Abstract
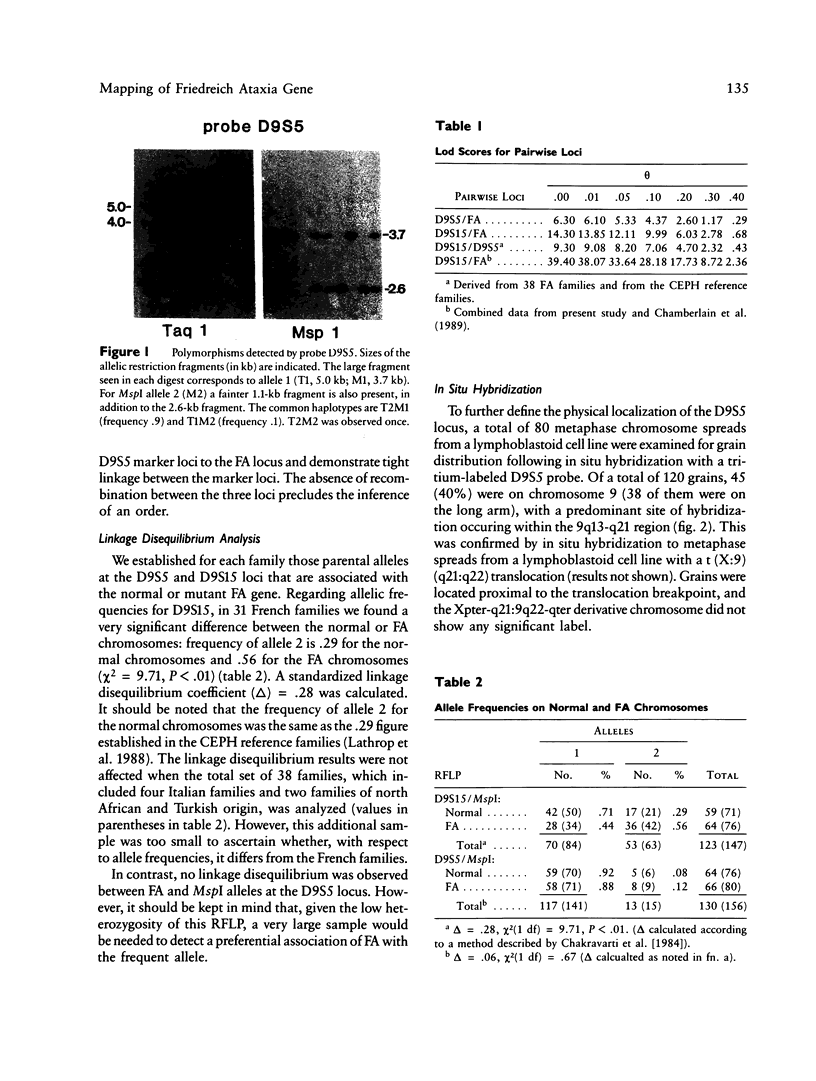
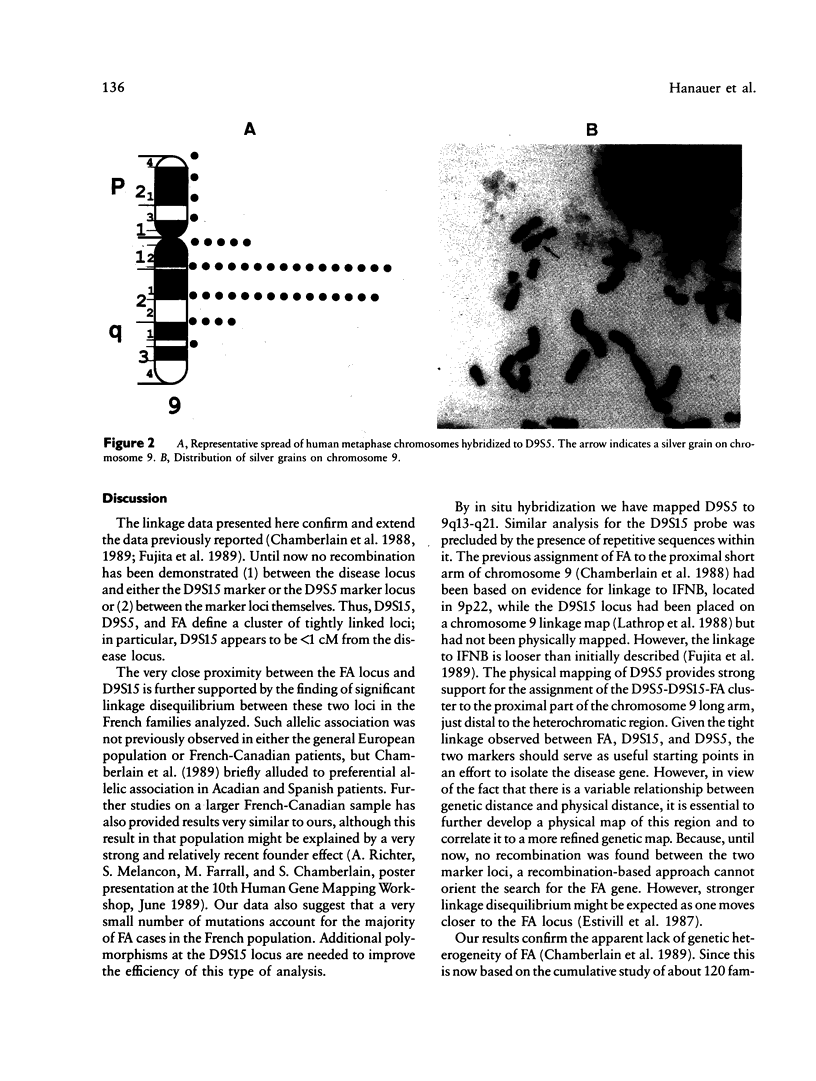
Chamberlain et al. have assigned the gene for Friedreich ataxia (FA), a recessive neurodegenerative disorder, to chromosome 9, and have proposed a regional localization in the proximal short arm (9p22-cen), on the basis of linkage to D9S15 and to interferon-beta (IFNB), the latter being localized in 9p22. We confirmed more recently the close linkage to D9S15 in another set of families but found much looser linkage to IFNB. We also reported another closely linked marker, D9S5. Additional families have now been studied, and our updated lod scores are z = 14.30 at theta = .00 for D9S15-FA linkage and z = 6.30 at theta = .00 for D9S5-FA linkage. Together with the recent data of Chamberlain et al., this shows that D9S15 is very likely within 1 cM of the FA locus. We have found very significant linkage disequilibrium (delta Std = .28, chi 2 = 9.71, P less than .01) between FA and the D9S15 MspI RFLP in French families, which further supports the very close proximity of these two loci. No recombination between D9S5 and D9S15 was found in the FA families or Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain families (z = 9.30 at theta = .00). Thus D9S5, D9S15, and FA define a cluster of tightly linked loci. We have mapped D9S5 by in situ hybridization to 9q13-q21, and, accordingly, we assign the D9S5, D9S15, and FA cluster to the proximal part of chromosome 9 long arm, close to the heterochromatic region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbeau A. The Quebec Cooperative Study of Friedreich's Ataxia: 1974-1984--10 years of research. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Nov;11(4 Suppl):646–660. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100035228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanella G., Filla A., DeFalco F., Mansi D., Durivage A., Barbeau A. Friedreich's ataxia in the south of Italy: a clinical and biochemical survey of 23 patients. Can J Neurol Sci. 1980 Nov;7(4):351–357. