Abstract
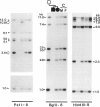
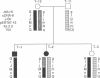
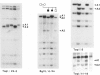
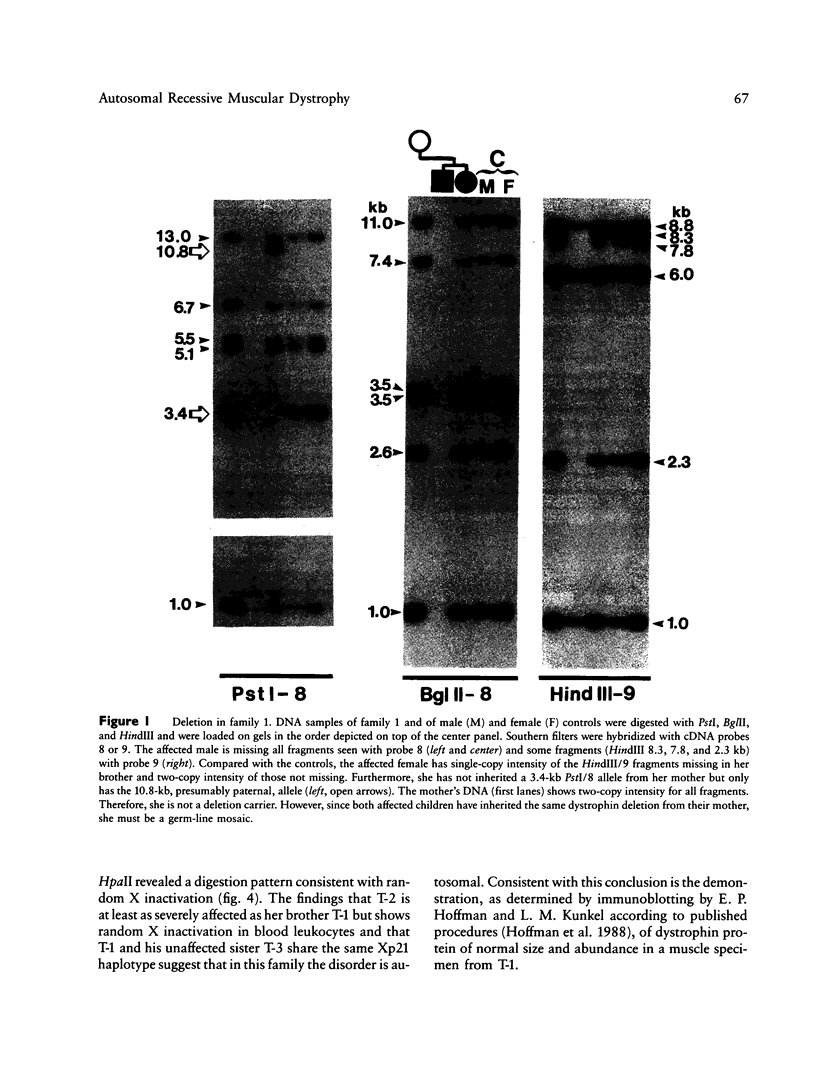
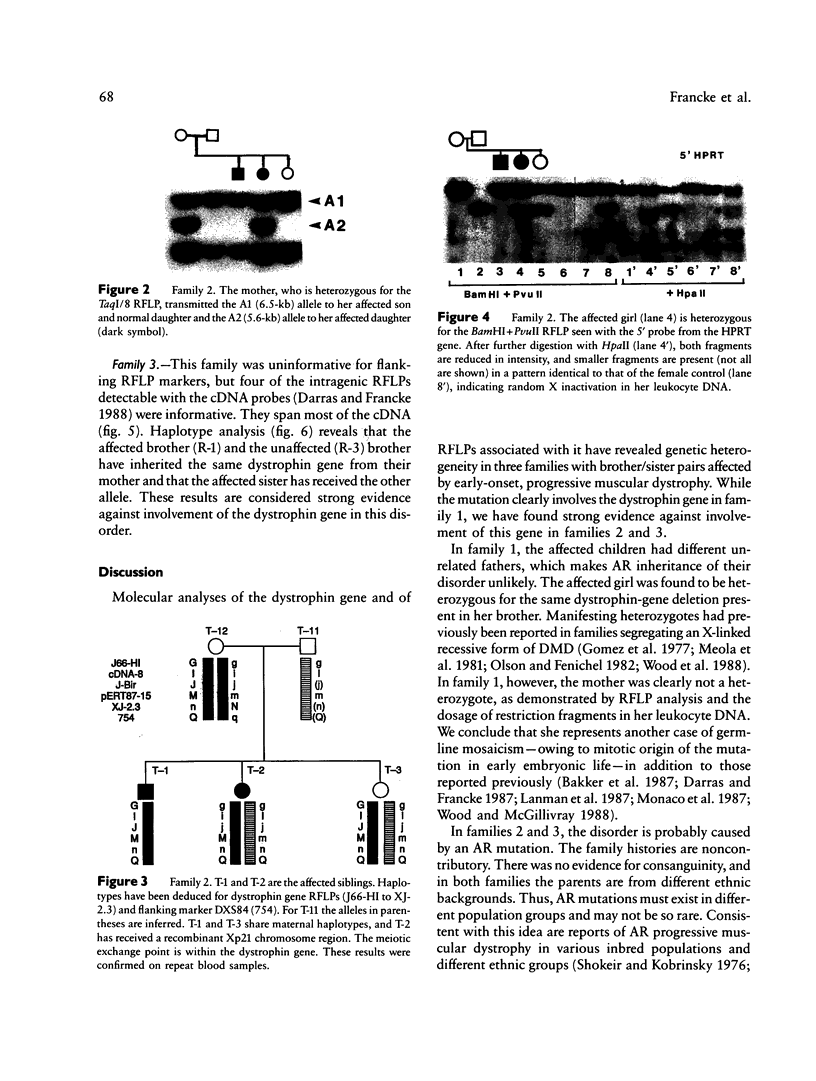
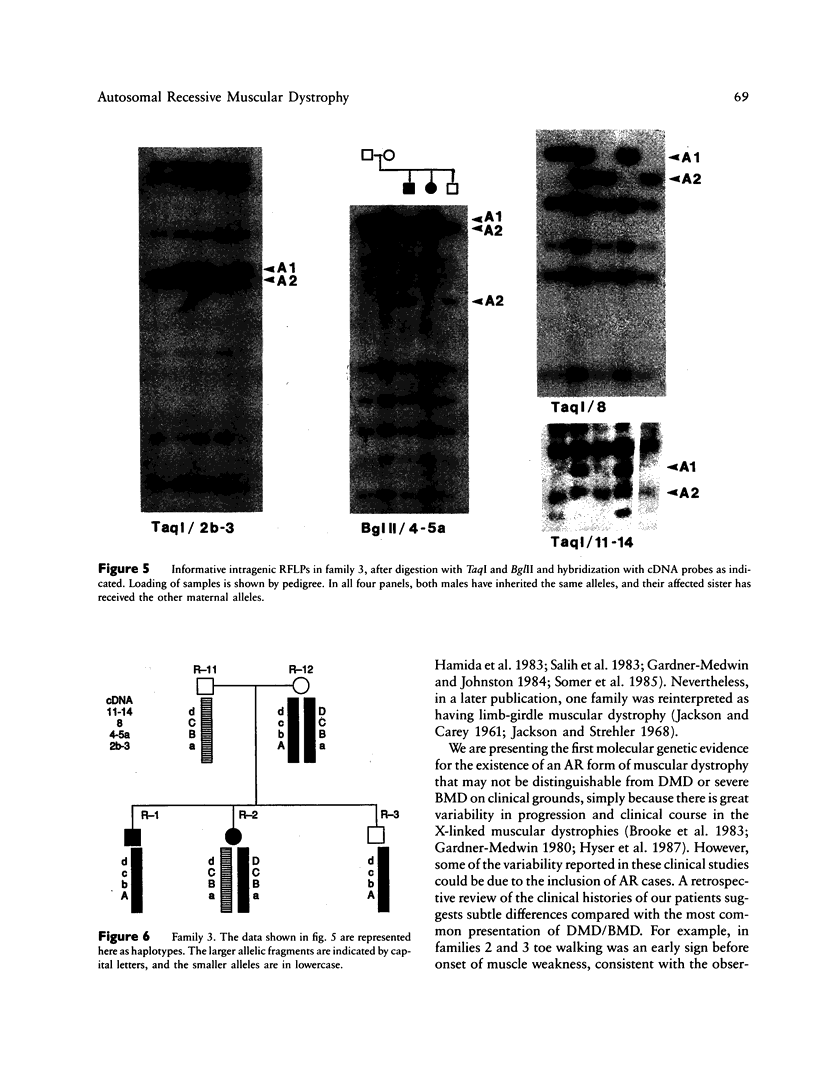
An autosomal recessive (AR) form of muscular dystrophy that clinically resembles Duchenne/Becker types exists, but its frequency is unknown. We have studied three unrelated affected brother/sister pairs and their families for deletions and polymorphisms with the entire dystrophin cDNA and other DNA probes from the Xp21 region to test for involvement of the DMD locus. In family 1 a large intragenic deletion was found in the affected male. The affected sister was heterozygous for this deletion, but the mother was not, implying germinal mosaicism. In family 2, no deletion was detected in the affected male. RFLP analysis revealed that the affected male and an unaffected sister shared a complete Xp21 haplotype while the affected sister had inherited a recombinant Xp21 region resulting from a crossover between pERT 87-15 and J-Bir. Only the 5' region of the dystrophin gene was shared with the affected boy. X-inactivation studies using a polymorphism in the 5'-flanking region of the HPRT gene, in conjunction with methylation-sensitive enzymes, revealed random X inactivation in the affected girl's leukocytes. In a muscle biopsy from the affected male, the dystrophin protein was present in normal amount and size. Family 3 was informative for four RFLPs detected with dystrophin cDNA probes which span the entire gene. The affected male was found to share the complete dystrophin RFLP haplotype with his unaffected brother, while his affected sister had inherited the other maternal haplotype. It is concluded that the clinical presentation of early-onset, progressive muscular dystrophy in a male and in his karyotypically normal sister can be caused by mutations at different loci. While in family 1 a deletion in the dystrophin gene is responsible, this gene does not appear to be involved in families 2 and 3.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas F., Bikker H., van Ommen G. J., de Vijlder J. J. Unusual scarcity of restriction site polymorphism in the human thyroglobulin gene. A linkage study suggesting autosomal dominance of a defective thyroglobulin allele. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):301–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00291357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E., Van Broeckhoven C., Bonten E. J., van de Vooren M. J., Veenema H., Van Hul W., Van Ommen G. J., Vandenberghe A., Pearson P. L. Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):554–556. doi: 10.1038/329554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hamida M., Fardeau M., Attia N. Severe childhood muscular dystrophy affecting both sexes and frequent in Tunisia. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Sep;6(7):469–480. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla E., Samitt C. E., Miranda A. F., Hays A. P., Salviati G., DiMauro S., Kunkel L. M., Hoffman E. P., Rowland L. P. