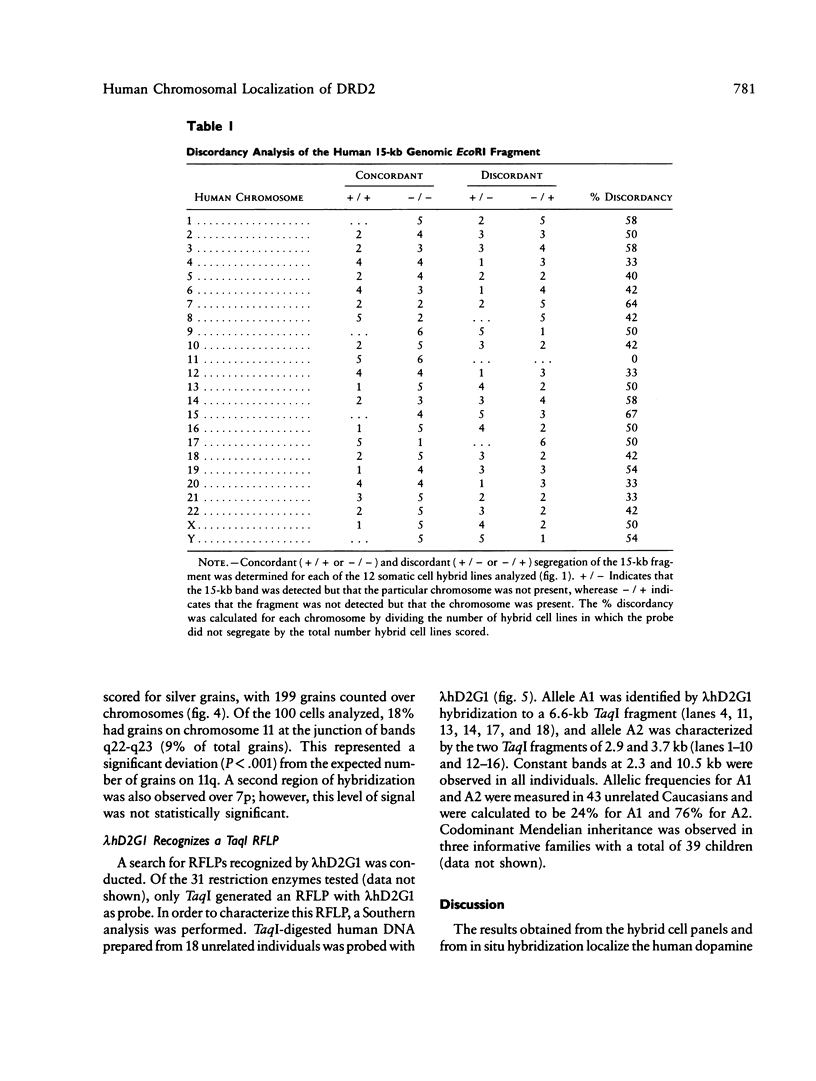
Abstract
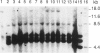
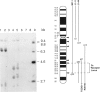
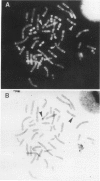
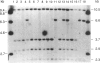
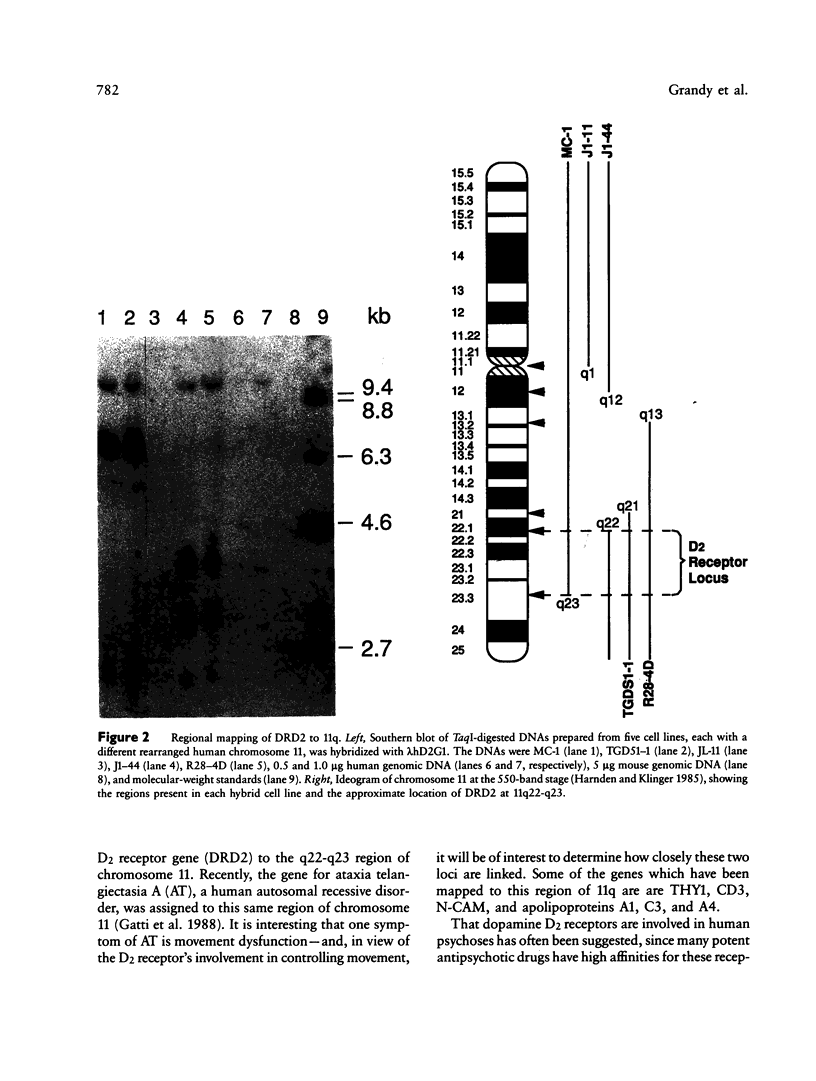
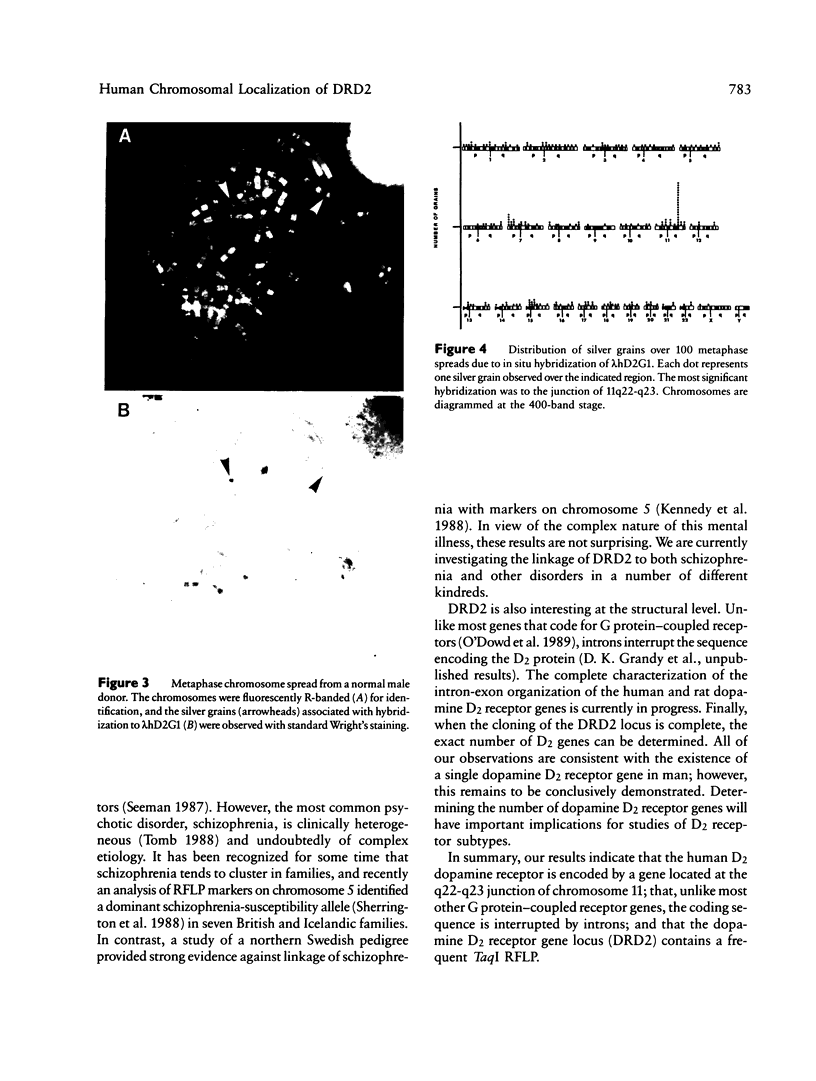
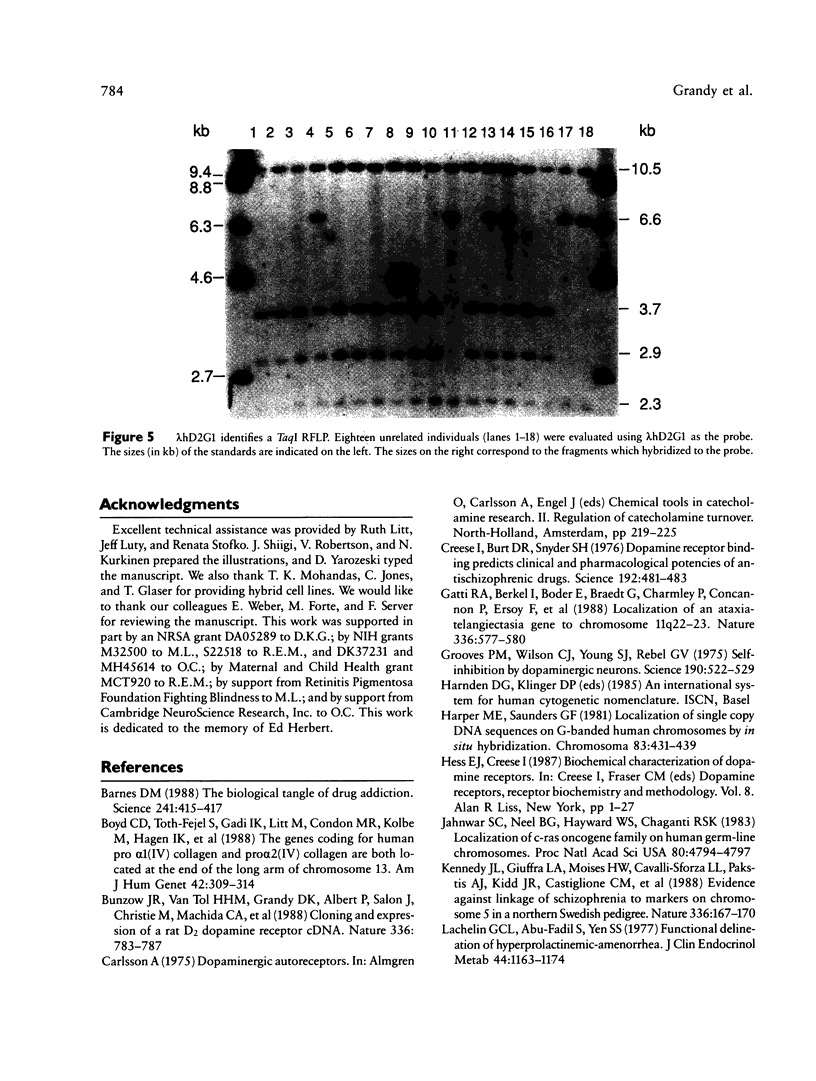
Human dopaminergic neurons are involved in the control of hormone secretion, voluntary movement, and emotional behavior. Mediating these effects are the dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. These macromolecules belong to a large family of related sequences known as the G protein-coupled receptors. The D2 receptors have been of special interest because they bind, with high affinity and specificity, many of the commonly prescribed antipsychotic drugs. We previously isolated a full-length cDNA clone of the rat D2 receptor. When a chromosome mapping panel was probed with the rat D2 receptor cDNA a 15-kb EcoRI restriction fragment was identified and localized to human chromosome 11. The rat cDNA was also used to clone a human genomic fragment, lambda hD2G1, which contains the last coding exon of the D2 receptor gene (DRD2) and 16.5 kb of 3' flanking sequence. Hybridization of lambda hD2G1 to a chromosome 11 regional mapping panel localized DRD2 to 11q. In situ hybridization of lambda hD2G1 to metaphase chromosomes refined this assignment to the q22-q23 junction of chromosome 11. A search for RFLPs associated with D2DR identified a frequent two-allele TaqI RFLP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. M. The biological tangle of drug addiction. