Abstract
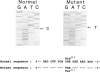
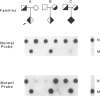
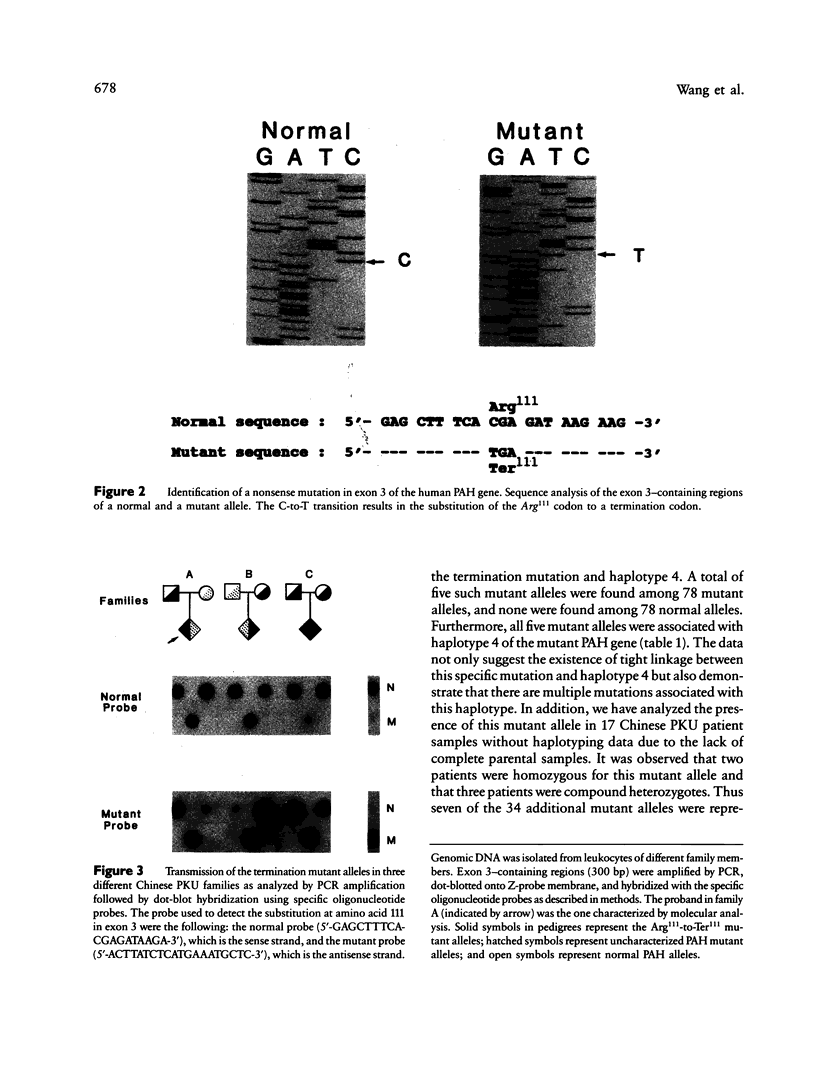
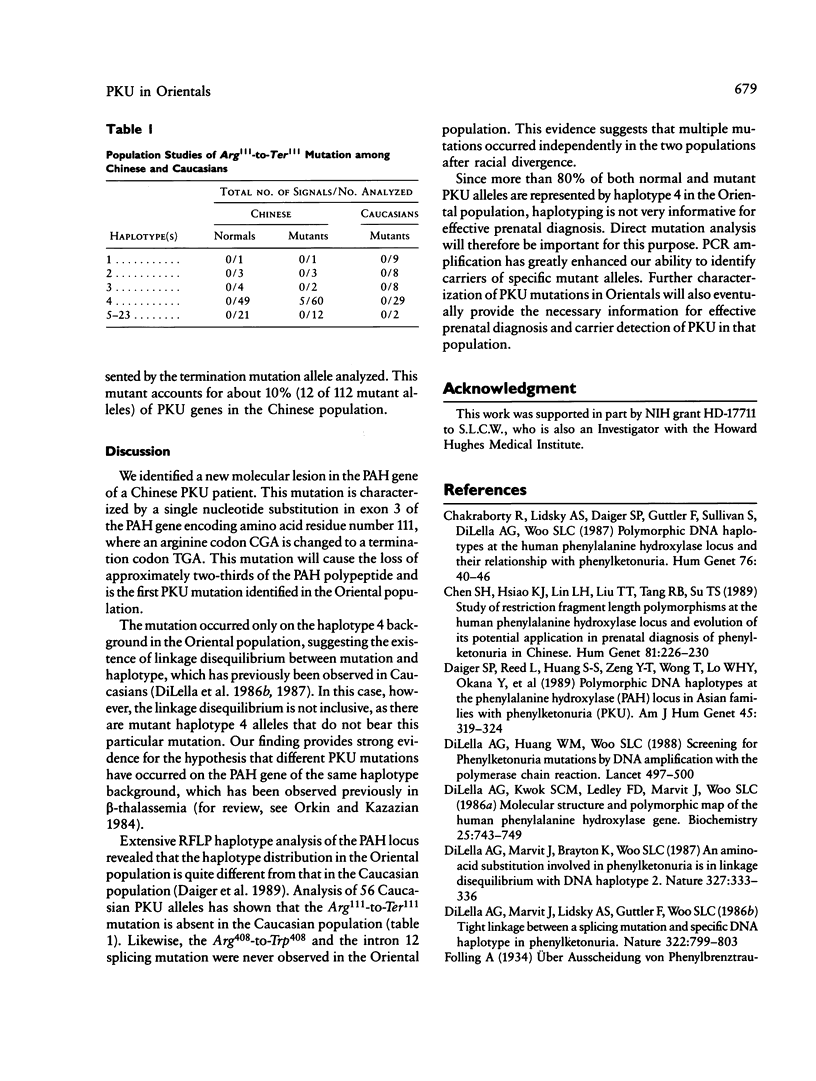
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a common metabolic disorder among Chinese, with a prevalence of about 1 in 16,500 births. This frequency is very similar to that among Caucasians. Individual exons of the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene with flanking introns were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and cloned into M13 for sequence analysis. An Arg111-to-Ter111 mutation has been identified in exon 3 of the PAH gene in a Chinese PKU patient. The mutation is in linkage disequilibrium with the mutant haplotype 4 alleles which are the most prevalent haplotype among the Orientals. The mutation accounts for about 10% of the Chinese PKU alleles and is absent from the Caucasians, demonstrating that independent mutational events have occurred in the PAH locus after racial divergence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chakraborty R., Lidsky A. S., Daiger S. P., Güttler F., Sullivan S., Dilella A. G., Woo S. L. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and their relationship with phenylketonuria. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00283048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Hsiao K. J., Lin L. H., Liu T. T., Tang R. B., Su T. S. Study of restriction fragment length polymorphisms at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and evaluation of its potential application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria in Chinese. Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;81(3):226–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00278993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Reed L., Huang S. S., Zeng Y. T., Wang T., Lo W. H., Okano Y., Hase Y., Fukuda Y., Oura T. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in Asian families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):319–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Huang W. M., Woo S. L. Screening for phenylketonuria mutations by DNA amplification with the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1988 Mar 5;1(8584):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., Marvit J., Woo S. L. Molecular structure and polymorphic map of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):743–749. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Brayton K., Woo S. L. An amino-acid substitution involved in phenylketonuria is in linkage disequilibrium with DNA haplotype 2. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):333–336. doi: 10.1038/327333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Marvit J., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Tight linkage between a splicing mutation and a specific DNA haplotype in phenylketonuria. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):799–803. doi: 10.1038/322799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE R., SUSI A. A SIMPLE PHENYLALANINE METHOD FOR DETECTING PHENYLKETONURIA IN LARGE POPULATIONS OF NEWBORN INFANTS. Pediatrics. 1963 Sep;32:338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güttler F. Hyperphenylalaninemia: diagnosis and classification of the various types of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1980;280:1–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Grenett H. E., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Woo S. L. Gene transfer and expression of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.3856322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Koch R., Jew K., Beaudet A., O'Brien W. E., Bartos D. P., Woo S. L. Phenylalanine hydroxylase expression in liver of a fetus with phenylketonuria. J Pediatr. 1988 Sep;113(3):463–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80629-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Woo S. L. Prenatal diagnosis of classic phenylketonuria by DNA analysis. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):549–551. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidsky A. S., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Kwok S. C., Daiger S. P., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Extensive restriction site polymorphism at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and application in prenatal diagnosis of phenylketonuria. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):619–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvit J., DiLella A. G., Brayton K., Ledley F. D., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. GT to AT transition at a splice donor site causes skipping of the preceding exon in phenylketonuria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5613–5628. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scriver C. R., Clow C. L. Phenylketonuria and other phenylalanine hydroxylation mutants in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:179–202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Lidsky A. S., Güttler F., Chandra T., Robson K. J. Cloned human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene allows prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of classical phenylketonuria. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):151–155. doi: 10.1038/306151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. Molecular basis and population genetics of phenylketonuria. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):1–7. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]