Abstract
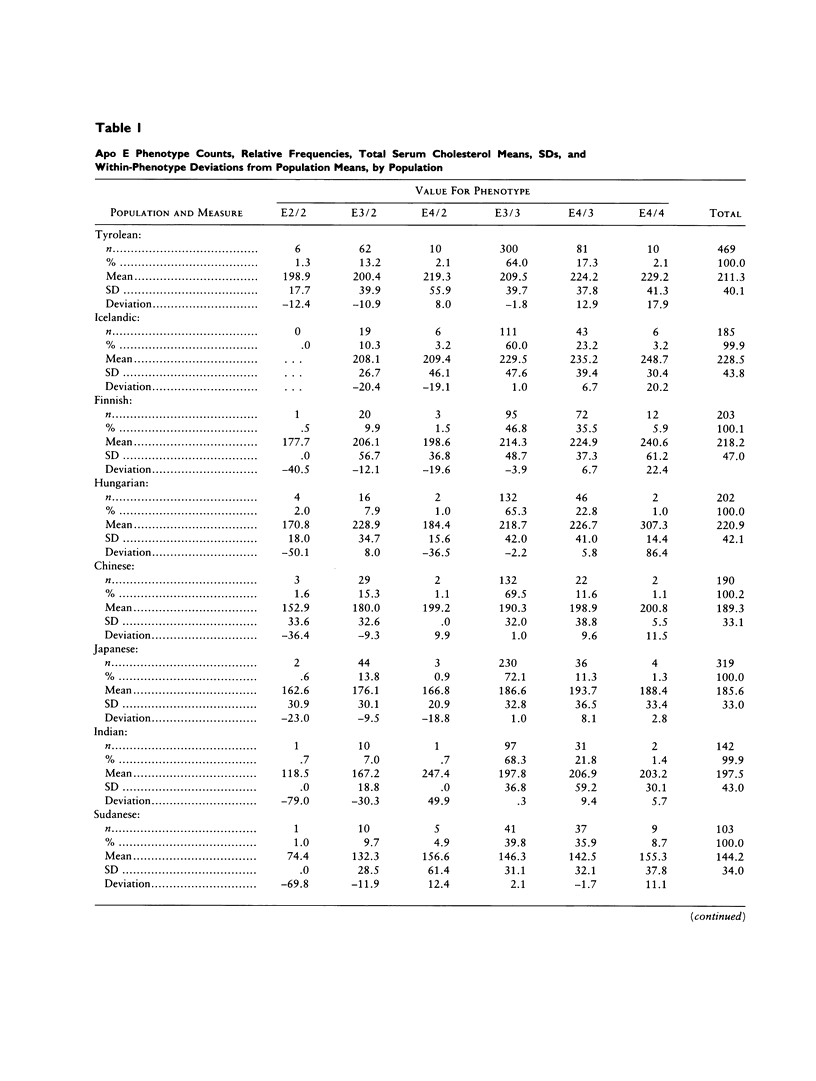
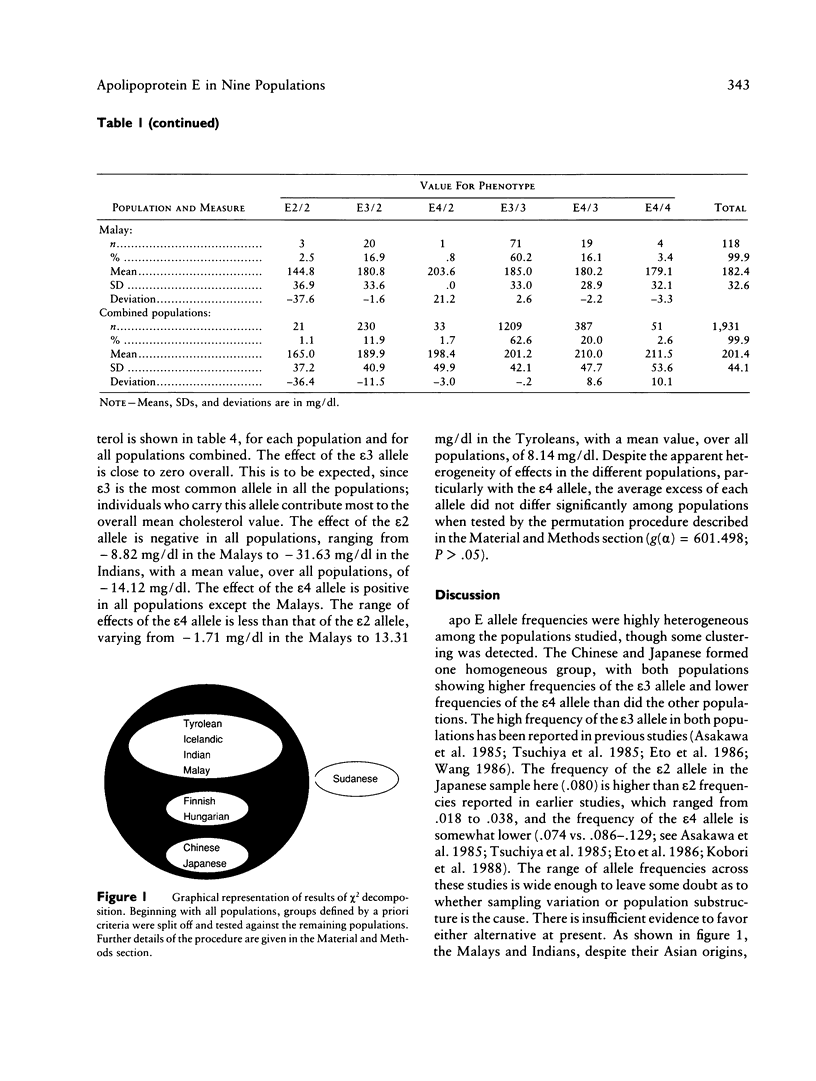
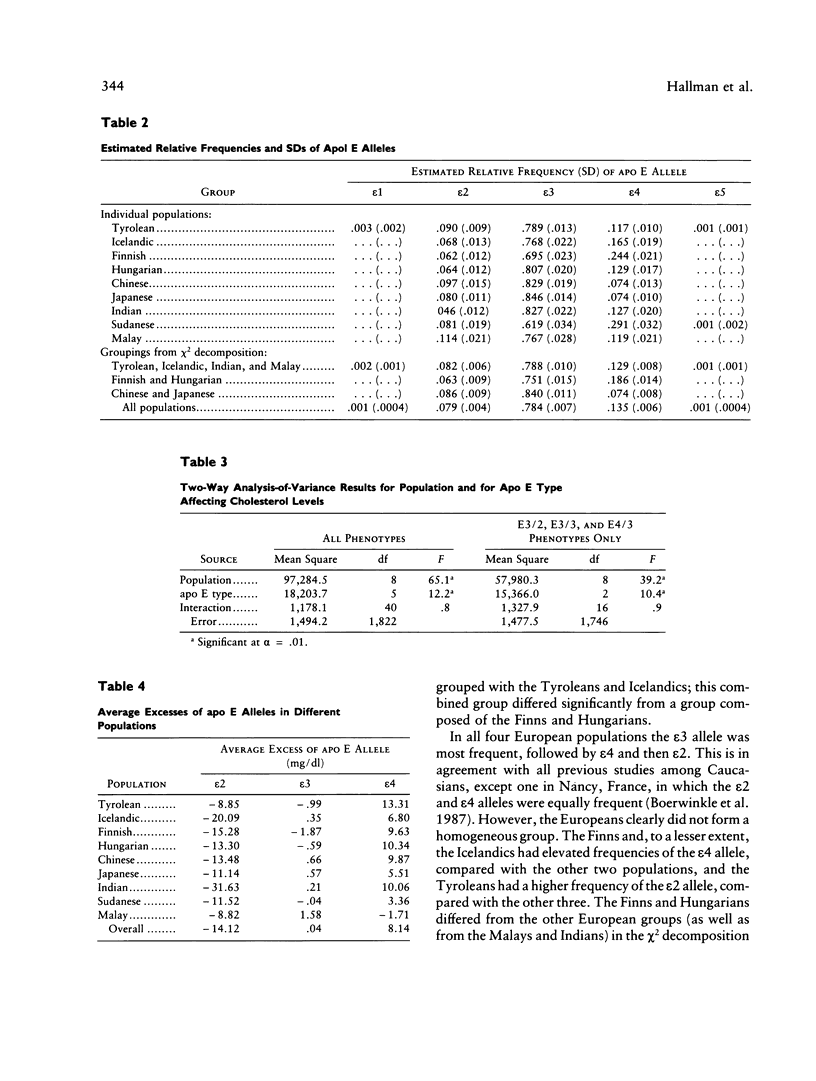
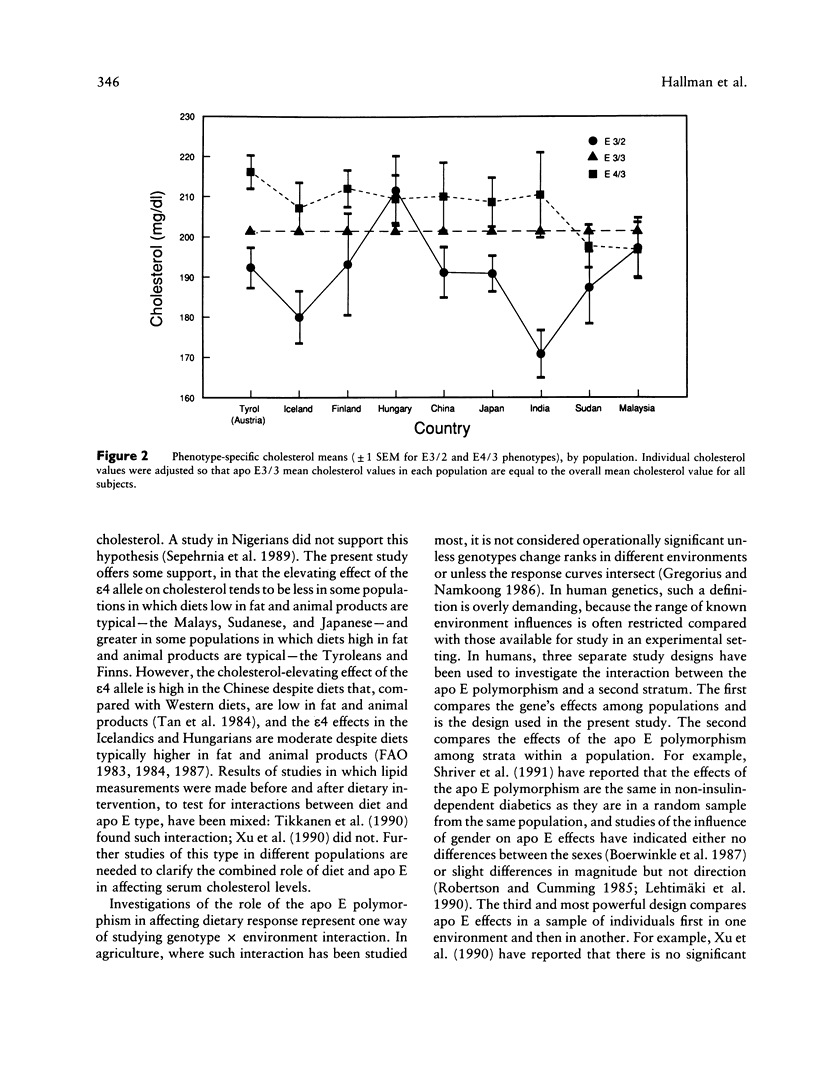
Application of uniform methods for measuring the apolipoprotein (apo) E polymorphism and plasma cholesterol levels in nine populations (Tyrolean, Sudanese, Indian, Chinese, Japanese, Hungarian, Icelandic, Finnish, and Malay) revealed significant heterogeneity among them in apo E type frequencies and mean cholesterol levels. The major apo E types in all populations were E3/2 (frequency range from 7.0% in Indians to 16.9% in Malays), E3/3 (frequency range from 39.8% in Sudanese to 72.1% in Japanese), and E3/4 (frequency range from 11.3% in Japanese to 35.9% in Sudanese). Mean cholesterol levels ranged from 144.2 mg/dl in the Sudanese to 228.5 mg/dl in the Icelandics. Two-way analysis of variance of the effect of population and apo E type on cholesterol levels showed no significantly interaction effect, indicating that the effects of apo E type on cholesterol levels do not differ significantly among the populations. The overall average excess for the epsilon 2 allele was -14.12 mg/dl (range -31.63 to -8.82 mg/dl); for the epsilon 3 allele, 0.04 mg/dl (range -1.87 to 1.58 mg/dl; and for the epsilon 4 allele, 8.14 mg/dl (range -1.71 to 13.31 mg/dl). Despite the apparent heterogeneity in these values, especially for the epsilon 4 allele, comparison of the average excesses by a method of repeated sampling with random permutations revealed no significant difference in effects among populations. These data indicate that a given apo E allele acts in a relatively uniform manner in different populations despite differences in genetic background and environmental factors.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asakawa J., Takahashi N., Rosenblum B. B., Neel J. V. Two-dimensional gel studies of genetic variation in the plasma proteins of Amerindians and Japanese. Hum Genet. 1985;70(3):222–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00273446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Ihrke G., Herz J., Stanley K. K. The LDL-receptor-related protein, LRP, is an apolipoprotein E-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):162–164. doi: 10.1038/341162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Sing C. F. The use of measured genotype information in the analysis of quantitative phenotypes in man. III. Simultaneous estimation of the frequencies and effects of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism and residual polygenetic effects on cholesterol, betalipoprotein and triglyceride levels. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;51(Pt 3):211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb00874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Simultaneous effects of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism on apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein B, and cholesterol metabolism. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):104–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Visvikis S., Welsh D., Steinmetz J., Hanash S. M., Sing C. F. The use of measured genotype information in the analysis of quantitative phenotypes in man. II. The role of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism in determining levels, variability, and covariability of cholesterol, betalipoprotein, and triglycerides in a sample of unrelated individuals. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;27(3):567–582. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthillier D., Sing C. F., Davignon J. Apolipoprotein E phenotyping with a single gel method: application to the study of informative matings. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1060–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Lukka M., Kuusi T., Nikkilä E., Utermann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in the Finnish population: gene frequencies and relation to lipoprotein concentrations. J Lipid Res. 1986 Mar;27(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto M., Watanabe K., Ishii K. Reciprocal effects of apolipoprotein E alleles (epsilon 2 and epsilon 4) on plasma lipid levels in normolipidemic subjects. Clin Genet. 1986 Jun;29(6):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falase A. O., Cole T. O., Osuntokun B. O. Myocardial infarction in Nigerians. Trop Geogr Med. 1973 Jun;25(2):147–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer D. S. A note on Fisher's 'average effect' and 'average excess'. Genet Res. 1985 Dec;46(3):337–347. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300022825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Stark D., Wilson D., Brewer H. B., Jr Abnormal in vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein E4 in humans. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):815–821. doi: 10.1172/JCI112645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding R. M., Sokal R. R. Classification of the European language families by genetic distance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9370–9372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Defective hepatic lipoprotein receptor binding of beta-very low density lipoproteins from type III hyperlipoproteinemic patients. Importance of apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):860–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobori S., Nakamura N., Uzawa H., Shichiri M. Influence of apolipoprotein E polymorphism on plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels, and clinical characteristics of type III hyperlipoproteinemia due to apolipoprotein E phenotype E2/2 in Japan. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Jan;69(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtimäki T., Moilanen T., Viikari J., Akerblom H. K., Ehnholm C., Rönnemaa T., Marniemi J., Dahlen G., Nikkari T. Apolipoprotein E phenotypes in Finnish youths: a cross-sectional and 6-year follow-up study. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON E. S., HARTLEY H. O. Charts of the power function for analysis of variance tests, derived from the non-central F-distribution. Biometrika. 1951 Jun;38(1-2):112–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. H., Nichols A. V., Dell R. B., Ramakrishnan R., Lindgren F. T., Gong E. L., Blum C. B., Goodman D. S. Lack of relationship in humans of the parameters of body cholesterol metabolism with plasma levels of subfractions of HDL or LDL, or with apoE isoform phenotype. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jun;27(6):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson F. W., Cumming A. M. Effects of apoprotein E polymorphism on serum lipoprotein concentration. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):283–292. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Utermann G., Weber W., Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Innerarity T. L. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepehrnia B., Kamboh M. I., Adams-Campbell L. L., Bunker C. H., Nwankwo M., Majumder P. P., Ferrell R. E. Genetic studies of human apolipoproteins. X. The effect of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism on quantitative levels of lipoproteins in Nigerian blacks. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):586–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriver M. D., Boerwinkle E., Hewett-Emmett D., Hanis C. L. Frequency and effects of apolipoprotein E polymorphism in Mexican-American NIDDM subjects. Diabetes. 1991 Mar;40(3):334–337. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.3.