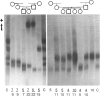
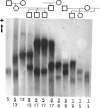
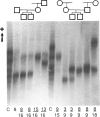
Abstract
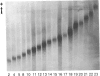
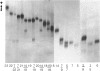
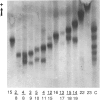
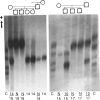
Elevated plasma lipoprotein (a) (LP(a] levels are an independent predictor of the development of premature atherosclerosis in humans. The LP(a) particle consists of two disulfide-linked proteins, apolipoprotein (APO) B and APO(a). The APO(a) is a highly glycosylated protein which carries the LP(a) antigen. Genetic polymorphism in the APO(a) molecule has been reported, and, depending on the sensitivity of the method used, 6-11 alleles at the APO(a) structural locus have been documented in the literature. In this investigation, we have used a high-resolution SDS-agarose electrophoresis method followed by immunoblotting to screen APO(a) polymorphism in 54 families with 130 offspring. This method identified a total of 23 different APO(a) isoforms, and their genetic basis was confirmed in families. In addition to the detectable products of 23 APO(a) alleles, the family data predict the existence of a "null" allele. Of the total 270 individuals tested, 209 (77.4%) revealed double-banded phenotypes and 61 (22.6%) revealed single-banded phenotypes. In the unrelated sample of 140 individuals, however, 114 (81.4%) and 26 (18.6%) had double- and single-banded phenotypes, respectively. When the segregation pattern of single-banded phenotypes in the unrelated sample was followed in families, only nine (6.4%) were found to be true homozygotes, and the remaining 17 (12.2%) were classified as heterozygotes for the null allele. Of the 276 possible phenotypes predicted for 23 alleles in a large population, we observed 115 (42%) phenotypes in our restricted sample. On the basis of our results from the family data, we hypothesize the existence of at least 24 alleles, including a null allele, at the APO(a) structural locus.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Adolphson J. L., Hazzard W. R. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., Seidel D. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Dec;62(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K. A NEW SERUM TYPE SYSTEM IN MAN--THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Plasma lipoproteins: teaching old dogmas new tricks. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):113–114. doi: 10.1038/330113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlen G. H., Guyton J. R., Attar M., Farmer J. A., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Association of levels of lipoprotein Lp(a), plasma lipids, and other lipoproteins with coronary artery disease documented by angiography. Circulation. 1986 Oct;74(4):758–765. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.4.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., Hegele R. A., Hass P. E., Emi M., Wu L. L., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M., Williams R. R., White R. L., Lalouel J. M. Genetic linkage between lipoprotein(a) phenotype and a DNA polymorphism in the plasminogen gene. Genomics. 1988 Oct;3(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrington P. N., Ishola M., Hunt L., Arrol S., Bhatnagar D. Apolipoproteins (a), AI, and B and parental history in men with early onset ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1070–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91895-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Fless G. M., Kohr W. J., McLean J. W., Xu Q. T., Miller C. G., Lawn R. M., Scanu A. M. Partial amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein(a) shows that it is homologous to plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3224–3228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Ghanem K. I., Guevara J., Jr, Nava M. L., Patsch W., Morrisett J. D. Polymorphic forms of human apolipoprotein[a]: inheritance and relationship of their molecular weights to plasma levels of lipoprotein[a]. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Edelberg J. M., Pizzo S. V. Further characterization of the cellular plasminogen binding site: evidence that plasminogen 2 and lipoprotein a compete for the same site. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Gavish D., Breslow J. L., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein(a) modulation of endothelial cell surface fibrinolysis and its potential role in atherosclerosis. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):303–305. doi: 10.1038/339303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Gordon B. R., Parker T. S. Plasmin catalyzes binding of lipoprotein (a) to immobilized fibrinogen and fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3847–3851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Williams R. R. Three alleles for quantitative Lp(a). Genet Epidemiol. 1986;3(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasstedt S. J., Wilson D. E., Edwards C. Q., Cannon W. N., Carmelli D., Williams R. R. The genetics of quantitative plasma Lp(a): analysis of a large pedigree. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Oct;16(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Britten M. L., Manis G. S., Rainwater D. L. Apolipoprotein(a) (Apo(a)) glycoprotein isoforms result from size differences in Apo(a) mRNA in baboons. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6013–6016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler G., Harnoncourt F., Paschke E., Mirtl W., Pfeiffer K. H., Kostner G. M. Lipoprotein Lp(a). A risk factor for myocardial infarction. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):398–401. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.4.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Költringer P. Lipoprotein(a) in ischemic cerebrovascular disease: a new approach to the assessment of risk for stroke. Neurology. 1987 Mar;37(3):513–515. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.3.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschinsky M. L., Beisiegel U., Henne-Bruns D., Eaton D. L., Lawn R. M. Apolipoprotein(a) size heterogeneity is related to variable number of repeat sequences in its mRNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):640–644. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Dieplinger H., Hoye E., Utermann G. Lp(a) phenotyping by immunoblotting with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):212–216. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Gersdorf E., Menzel H. J., Duba C., Cleve H., Humphries S., Utermann G. The gene for the Lp(a)-specific glycoprotein is closely linked to the gene for plasminogen on chromosome 6. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00293891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J. Lipoprotein(a). A unique risk factor for atherothrombotic disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5):672–679. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Fless G. M., Levin E. G., Scanu A. M., Plow E. F. A potential basis for the thrombotic risks associated with lipoprotein(a). Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):301–303. doi: 10.1038/339301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll P. P., Michels V. V., Weidman W. H., Kottke B. A. Genetic determination of plasma apolipoprotein AI in a population-based sample. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;44(1):124–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Berg K., Dahlen G., Ferrell R. E., Rhoads G. G. Genetics of the Lp lipoprotein in Japanese-Americans. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai A., Miyahara T., Fujimoto N., Matsuda M., Kameyama M. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Feb;59(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater D. L., Manis G. S., VandeBerg J. L. Hereditary and dietary effects on apolipoprotein[a] isoforms and Lp[a] in baboons. J Lipid Res. 1989 Apr;30(4):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengren A., Wilhelmsen L., Eriksson E., Risberg B., Wedel H. Lipoprotein (a) and coronary heart disease: a prospective case-control study in a general population sample of middle aged men. BMJ. 1990 Dec 1;301(6763):1248–1251. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6763.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandkamp M., Funke H., Schulte H., Köhler E., Assmann G. Lipoprotein(a) is an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction at a young age. Clin Chem. 1990 Jan;36(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Schultz J. S., Shreffler D. C. The genetics of the Lp antigen. II. A family study and proposed models of genetic control. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;38(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Gendler S., Griffiths B., Corney G., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Bramwell M. E. The human tumour-associated epithelial mucins are coded by an expressed hypervariable gene locus PUM. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):82–84. doi: 10.1038/328082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Duba C., Menzel H. J. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):47–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00291233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hoppichler F., Dieplinger H., Seed M., Thompson G., Boerwinkle E. Defects in the low density lipoprotein receptor gene affect lipoprotein (a) levels: multiplicative interaction of two gene loci associated with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4171–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., Seitz C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00291232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a). Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):904–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2530631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Guttormsen S. A., Schultz J. S. Linkage between the loci for the Lp(a) lipoprotein (LP) and plasminogen (PLG). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):80–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00291716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]