Abstract
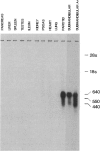
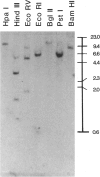
A cDNA coding for histatin 1 was isolated from a human submandibular-gland library and sequenced. This cDNA was used to probe RNAs isolated from a variety of tissues to investigate tissue-specific regulation and to determine whether histatins might play a role other than in the oral cavity. The same probe was also used for Southern blot analysis of human genomic DNA restricted with various enzymes, and it showed that the genes coding for histatins are on the same chromosome. In situ hybridization of the cDNA probe to metaphase chromosome spreads was performed to determine chromosomal location of the genes for histatins. A genomic fragment isolated using the cDNA probe was also hybridized to chromosome spreads, and the same chromosome was identified. The genes for histatins are located on chromosome 4, band q13. We have shown that three histatin mRNAs are expressed in human parotid and submandibular glands but in none of the other tissues studied. These results suggest that histatins are specific to salivary secretions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball S. P., Cook P. J., Mars M., Buckton K. E. Linkage between dentinogenesis imperfecta and Gc. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 Jan 1;46(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughman J. A., Beaty T. H., Yang P., Goodman S. B., Wooten R. K., Suzuki J. B. Problems of genetic model testing in early onset periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1988 May;59(5):332–337. doi: 10.1902/jop.1988.59.5.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughman J. A., Halloran S. L., Roulston D., Schwartz S., Suzuki J. B., Weitkamp L. R., Wenk R. E., Wooten R., Cohen M. M. An autosomal-dominant form of juvenile periodontitis: its localization to chromosome 4 and linkage to dentinogenesis imperfecta and Gc. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1986;6(4):341–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Modest E. J. Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma. 1970;30(2):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00282002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P., Ridall A. L., Levine M. J. Human submandibular gland statherin and basic histidine-rich peptide are encoded by highly abundant mRNA's derived from a common ancestral sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):784–790. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. C., Wolff A., Yeh C. K., Atkinson J. C., Baum B. J. Saliva inhibits HIV-1 infectivity. J Am Dent Assoc. 1988 May;116(6):635–637. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1988.0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Smith D. J., Schluckebier S. K., Moreno E. C. Relationship between concentration of human salivary statherin and inhibition of calcium phosphate precipitation in stimulated human parotid saliva. J Dent Res. 1984 Jun;63(6):857–863. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630060901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I. The interaction of human parotid salivary proteins with hydroxyapatite. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Dec;18(12):1517–1529. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill D. B., Fry H. R. Treatment of localized juvenile periodontitis (periodontosis). A review. J Periodontol. 1987 Jan;58(1):1–8. doi: 10.1902/jop.1987.58.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay B. J., Denepitiya L., Iacono V. J., Krost S. B., Pollock J. J. Growth-inhibitory and bactericidal effects of human parotid salivary histidine-rich polypeptides on Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):695–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.695-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Hay D. I., Smith D. J., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F. Molecular basis of salivary proline-rich protein and peptide synthesis: cell-free translations and processing of human and macaque statherin mRNAs and partial amino acid sequence of their signal peptides. J Dent Res. 1987 Feb;66(2):462–466. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660021301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Xu T., McMillian F. M., Levitz S. M., Diamond R. D., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F. Histatins, a novel family of histidine-rich proteins in human parotid secretion. Isolation, characterization, primary structure, and fungistatic effects on Candida albicans. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7472–7477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Yang Y. C., Diamond R. D., Hyslop D., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F. The primary structure and functional characterization of the neutral histidine-rich polypeptide from human parotid secretion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1177–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. J., Denepitiya L., MacKay B. J., Iacono V. J. Fungistatic and fungicidal activity of human parotid salivary histidine-rich polypeptides on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):702–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.702-707.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini L. M., Carlock L. R., Johnson G. W., Azen E. A. cDNA cloning and chromosomal localization (4q11-13) of a gene for statherin, a regulator of calcium in saliva. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):1048–1060. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]