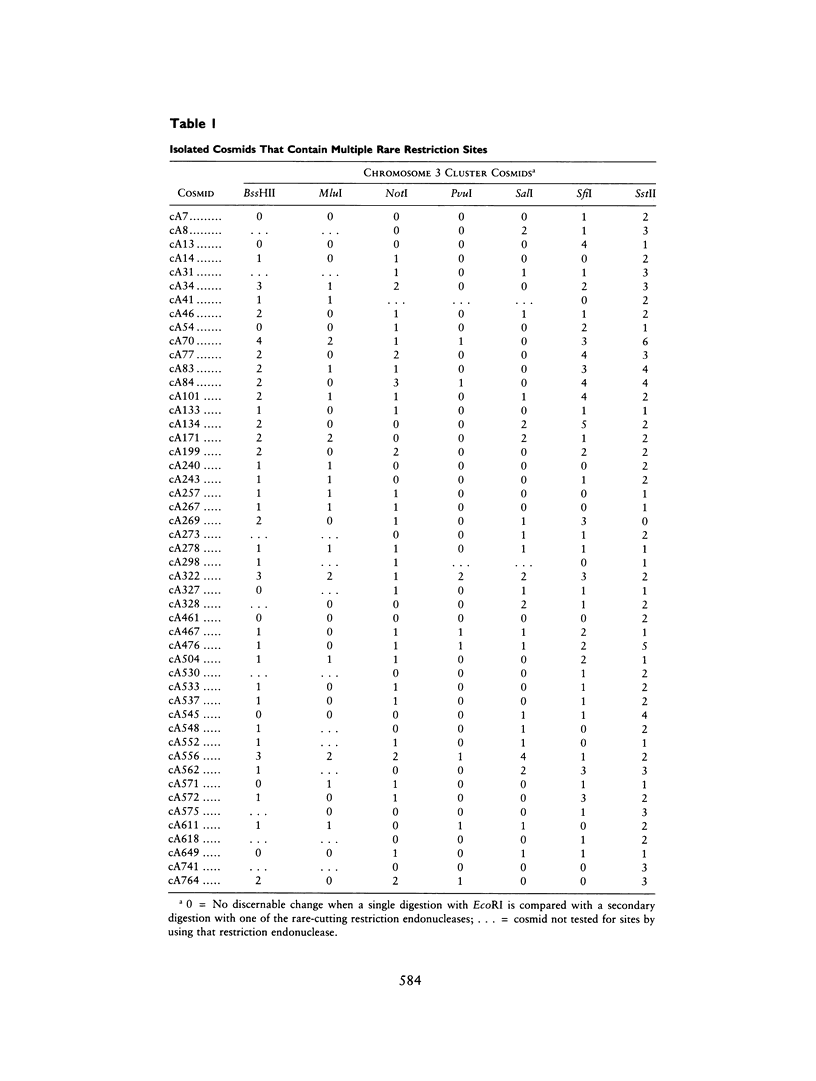
We tested 519 chromosome 3-specific cosmids for the presence of rare restriction-endonuclease sites in a search for cosmids containing HTF islands. We have identified 49 cosmids (9% of those tested) that contain multiple rare restriction-endonuclease sites. The cosmids were digested with several common cutting restriction endonucleases to liberate small fragments which were tested as unique-sequence chromosome 3-specific hybridization probes and for evolutionary sequence conservation. Unique-sequence hybridization probes isolated from the cosmids were hybridized to a somatic cell hybrid deletion mapping panel to subchromosomally localize the cosmids. Fragments from many of these cosmids demonstrated conservation of sequence through evolution, and these fragments hybridize to distinct transcripts. These cosmids should therefore prove a useful resource for the identification of many chromosome 3-specific genes, in addition to having potential use as linking clones for pulsed-field gel mapping studies.