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3393909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. D., Toth-Fejel S. E., Gadi I. K., Litt M., Condon M. R., Kolbe M., Hagen I. K., Kurkinen M., Mackenzie J. W., Magenis E. The genes coding for human pro alpha 1(IV) collagen and pro alpha 2(IV) collagen are both located at the end of the long arm of chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):309–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Burt D. R., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):481–483. doi: 10.1126/science.3854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatti R. A., Berkel I., Boder E., Braedt G., Charmley P., Concannon P., Ersoy F., Foroud T., Jaspers N. G., Lange K. Localization of an ataxia-telangiectasia gene to chromosome 11q22-23. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):577–580. doi: 10.1038/336577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Wilson C. J., Young S. J., Rebec G. V. Self-inhibition by dopaminergic neurons. Science. 1975 Nov 7;190(4214):522–528. doi: 10.1126/science.242074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhanwar S. C., Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Chaganti R. S. Localization of c-ras oncogene family on human germ-line chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4794–4797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. L., Giuffra L. A., Moises H. W., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Pakstis A. J., Kidd J. R., Castiglione C. M., Sjogren B., Wetterberg L., Kidd K. K. Evidence against linkage of schizophrenia to markers on chromosome 5 in a northern Swedish pedigree. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):167–170. doi: 10.1038/336167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachelin G. C., Abu-fadil S., Yen S. S. Functional delineation of hyperprolactinemic-amenorrhea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jun;44(6):1163–1174. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-6-1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T., Seeman P., Rajput A., Farley I. J., Hornykiewicz O. Receptor basis for dopaminergic supersensitivity in Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):59–61. doi: 10.1038/273059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslen C. L., Jones C., Glaser T., Magenis R. E., Sheehy R., Kellogg J., Litt M. Seven polymorphic loci mapping to human chromosomal region 11q22-qter. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Synder S. H. Relationship of neuroleptic drug effects at brain dopamine, serotonin, alpha-adrenergic, and histamine receptors to clinical potency. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Dec;137(12):1518–1522. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.12.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawin V. L., Skalka A. M., Wray W. Simultaneous observation of quinacrine bands and silver grains on radiolabeled metaphase chromosomes. Histochemistry. 1978 Dec 28;59(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00506472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer D. Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):190–193. doi: 10.1159/000131482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse. 1987;1(2):133–152. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Lee T. Antipsychotic drugs: direct correlation between clinical potency and presynaptic action on dopamine neurons. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1217–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.1145194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Ulpian C., Bergeron C., Riederer P., Jellinger K., Gabriel E., Reynolds G. P., Tourtellotte W. W. Bimodal distribution of dopamine receptor densities in brains of schizophrenics. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6147018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Brynjolfsson J., Petursson H., Potter M., Dudleston K., Barraclough B., Wasmuth J., Dobbs M., Gurling H. Localization of a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 5. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):164–167. doi: 10.1038/336164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Meldolesi J. Mechanisms of signal transduction at the dopamine D2 receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):74–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. I., Ganong W. F. Role of brain monoamines and histamine in regulation of anterior pituitary secretion. Physiol Rev. 1978 Oct;58(4):905–976. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]