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: deficiency of dystrophin at the muscle cell surface. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Munro E., Ray P., Worton R., Monaco T., Kunkel L., Craig I. Molecular heterogeneity of translocations associated with muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1987 Apr;31(4):265–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Fenichel G. M., Griggs R. C., Mendell J. R., Moxley R., Miller J. P., Province M. A. Clinical investigation in Duchenne dystrophy: 2. Determination of the "power" of therapeutic trials based on the natural history. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):91–103. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. S., Speer A., Rosenthal A., Forrest S. M., Smith T. J., Edwards Y., Flint T., Hill D., Davies K. E. Deletions of fetal and adult muscle cDNA in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3277–3283. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Blattner P., Harper J. F., Spiro A. J., Alter S., Francke U. Intragenic deletions in 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)/Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) families studied with the dystrophin cDNA: location of breakpoints on HindIII and BglII exon-containing fragment maps, meiotic and mitotic origin of the mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):620–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Francke U. A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):556–558. doi: 10.1038/329556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Harper J. F., Francke U. Prenatal diagnosis and detection of carriers with DNA probes in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 16;316(16):985–992. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704163161604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M., Francke U. Direct method for prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy using the entire dystrophin cDNA. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Mar;29(3):713–726. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIER P., BAMATTER F., KLEIN D. MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY (DUCHENNE) IN A GIRL WITH TURNER'S SYNDROME. J Med Genet. 1965 Mar;2(1):38–46. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Winkelstein J. A., Civin C. I., Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B. Carrier detection in X-linked agammaglobulinemia by analysis of X-chromosome inactivation. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):427–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest S. M., Cross G. S., Flint T., Speer A., Robson K. J., Davies K. E. Further studies of gene deletions that cause Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D. Clinical features and classification of the muscular dystrophies. Br Med Bull. 1980 May;36(2):109–115. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D., Johnston H. M. Severe muscular dystrophy in girls. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Apr;64(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez M. R., Engel A. G., Dewald G., Peterson H. A. Failure of inactivation of Duchenne dystrophy X-chromosome in one of female identical twins. Neurology. 1977 Jun;27(6):537–541. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.6.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Fischbeck K. H., Brown R. H., Johnson M., Medori R., Loike J. D., Harris J. B., Waterston R., Brooke M., Specht L. Characterization of dystrophin in muscle-biopsy specimens from patients with Duchenne's or Becker's muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 26;318(21):1363–1368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805263182104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyser C. L., Province M., Griggs R. C., Mendell J. R., Fenichel G. M., Brooke M. H., Miller J. P., Polakowska R., Doherty R. A., Quirk S. Genetic heterogeneity in Duchenne dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):553–555. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON C. E., CAREY J. H. Progressive muscular dystrophy: autosomal recessive type. Pediatrics. 1961 Jul;28:77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. E., Strehler D. A. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy: clinical manifestations and detection of preclinical disease. Pediatrics. 1968 Feb;41(2):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Bernard H. U., Friedmann T. Isolation of a genomic clone partially encoding human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5038–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith D. H., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Active X chromosome DNA is unmethylated at eight CCGG sites clustered in a guanine-plus-cytosine-rich island at the 5' end of the gene for phosphoglycerate kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4122–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanman J. T., Jr, Pericak-Vance M. A., Bartlett R. J., Chen J. C., Yamaoka L., Koh J., Speer M. C., Hung W. Y., Roses A. D. Familial inheritance of a DXS164 deletion mutation from a heterozygous female. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;41(2):138–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meola G., Scarpini E., Silani V., Scarlato G. Manifesting carrier of x-linked Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1981 Mar;49(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(81)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Bonilla E., Martucci G., Moraes C. T., Hays A. P., Dimauro S. Immunocytochemical study of dystrophin in muscle cultures from patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and unaffected control patients. Am J Pathol. 1988 Sep;132(3):410–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Colletti-Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Localization and cloning of Xp21 deletion breakpoints involved in muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00281063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson B. J., Fenichel G. M. Progressive muscle disease in a young woman with family history of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1982 Jun;39(6):378–380. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510180056015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn A. S., Lisak R. P., Rowland L. P. Muscular dystrophy in young girls. Neurology. 1970 Feb;20(2):147–159. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salih M. A., Omer M. I., Bayoumi R. A., Karrar O., Johnson M. Severe autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy in an extended Sudanese kindred. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983 Feb;25(1):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1983.tb13720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokeir M. H., Kobrinsky N. L. Autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy in Manitoba Hutterites. Clin Genet. 1976 Feb;9(2):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somer H., Voutilainen A., Knuutila S., Kaitila I., Rapola J., Leinonen H. Duchenne-like muscular dystrophy in two sisters with normal karyotypes: evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance. Clin Genet. 1985 Aug;28(2):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. M. Four cases of Duchenne-type muscular dystrophy in girls. Med J Aust. 1972 Nov 4;2(19):1066–1069. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb103721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Feinberg A. P. Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to determine the clonal origin of human tumors. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):642–645. doi: 10.1126/science.2982210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., McGillivray B. C. Germinal mosaicism in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):282–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00291677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S., Shukin R. J., McGillivray B. C., Ray P. N., Worton R. G. A grandpaternally derived de novo deletion within Xp21 initially presenting in carrier females diagnosed as Kugelberg-Welander syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Feb;29(2):419–423. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulfsberg E. A., Skoglund R. R. Duchenne muscular dystrophy in a 46 XY female. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1986 May;25(5):276–278. doi: 10.1177/000992288602500509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Breteler E. G., Pearson P. L., van Ommen G. J. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):640–642. doi: 10.1038/329640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Bertelson C., Ginjaar H. B., den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Chelly J., Matton M., van Essen A. J., Bartley J., Kunkel L. M. Long-range genomic map of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: isolation and use of J66 (DXS268), a distal intragenic marker. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]