Abstract
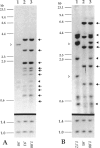
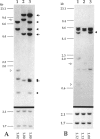
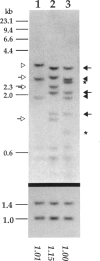
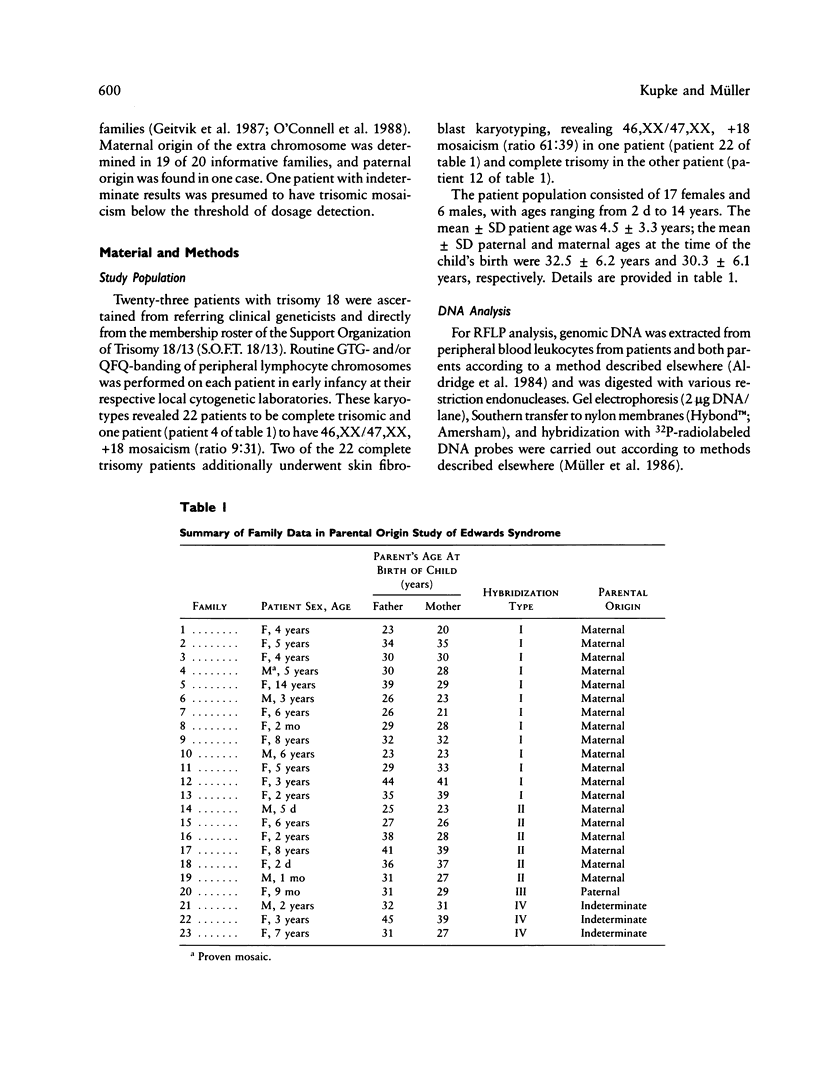
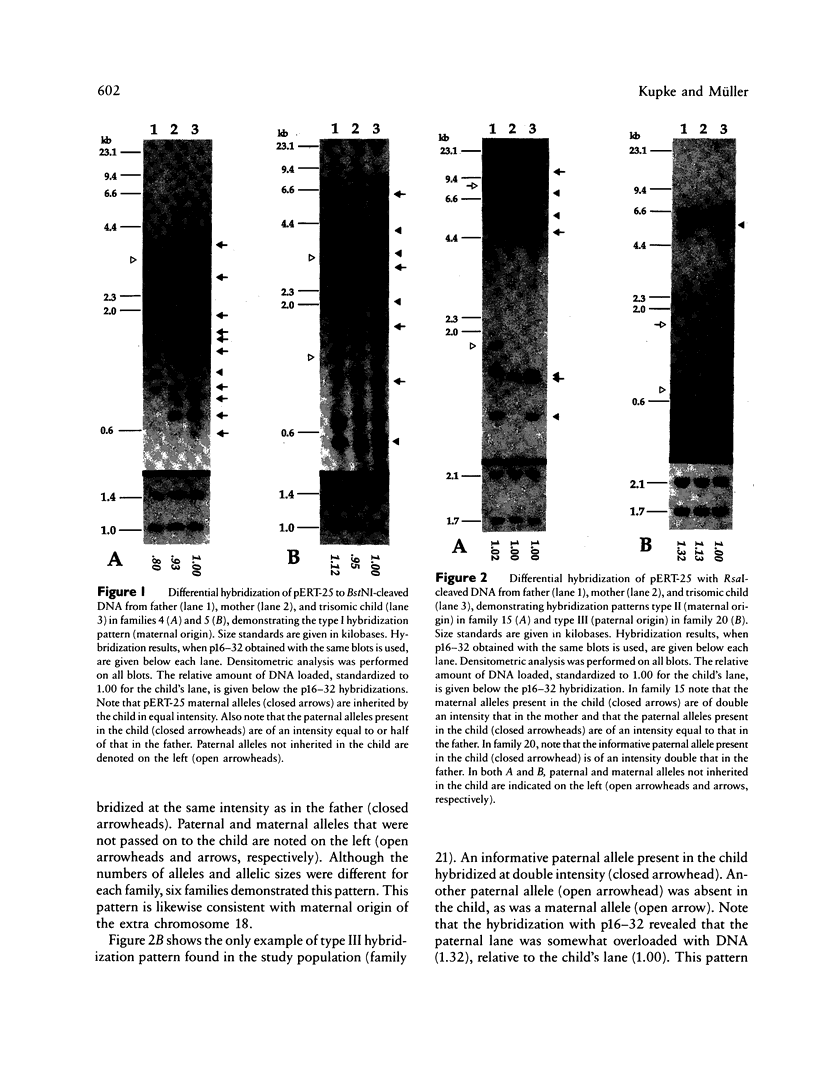
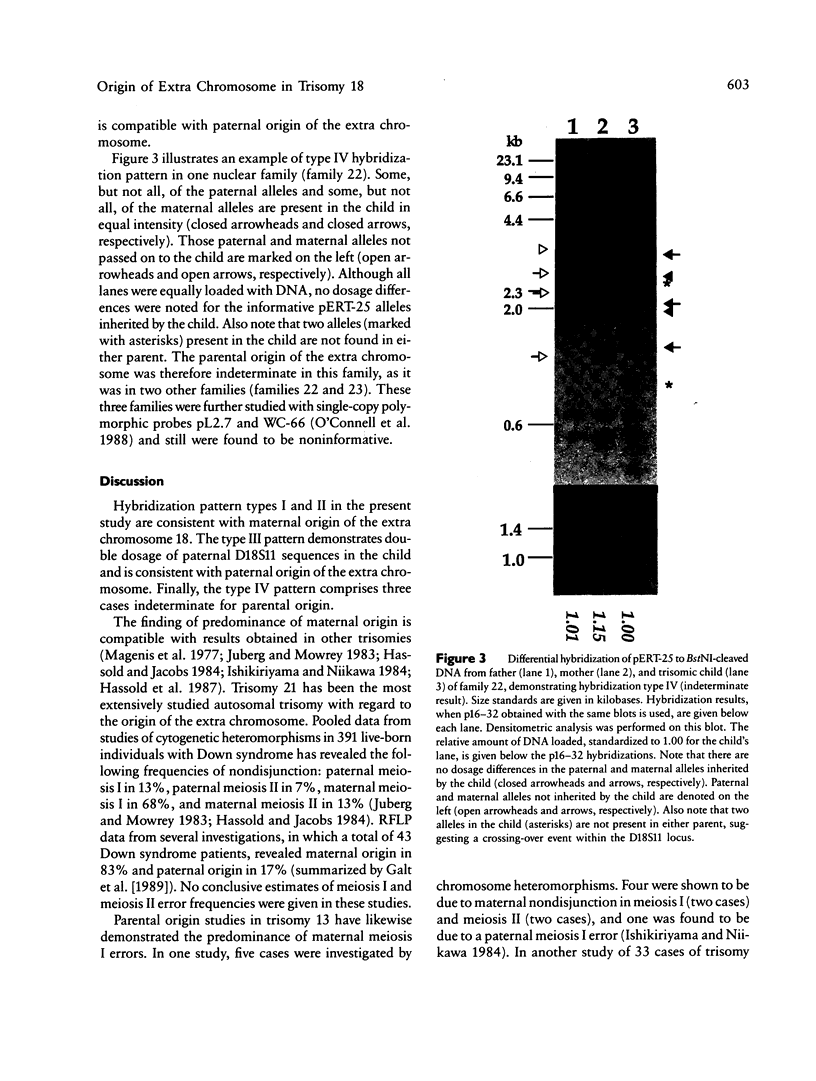
The parental origin of the supernumerary chromosome 18 was investigated by RFLP analysis in 23 individuals with Edwards syndrome. All families were studied with the DNA probe pERT-25, which recognizes a locus of highly polymorphic tandemly repeated DNA sequences on chromosome 18. The extra chromosome was found to be of maternal origin in 19 patients (95%), of paternal origin in one patient (5%), and indeterminate in three patients. In one of the three indeterminate cases, a mosaic, an apparent recombination event had taken place within the pERT-25 locus. The overall high degree of informativeness of pERT-25 illustrates the power of a chromosome-specific variable-number tandem repeat probe (VNTR) in parental origin studies of aneuploidy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Chakravarti A., Warren A. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Wong C., Halloran S. L., Metaxotou C. Reduced recombination rate on chromosomes 21 that have undergone nondisjunction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):185–190. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu A., Verma R. S. The heteromorphic marker on chromosome 18 using restriction endonuclease AluI. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;38(4):549–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. E., Pearn J. H., Bell J., Martin N., Anderson N. G. Survival in trisomy 18. Life tables for use in genetic counselling and clinical paediatrics. Clin Genet. 1985 Jan;27(1):59–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A. The probability of detecting the origin of nondisjunction of autosomal trisomies. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):639–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galt J., Boyd E., Connor J. M., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Isolation of chromosome-21-specific DNA probes and their use in the analysis of nondisjunction in Down syndrome. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):113–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00293885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geitvik G. A., Høyheim B., Gedde-Dahl T., Grzeschik K. H., Lothe R., Tomter H., Olaisen B. The Kidd (JK) blood group locus assigned to chromosome 18 by close linkage to a DNA-RFLP. Hum Genet. 1987 Nov;77(3):205–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00284470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Lalande M., Stroh H., Bruns G., Flint A., Latt S. A. Construction of a chromosome 16-enriched phage library and characterization of several DNA segments from 16p. Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;77(2):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00272372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T. J., Jacobs P. A. Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:69–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T., Jacobs P. A., Leppert M., Sheldon M. Cytogenetic and molecular studies of trisomy 13. J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;24(12):725–732. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.12.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes M. E., Cole J., Palmer C. G., Reed T. Clinical experience with trisomies 18 and 13. J Med Genet. 1978 Feb;15(1):48–60. doi: 10.1136/jmg.15.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Rates of chromosome abnormalities at different maternal ages. Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Sep;58(3):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikiriyama S., Niikawa N. Origin of extra chromosome in Patau syndrome. Hum Genet. 1984;68(3):266–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00418400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juberg R. C., Mowrey P. N. Origin of nondisjunction in trisomy 21 syndrome: all studies compiled, parental age analysis, and international comparisons. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Sep;16(1):111–116. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320160117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh T., Tonoki H., Matsumoto T., Tsukahara M., Niikawa N. Origin of the extra chromosome in trisomy 18. A study on five patients using a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):377–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00282181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T. A prospective psychological and cytogenetic study of three girls with mosaic mongolism. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jul;68(4):593–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb05061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Overton K. M., Chamberlin J., Brady T., Lovrien E. Parental origin of the extra chromosome in Down's syndrome. Hum Genet. 1977 Jun 10;37(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00293766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta L., Shannon R. S., Duckett D. P., Young I. D. Trisomy 18 in a 13 year old girl. J Med Genet. 1986 Jun;23(3):256–257. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.3.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Donlon T. A., Harris P., Rose E., Hoffman E., Bruns G. P., Latt S. A. Highly polymorphic DNA sequences in the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 18. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(1):16–20. doi: 10.1159/000132418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Lalande M., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Moderately repeated DNA sequences specific for the short arm of the human Y chromosome are present in XX males and reduced in copy number in an XY female. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1325–1340. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Sillesen I. Incidence of chromosome aberrations among 11148 newborn children. Humangenetik. 1975 Oct 20;30(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00273626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., Müller U., Lalouel J. M., White R. Twelve loci form a continuous linkage map for human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. G., Towner J. W., Forsman I. Decreasing mosaicism in Down's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1980 May;17(5):335–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]