Abstract
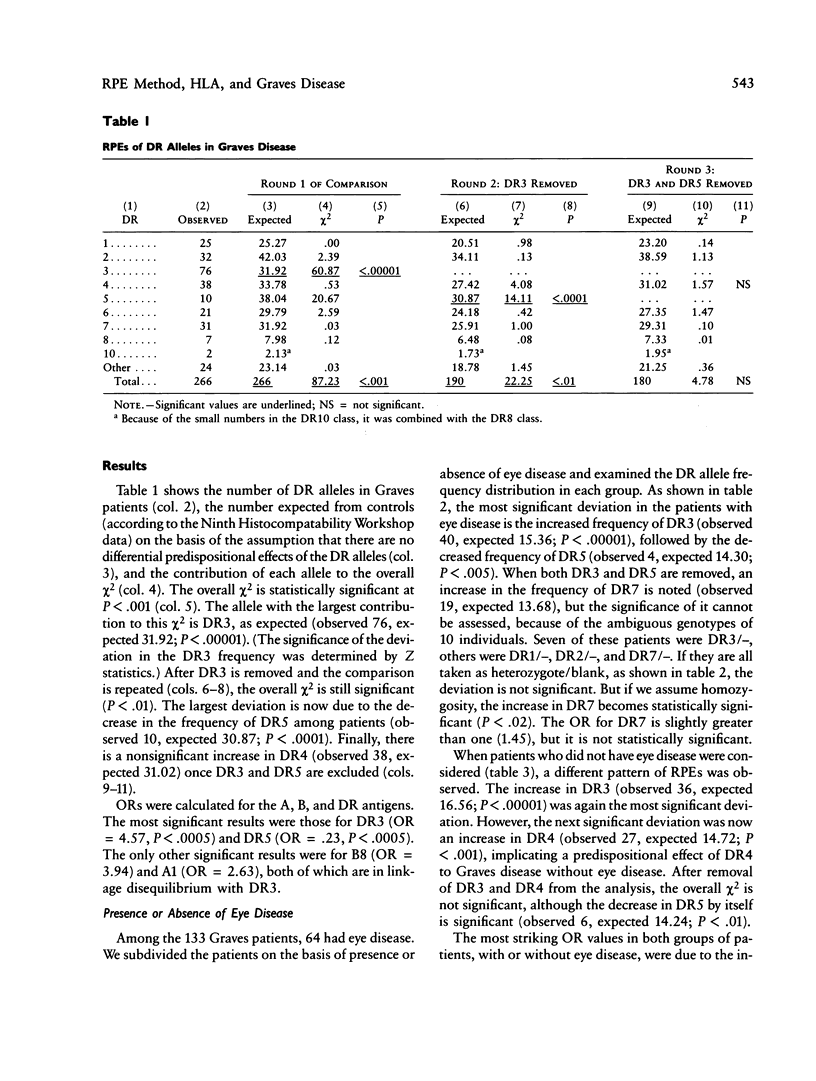
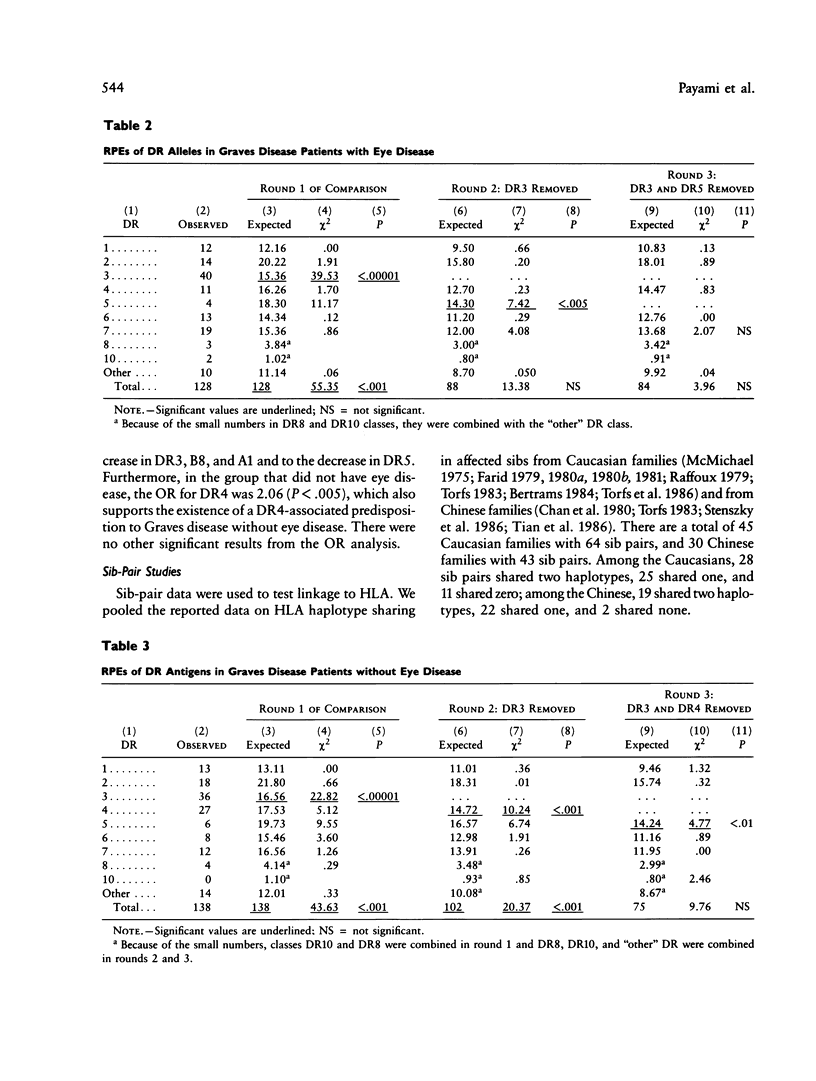
A method is described to reveal the relative predispositional effects (RPEs) (predisposing, protective, or neutral) of the HLA alleles or of any other marker system that is associated with a disease. When the disease is associated with two or more alleles of a locus, the RPE method identifies the associations sequentially according to their strength; thus the problem that a strong association with one allele can create misleading deviations in the frequencies of other alleles is alleviated. Using this method, we have examined the relative effects of HLA-DR alleles in susceptibility to Graves disease in the Caucasian population. The well-established positive association with DR3 was confirmed as the strongest effect. In addition, a negative association was found between DR5 and Graves disease. The reduced frequency of DR5 among patients is statistically significant and is not a result of the increase in DR3. Finally, when patients were divided according to the presence or absence of eye disease, the latter showed a significant increase in the frequency of DR4. With family data, linkage to HLA of Graves disease was established in both Caucasian and Chinese families by the sib-pair method.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allannic H., Fauchet R., Lorcy Y., Heim J., Gueguen M., Leguerrier A. M., Genetet B. HLA and Graves' disease: an association with HLA-DRw3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):863–867. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allannic H., Fauchet R., Lorcy Y., Phengsavath H., Gueguen M., Knoi T. D., Genetet B., Le Gall J. Y. Properdin factor B (Bf) and glyoxalase in Graves' disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Jan;102(1):57–61. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech K., Lumholtz B., Nerup J., Thomsen M., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A., Siersbaek-Nielsen K., Hansen J. M., Larsen J. H. HLA antigens in Graves' disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1977 Nov;86(3):510–516. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0860510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. H., Yeo P. P., Cheah J. S., Lim P. HlA haplotype sharing in affected siblings in multiple case Chinese families with thyrotoxicosis. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Sep;16(3):258–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Larsen B., Payne R., Noel E. P., Sampson L. Polyglandular autoimmune disease and HLA. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Jul;16(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Moens H., Larsen B., Payne R., Saltman K., Fifield F., Ingram D. W. HLA haplotypes in familial Graves' disease. Tissue Antigens. 1980 May;15(5):492–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Sampson L., Noel E. P., Barnard J. M., Mandeville R., Larsen B., Marshall W. H., Carter N. D. A study of human leukocyte D locus related antigens in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):108–113. doi: 10.1172/JCI109263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Thompson C. HLA and autoimmune endocrine disease 1985. Mol Biol Med. 1986 Feb;3(1):85–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E. Some epistatic two-locus models of disease. I. Relative risks and identity-by-descent distributions in affected sib pairs. