Abstract
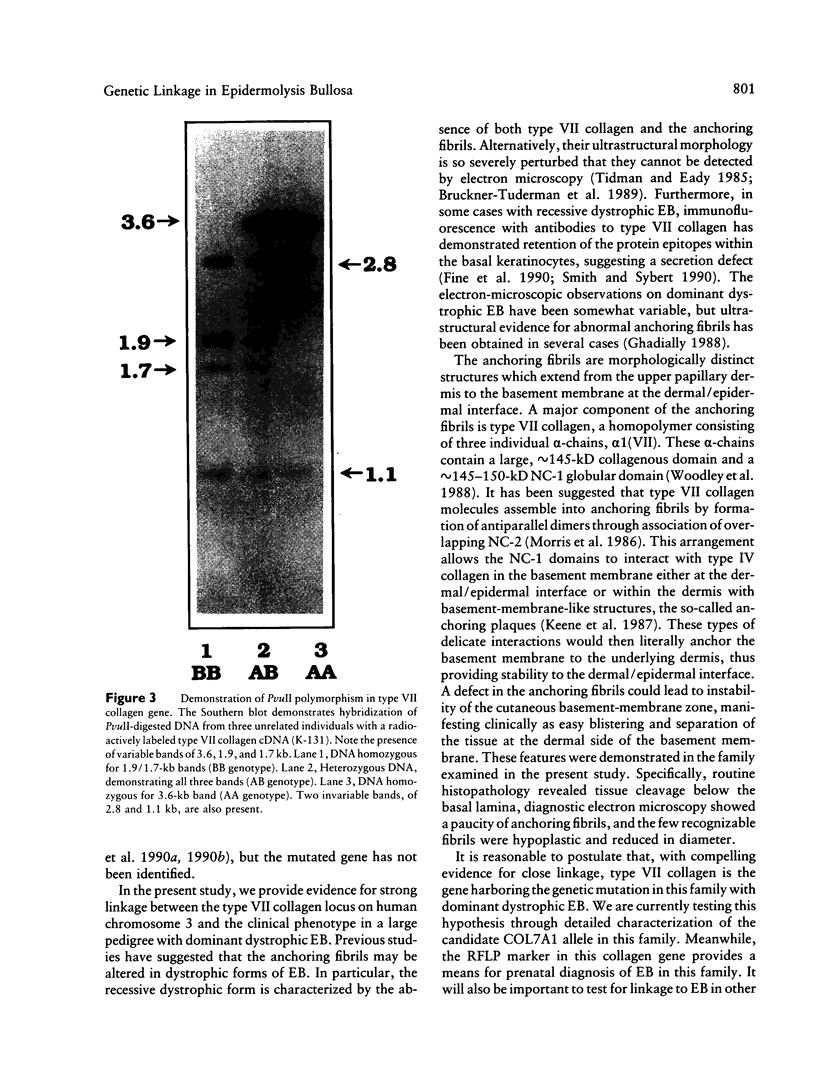
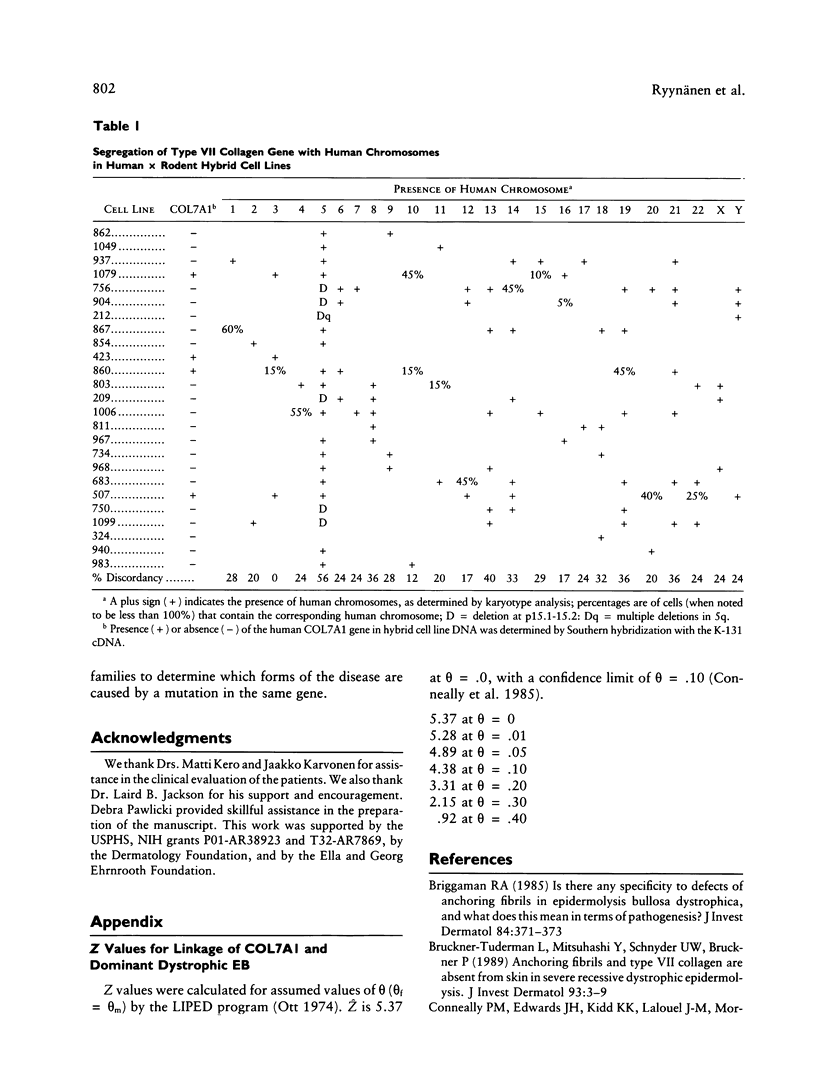
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a heterogeneous group of heritable blistering disorders affecting the skin and the mucous membranes. Previous ultrastructural studies on the dystrophic (scarring) forms of EB have demonstrated abnormalities in the anchoring fibrils, morphologically distinct structures below the basal lamina at the dermal/epidermal basement membrane zone. Type VII collagen is the major collagenous component of the anchoring fibrils, and it is therefore a candidate gene for mutations in some families with dystrophic forms of EB. In this study, we performed genetic linkage analyses in a large kindred with dominant dystrophic EB. A 1.9-kb type VII collagen cDNA clone was used to identify a PvuII RFLP to follow the inheritance of the gene. This RFLP cosegregated with the EB phenotype in this family, strongly supporting genetic linkage (Z = 5.37; theta = .0). In addition, we assigned the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) to chromosome 3 by hybridization to a panel of human x rodent somatic cell hybrids. These data demonstrate very close genetic linkage between the clinical phenotype in this family and the polymorphism in the type VII collagen gene mapped to chromosome 3. The absence of recombination between EB and the type VII collagen gene locus, as well as the observed abnormalities in the anchoring fibrils, strongly suggest that this collagen gene is the mutant locus in this kindred.
Full text
PDF

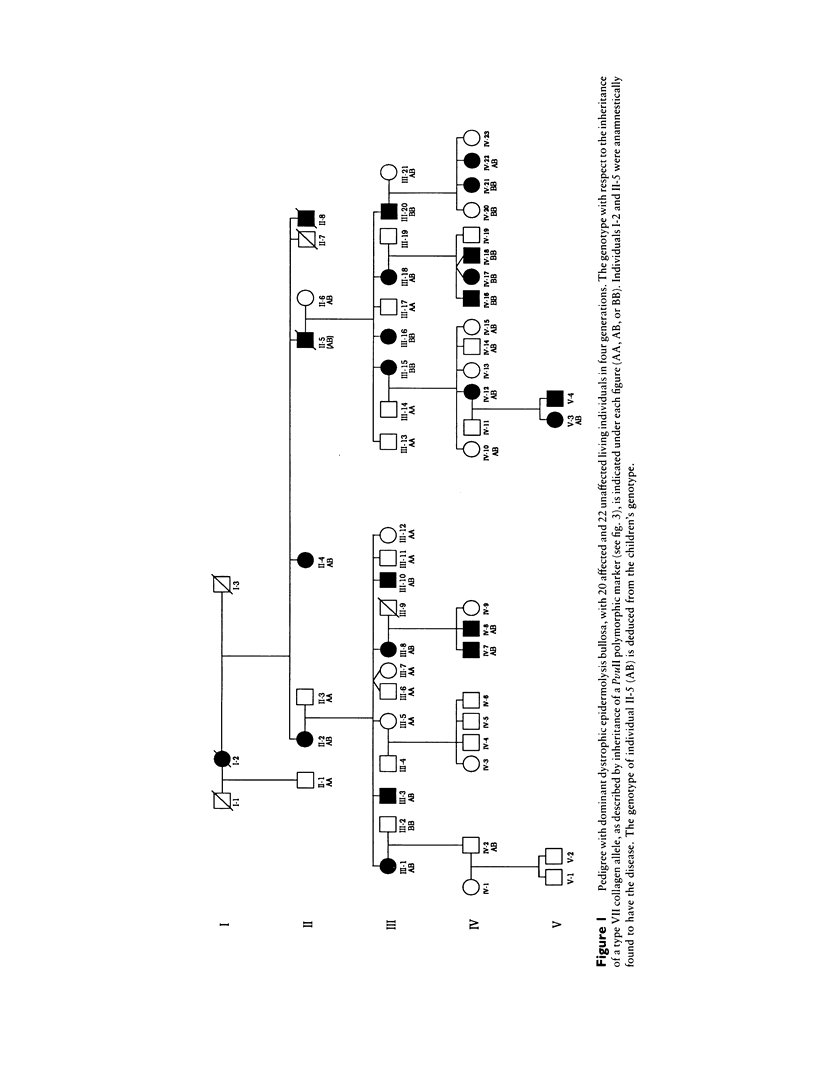
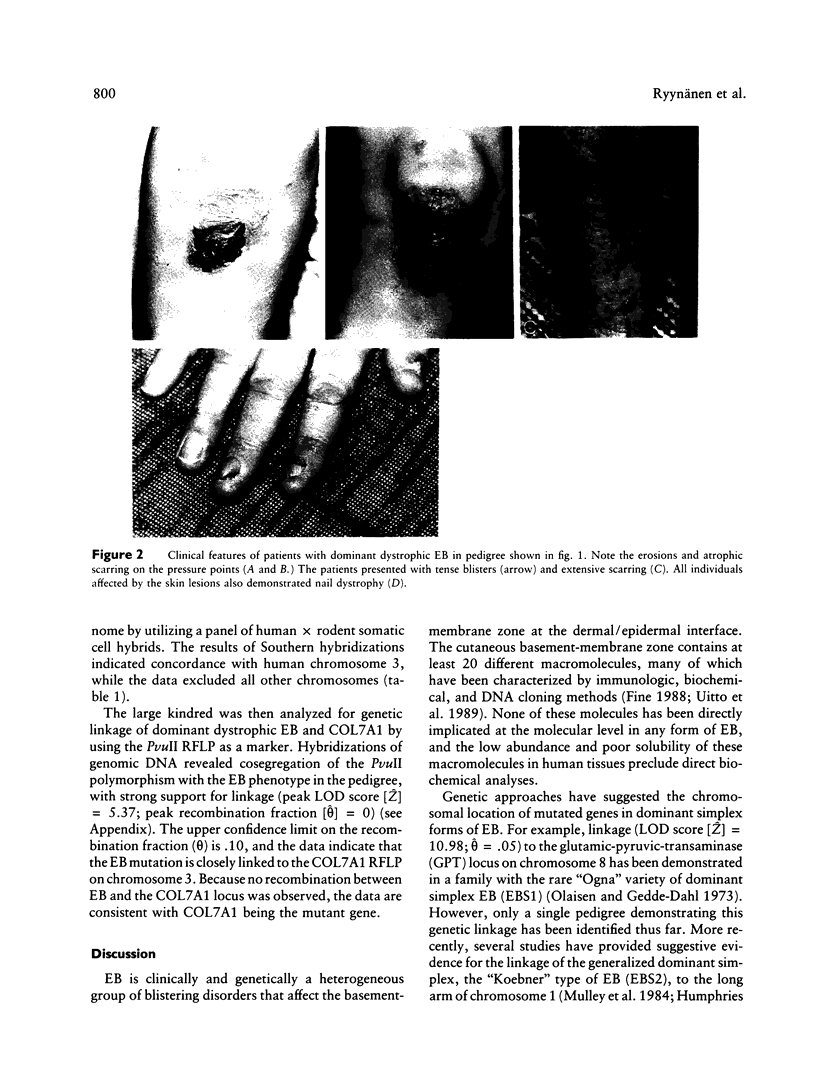

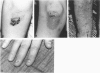
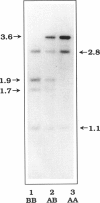
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggaman R. A. Is there any specificity to defects of anchoring fibrils in epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica, and what does this mean in terms of pathogenesis? J Invest Dermatol. 1985 May;84(5):371–373. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner-Tuderman L., Mitsuhashi Y., Schnyder U. W., Bruckner P. Anchoring fibrils and type VII collagen are absent from skin in severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Jul;93(1):3–9. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. D. Antigenic features and structural correlates of basement membranes. Relationship to epidermolysis bullosa. Arch Dermatol. 1988 May;124(5):713–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. D., Bauer E. A., Briggaman R. A., Carter D. M., Eady R. A., Esterly N. B., Holbrook K. A., Hurwitz S., Johnson L., Lin A. Revised clinical and laboratory criteria for subtypes of inherited epidermolysis bullosa. A consensus report by the Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Classification of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Jan;24(1):119–135. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(91)70021-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. D., Horiguchi Y., Stein D. H., Esterly N. B., Leigh I. M. Intraepidermal type VII collagen. Evidence for abnormal intracytoplasmic processing of a major basement membrane protein in rare patients with dominant and possibly localized recessive forms of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Feb;22(2 Pt 1):188–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. M., Sheils D., Lawler M., Farrar G. J., McWilliam P., Kenna P., Bradley D. G., Sharp E. M., Gaffney E. F., Young M. Epidermolysis bullosa: evidence for linkage to genetic markers on chromosome 1 in a family with the autosomal dominant simplex form. Genomics. 1990 Jul;7(3):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90171-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M., Nagayoshi T., Sheils D., Humphries P., Uitto J. Human nidogen gene: identification of multiple RFLP and exclusion as candidate gene in a family with epidermolysis bullosa (EBS2) with evidence for linkage to chromosome 1. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Nov;95(5):568–570. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12505546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Sakai L. Y., Lunstrum G. P., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen forms an extended network of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):611–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kero M. Epidermolysis bullosa in Finland. Clinical features, morphology and relation to collagen metabolism. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1984;110:1–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Weaver E. J., Struyk A. F., Knobloch W. H., King R. A., Norris K., Shamban A., Uitto J., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Genetic linkage analysis of hereditary arthro-ophthalmopathy (Stickler syndrome) and the type II procollagen gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunstrum G. P., Kuo H. J., Rosenbaum L. M., Keene D. R., Glanville R. W., Sakai L. Y., Burgeson R. E. Anchoring fibrils contain the carboxyl-terminal globular domain of type VII procollagen, but lack the amino-terminal globular domain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13706–13712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunstrum G. P., Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Large complex globular domains of type VII procollagen contribute to the structure of anchoring fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9042–9048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. P., Keene D. R., Glanville R. W., Bentz H., Burgeson R. E. The tissue form of type VII collagen is an antiparallel dimer. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5638–5644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulley J. C., Nicholls C. M., Propert D. N., Turner T., Sutherland G. R. Genetic linkage analysis of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Köbner type. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Nov;19(3):573–577. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr GPT--epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS Ogna) linkage in man. Hum Hered. 1973;23(3):189–196. doi: 10.1159/000152573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parente M. G., Chung L. C., Ryynänen J., Woodley D. T., Wynn K. C., Bauer E. A., Mattei M. G., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Human type VII collagen: cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6931–6935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen is a major structural component of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1577–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura D., Nomura K., Sugita Y., Mattei M. G., Chu M. L., Knowlton R., Uitto J. Bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1): cDNA cloning and mapping of the gene to the short arm of human chromosome 6. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):722–726. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90261-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. T., Sybert V. P. Intra-epidermal retention of type VII collagen in a patient with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Feb;94(2):261–264. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidman M. J., Eady R. A. Evaluation of anchoring fibrils and other components of the dermal-epidermal junction in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa by a quantitative ultrastructural technique. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 May;84(5):374–377. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Olsen D. R., Fazio M. J. Extracellular matrix of the skin: 50 years of progress. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Apr;92(4 Suppl):61S–77S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep13075039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Burgeson R. E., Lunstrum G., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Reese M. J., Briggaman R. A. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen is the globular carboxyl terminus of type VII procollagen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):683–687. doi: 10.1172/JCI113373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]