Full text
PDF

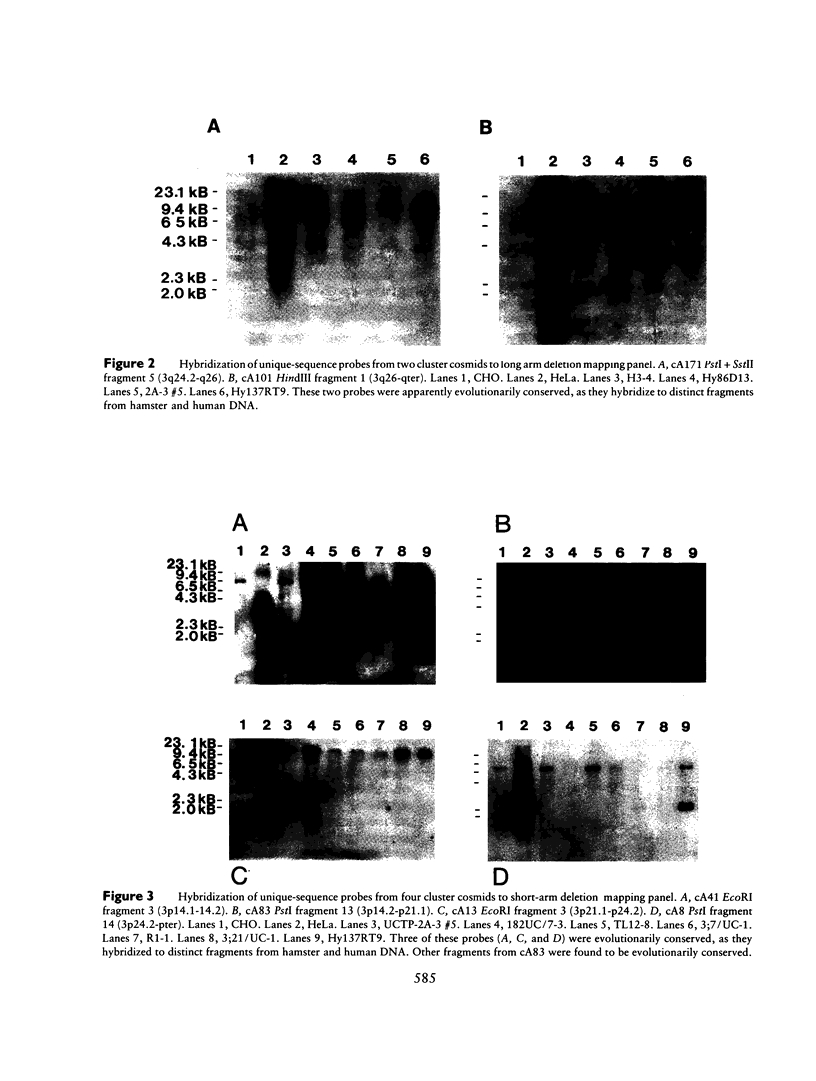
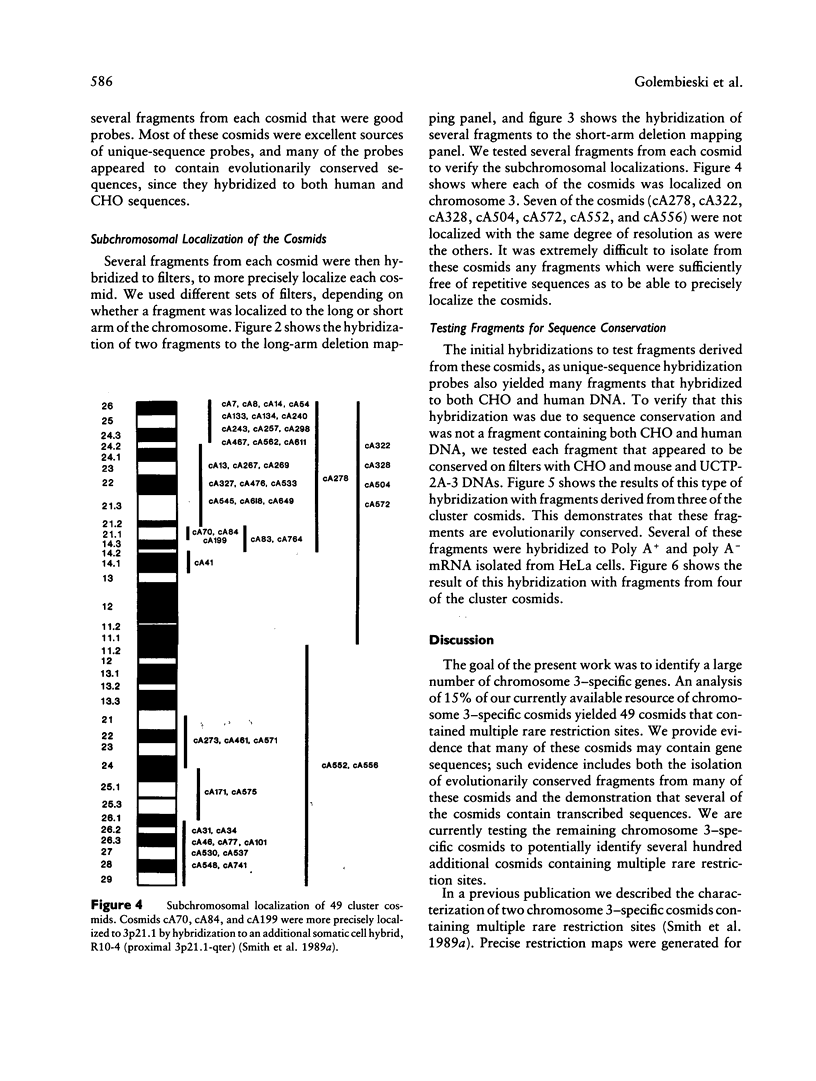
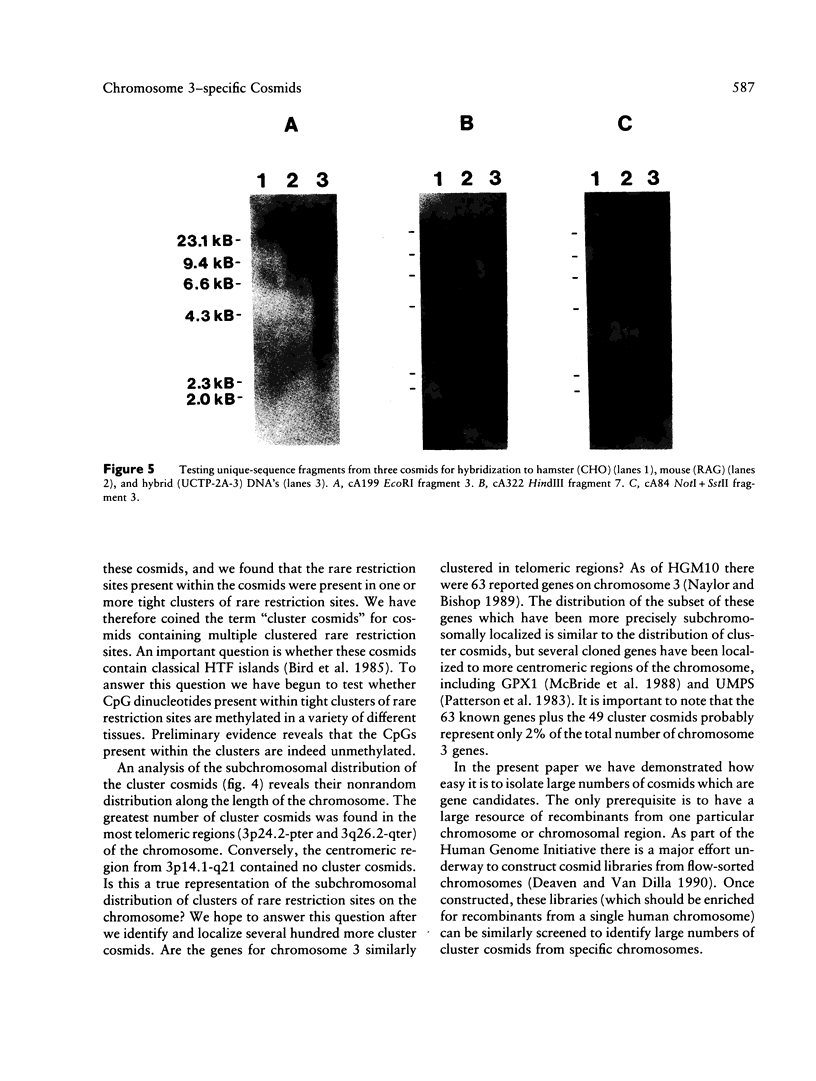


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Frommer M., Miller O. J., Macleod D. A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated, CpG-rich DNA. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Smith D., Wasmuth J. J. Genetic counterselective procedure to isolate interspecific cell hybrids containing single human chromosomes: construction of cell hybrids and recombinant DNA libraries specific for human chromosomes 3 and 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01560663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabkin H., Wright M., Jonsen M., Varkony T., Jones C., Sage M., Gold S., Morse H., Mendez M., Erickson P. Development of a somatic cell hybrid mapping panel and molecular probes for human chromosome 3. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):435–446. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90029-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mears J. G., Ramirez F., Leibowitz D., Nakamura F., Bloom A., Konotey-Ahulu F., Bank A. Changes in restricted human cellular DNA fragments containing globin gene sequences in thalassemias and related disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1222–1226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Bishop D. T. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 3. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):106–120. doi: 10.1159/000132783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Jones C., Morse H., Rumsby P., Miller Y., Davis R. Structural gene coding for multifunctional protein carrying orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and OMP decarboxylase activity is located on long arm of human chromosome 3. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 May;9(3):359–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01539144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. I., Golembieski W., Drabkin H., Kiousis S. Identification of two cosmids derived from within chromosomal band 3p21.1 that contain clusters of rare restriction sites and evolutionarily conserved sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):443–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. I., Golembieski W., Gilbert J. D., Kizyma L., Miller O. J. Overabundance of rare-cutting restriction endonuclease sites in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1173–1184. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. I., Mangrulker R., Geist R., Gilbert J., Kinsman K., Drabkin H., Golembieski W. Saturation of human chromosome 3 with unique sequence hybridization probes. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90268-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]