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Davignon J. Role of the apolipoprotein E polymorphism in determining normal plasma lipid and lipoprotein variation. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):268–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing C. F., Moll P. P. Genetics of variability of CHD risk. Int J Epidemiol. 1989;18(3 Suppl 1):S183–S195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton A. R., Sing C. F., Kessling A., Humphries S. A cladistic analysis of phenotype associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping. II. The analysis of natural populations. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1145–1154. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen M. J., Huttunen J. K., Ehnholm C., Pietinen P. Apolipoprotein E4 homozygosity predisposes to serum cholesterol elevation during high fat diet. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):285–288. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Yamanouchi Y., Onuki M., Yamakawa K., Miyazaki R., Taya T., Kondo I., Ohnuki M., Hamaguchi H. Frequencies of apolipoproteins E5 and E7 in apparently healthy Japanese. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1985 Dec;30(4):271–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01907964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Pruin N., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. III. Effect of a single polymorphic gene locus on plasma lipid levels in man. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Weisgraber K. H., Weber W., Mahley R. W. Genetic polymorphism of apolipoprotein E: a variant form of apolipoprotein E2 distinguished by sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Lipid Res. 1984 Apr;25(4):378–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. O. Coronary atherosclerosis in Nigeria. Br Heart J. 1971 Jan;33(1):95–100. doi: 10.1136/hrt.33.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu C. F., Boerwinkle E., Tikkanen M. J., Huttunen J. K., Humphries S. E., Talmud P. J. Genetic variation at the apolipoprotein gene loci contribute to response of plasma lipids to dietary change. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7(4):261–275. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370070405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., Utermann G., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Schonfeld G., Hazzard W. R. Proposed nomenclature of apoE isoproteins, apoE genotypes, and phenotypes. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):911–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



