Abstract
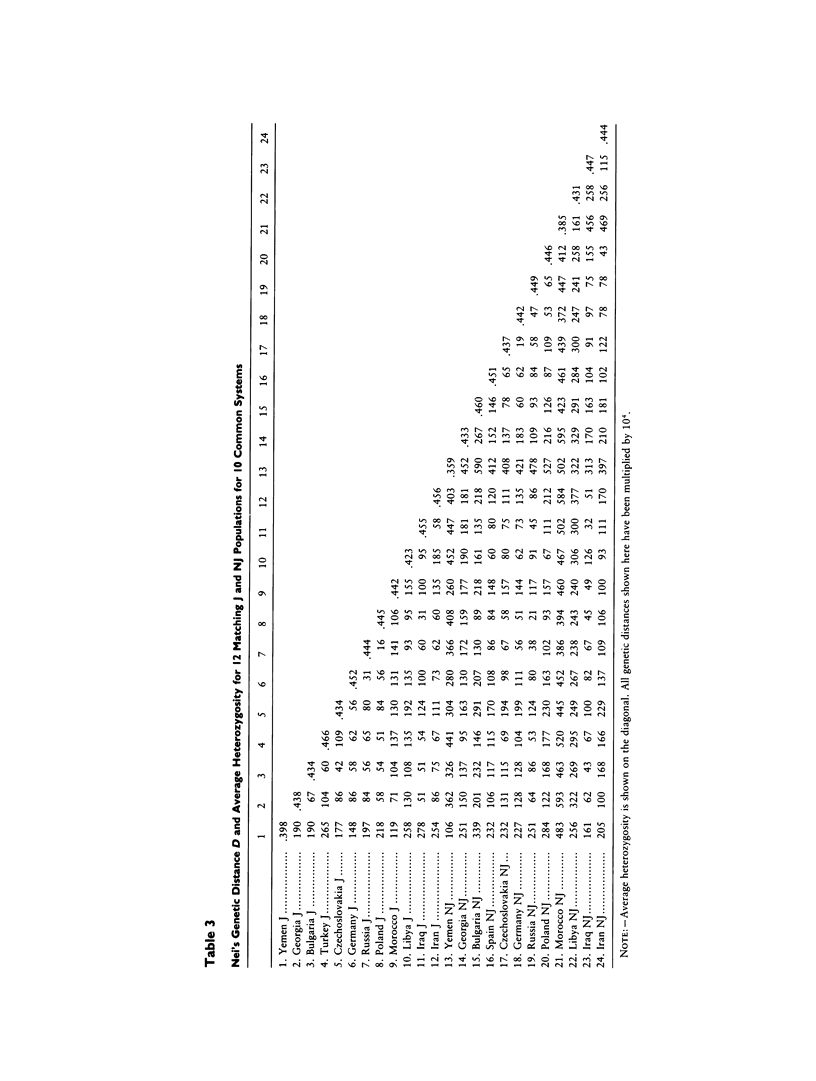
Genetic relations between various Jewish (J) and non-Jewish (NJ) populations were assessed using two sets of data. The first set contained 12 pairs of matched J and NJ populations from Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa, for which 10 common polymorphic genetic systems (13 loci) were available. The second set included 22 polymorphic genetic systems (26 loci) with various numbers of populations (ranging from 21 to 51) for each system. Therefore, each system was studied separately. Nei's standard genetic distance (D) matrices obtained for these two sets of data were tested against design matrices specifying hypotheses concerning the affiliations of the tested populations. The tests against single designs were carried out by means of Mantel tests. Our results consistently show lower distances among J populations than with their NJ neighbors, most simply explained by the common origin of the former. Yet, there is evidence also of genetic similarity between J and corresponding NJ populations, suggesting reciprocal gene flow between these populations or convergent selection in a common environment. The results of our study also indicate that stochastic factors are likely to have played a role in masking the descent relationships of the J populations.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COTTERMAN C. W. Regular two-allele and three-allele phenotype systems. I. Am J Hum Genet. 1953 Sep;5(3):193–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmelli D., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. The genetic origin of the Jews: a multivariate approach. Hum Biol. 1979 Mar;51(1):41–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Kenett R., Bonné-Tamir B. Analysis of biochemical genetic data on Jewish populations: II. Results and interpretations of heterogeneity indices and distance measures with respect to standards. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 May;31(3):341–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobyliansky E., Livshits G. Genetic composition of Jewish populations: diversity and inbreeding. Ann Hum Biol. 1983 Sep-Oct;10(5):453–463. doi: 10.1080/03014468300006661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobyliansky E., Micle S., Goldschmidt-Nathan M., Arensburg B., Nathan H. Jewish populations of the world: genetic likeness and differences. Ann Hum Biol. 1982 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–34. doi: 10.1080/03014468200005461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Nei M. Persistence of common alleles in two related populations or species. Genetics. 1977 Aug;86(4):901–914. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.4.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livshits G., Nei M. Relationships between intrapopulational and interpopulational genetic diversity in man. Ann Hum Biol. 1990 Nov-Dec;17(6):501–513. doi: 10.1080/03014469000001272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 1967 Feb;27(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokal R. R., Harding R. M., Oden N. L. Spatial patterns of human gene frequencies in Europe. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1989 Nov;80(3):267–294. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330800302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourdis J., Krimbas C. Accuracy of phylogenetic trees estimated from DNA sequence data. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Mar;4(2):159–166. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno Y., Nei M., Tajima F. Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. I. Distantly related species. J Mol Evol. 1982;18(6):387–404. doi: 10.1007/BF01840887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijsman E. M. Techniques for estimating genetic admixture and applications to the problem of the origin of the Icelanders and the Ashkenazi Jews. Hum Genet. 1984;67(4):441–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00291407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