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 May;33(3):381–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Thomson G., Payami H. The affected sib method. II. The intermediate model. Ann Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;47(Pt 3):225–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1983.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motro U., Thomson G. The affected sib method. I. Statistical features of the affected sib-pair method. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):525–538. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffoux C., Thomas J. L., Leclere J., Streiff F., Hartemann P. Lack of HLA association in a family with a high incidence of hyperthyroidism. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Sep;14(3):274–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleusener H., Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R., Kotulla P., Bogner U., Finke R., Meinhold H., Koppenhagen K., Wenzel K. W. HLA-DR3 and HLA-DR5 associated thyrotoxicosis--two different types of toxic diffuse goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):781–785. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenszky V., Kozma L., Balazs C., Farid N. R. HLA-DR associations with Graves' disease in eastern Hungary. Clin Invest Med. 1983;6(3):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenszky V., Kozma L., Balazś C., Bear J. C., Farid N. R. The role of HLA antigens in the manifestation and course of Graves' disease. Mol Biol Med. 1986 Feb;3(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. HLA DR antigens and susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1309–1317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G., Klitz W., Louis E. J., Lo S. K., Bertrams J., Baur M., Neugebauer M. HLA and IDDM predisposition: new aspects. Genet Epidemiol Suppl. 1986;1:363–368. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370030756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G., Robinson W. P., Kuhner M. K., Joe S., Klitz W. HLA and insulin gene associations with IDDM. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(1):155–160. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G., Robinson W. P., Kuhner M. K., Joe S., MacDonald M. J., Gottschall J. L., Barbosa J., Rich S. S., Bertrams J., Baur M. P. Genetic heterogeneity, modes of inheritance, and risk estimates for a joint study of Caucasians with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;43(6):799–816. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfs C. P., King M. C., Huey B., Malmgren J., Grumet F. C. Genetic interrelationship between insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, the autoimmune thyroid diseases, and rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):170–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


