Abstract
The mechanism of profound generalized iduronate sulfatase (IDS) deficiency in a developmentally delayed female with clinical Hunter syndrome was studied. Methylation-sensitive RFLP analysis of DNA from peripheral blood lymphocytes from the patient, using MspI/HpaII digestion and probing with M27 beta, showed that the paternal allele was resistant to HpaII digestion (i.e., was methylated) while the maternal allele was digested (i.e., was hypomethylated), indicating marked imbalance of X-chromosome inactivation in peripheral blood lymphocytes of the patient. Similar studies on DNA from maternal lymphocytes showed random X-chromosome inactivation. Among a total of 40 independent maternal fibroblast clones isolated by dilution plating and analyzed for IDS activity, no IDS- clone was found. Somatic cell hybrid clones containing at least one active human X chromosome were produced by fusion of patient fibroblasts with Hprt- hamster fibroblasts (RJK88) and grown in HAT-ouabain medium. Methylation-sensitive RFLP analysis of DNA from the hybrids showed that of the 22 clones that retained the DXS255 locus (M27 beta), all contained the paternal allele in the methylated (active) form. No clone was isolated containing only the maternal X chromosome, and in no case was the maternal allele hypermethylated. We postulate from these studies that the patient has MPS II as a result of a mutation resulting in both the disruption of the IDS locus on her paternal X chromosome and unbalanced inactivation of the nonmutant maternal X chromosome.
Full text
PDF



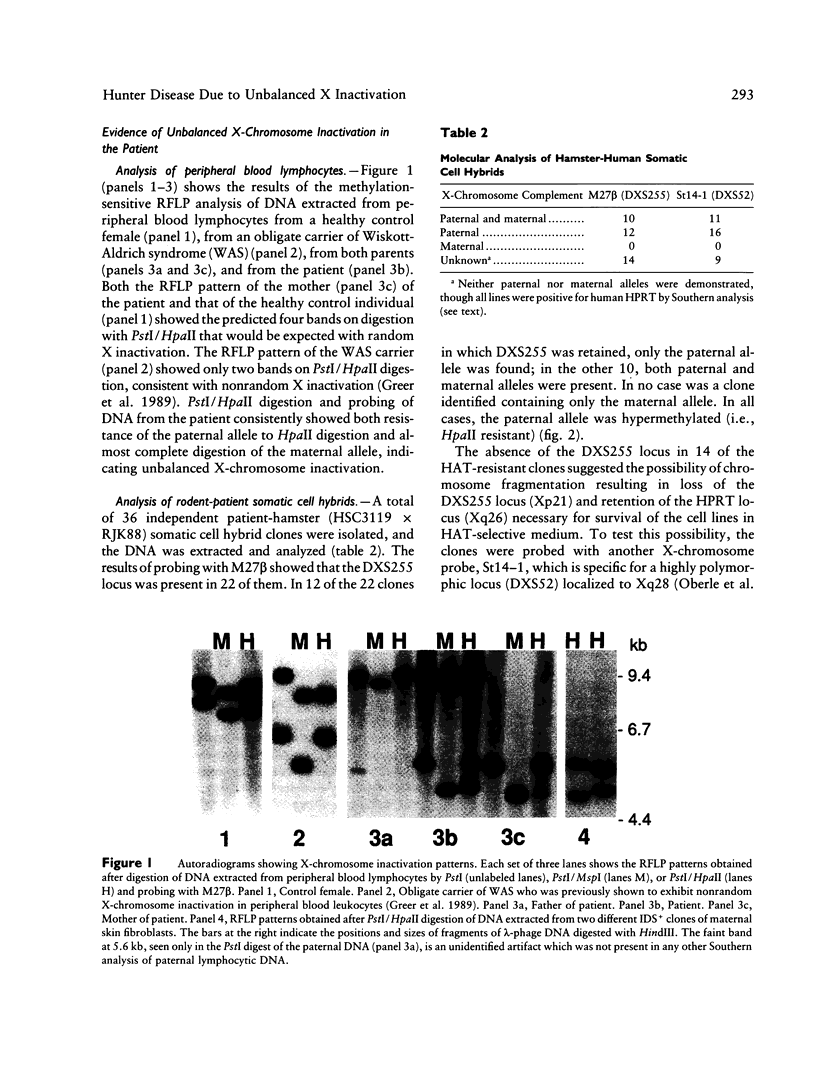



Images in this article
Selected References
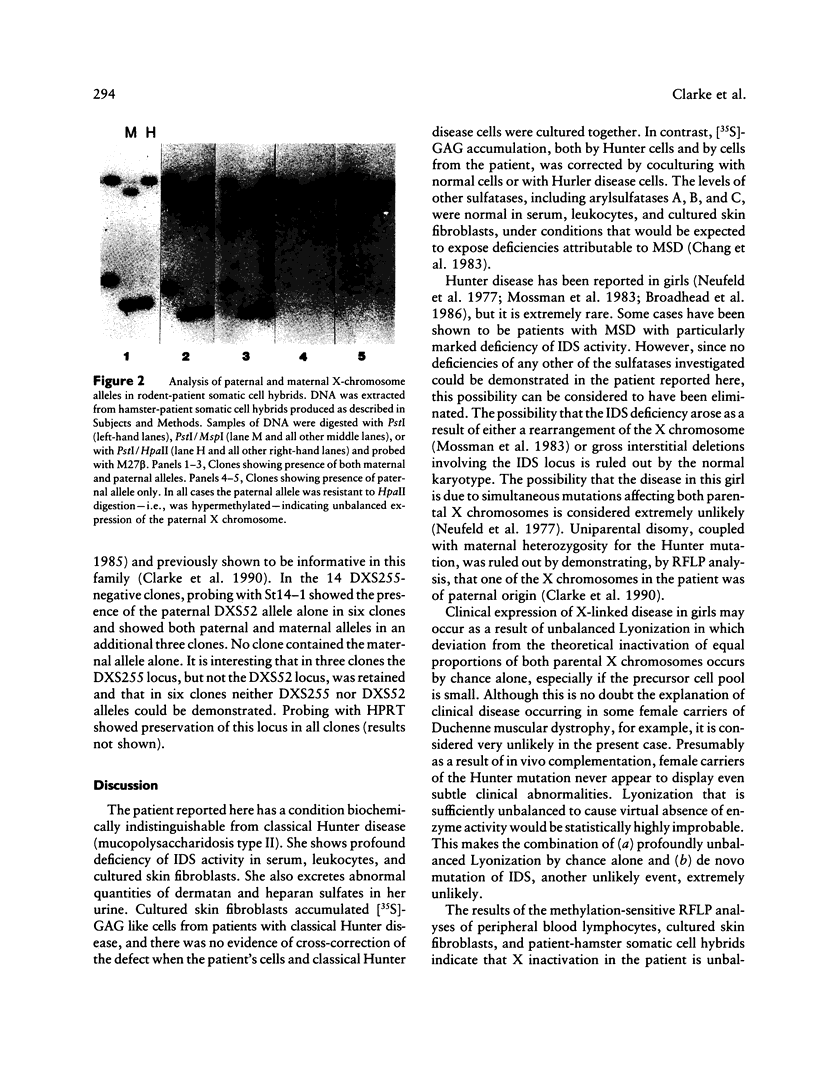
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer I. M., Young I. D., Rees D. W., Oladimeji A., Wusteman F. S., Harper P. S. Carrier detection in Hunter syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Sep;16(1):61–69. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach G., Eisenberg F., Jr, Cantz M., Neufeld E. F. The defect in the Hunter syndrome: deficiency of sulfoiduronate sulfatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2134–2138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth C. W., Nadler H. L. In vitro selection for the Hunter gene. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 22;288(12):636–636. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303222881220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadhead D. M., Kirk J. M., Burt A. J., Gupta V., Ellis P. M., Besley G. T. Full expression of Hunter's disease in a female with an X-chromosome deletion leading to non-random inactivation. Clin Genet. 1986 Nov;30(5):392–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Lafreniere R. G., Powers V. E., Sebastio G., Ballabio A., Pettigrew A. L., Ledbetter D. H., Levy E., Craig I. W., Willard H. F. Localization of the X inactivation centre on the human X chromosome in Xq13. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):82–84. doi: 10.1038/349082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Fraser N. J., Brown G. K. Differential methylation of the hypervariable locus DXS255 on active and inactive X chromosomes correlates with the expression of a human X-linked gene. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90543-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Joubert G., Davidson R. G. Non-selective isolation of human somatic cell hybrids by unit-gravity sedimentation. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):168–170. doi: 10.1038/278168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Rosa N. E., Ballantyne S. R., Davidson R. G. Biochemical variability of arylsulphatases -A, -B and -C in cultured fibroblasts from patients with multiple sulphatase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1983;6(4):167–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02310875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase D. S., Morris A. H., Ballabio A., Pepper S., Giannelli F., Adinolfi M. Genetics of Hunter syndrome: carrier detection, new mutations, segregation and linkage analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;50(Pt 4):349–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Willard H. F., Teshima I., Chang P. L., Skomorowski M. A. Hunter disease (mucopolysaccharidosis type II) in a karyotypically normal girl. Clin Genet. 1990 May;37(5):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly P. V., Di Ferrante N. Reliability of the Booth-Nadler technique for the detection of Hunter heterozygotes. Pediatrics. 1975 Sep;56(3):429–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluharty A. L., Stevens R. L., Davis L. L., Shapiro L. J., Kihara H. Presence of arylsulfatase A (ARS A) in multiple sulfatase deficiency disorder fibroblasts. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 May;30(3):249–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. J., Boyd Y., Craig I. Isolation and characterization of a human variable copy number tandem repeat at Xcen-p11.22. Genomics. 1989 Jul;5(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Deletion and amplification of the HGPRT locus in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1086–1096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel R. A., Leung A. Complementation analysis in Gaucher disease using single cell microassay techniques. Evidence for a single "Gaucher gene". Hum Genet. 1983;65(2):112–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00286645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel R. A., Leung A., Saunders M., Hösli P. Analysis of genetic complementation by whole-cell microtechniques in fibroblast heterokaryons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6520–6524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer W. L., Kwong P. C., Peacocke M., Ip P., Rubin L. A., Siminovitch K. A. X-chromosome inactivation in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: a marker for detection of the carrier state and identification of cell lineages expressing the gene defect. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. W., Liebaers I., Di Natale P., Neufeld E. F. Enzymic diagnosis of the genetic mucopolysaccharide storage disorders. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:439–456. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Bernard H. U., Friedmann T. Isolation of a genomic clone partially encoding human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5038–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Guern E., Couillin P., Oberlé I., Ravise N., Boue J. More precise localization of the gene for Hunter syndrome. Genomics. 1990 Jul;7(3):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90169-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Sprenkle J. A., Liebaers I., Scott J. F., Neufeld E. F. X-linked Hunter syndrome: the heterozygous phenotype in cell culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):448–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Geller R. L., Yen P. H., Rosendorff J., Bernstein R., Yoshida A., Shapiro L. J. Cytogenetic and molecular studies on a recombinant human X chromosome: implications for the spreading of X chromosome inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4954–4958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossman J., Blunt S., Stephens R., Jones E. E., Pembrey M. Hunter's disease in a girl: association with X:5 chromosomal translocation disrupting the Hunter gene. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Nov;58(11):911–915. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.11.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Liebaers I., Epstein C. J., Yatziv S., Milunsky A., Migeon B. R. The Hunter syndrome in females: is there an autosomal recessive form of iduronate sulfatase deficiency? Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):455–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyhan W. L., Bakay B., Connor J. D., Marks J. F., Keele D. K. Hemizygous expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in erythrocytes of heterozygotes for the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Drayna D., Camerino G., White R., Mandel J. L. The telomeric region of the human X chromosome long arm: presence of a highly polymorphic DNA marker and analysis of recombination frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prchal J. T., Carroll A. J., Prchal J. F., Crist W. M., Skalka H. W., Gealy W. J., Harley J., Malluh A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: cellular impairments and their implication for carrier detection. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1048–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. H., Upadhyaya M., Sarfarazi M., Harper P. S. Further evidence localising the gene for Hunter's syndrome to the distal region of the X chromosome long arm. J Med Genet. 1989 May;26(5):309–313. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.5.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Certoma A., Du Sart D., Kalitsis P., Leversha M., Fowler K., Sheffield L., Jack I., Danks D. M. Unusual X chromosome inactivation in a mentally retarded girl with an interstitial deletion Xq27: implications for the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;84(4):347–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00196232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi U., Kirschner D. A., Beauregard L., Page L., Kunkel L., Latt S. Cytologic and molecular analysis of 46,XXq- cells to identify a DNA segment that might serve as a probe for a putative human X chromosome inactivation center. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):33–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00289475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therman E., Patau K. Abnormal X chromosomes in man: origin, behavior and effects. Humangenetik. 1974;25(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00281002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therman E., Sarto G. E., Palmer C. G., Kallio H., Denniston C. Position of the human X inactivation center on Xq. Hum Genet. 1979;50(1):59–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00295590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Neufeld E. F. Iduronate sulfatase from human plasma. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:573–578. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Morris C. P., Anson D. S., Occhiodoro T., Bielicki J., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8531–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. Juvenile Sandhoff Disease: complementation tests with Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs disease using polyethylene glycol-induced cell fusion. Hum Genet. 1978 Apr 24;41(3):325–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00284766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]