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100022873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Nakamura Y., Krapcho K., Fujimoto E., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence pMCT112 on chromosome 9q (D9S15). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10614–10614. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10614-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain S., Shaw J., Rowland A., Wallis J., South S., Nakamura Y., von Gabain A., Farrall M., Williamson R. Mapping of mutation causing Friedreich's ataxia to human chromosome 9. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):248–250. doi: 10.1038/334248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain S., Shaw J., Wallis J., Rowland A., Chow L., Farrall M., Keats B., Richter A., Roy M., Melancon S. Genetic homogeneity at the Friedreich ataxia locus on chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;44(4):518–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Farrall M., Scambler P. J., Bell G. M., Hawley K. M., Lench N. J., Bates G. P., Kruyer H. C., Frederick P. A., Stanier P. A candidate for the cystic fibrosis locus isolated by selection for methylation-free islands. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):840–845. doi: 10.1038/326840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita R., Agid Y., Trouillas P., Seck A., Tommasi-Davenas C., Driesel A. J., Olek K., Grzeschik K. H., Nakamura Y., Mandel J. L. Confirmation of linkage of Friedreich ataxia to chromosome 9 and identification of a new closely linked marker. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):110–111. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy G., Barbeau A., Breton G., Lemieux B., Aube M., Leger C., Bouchard J. P. Clinical description and roentgenologic evaluation of patients with Friedreich's ataxia. Can J Neurol Sci. 1976 Nov;3(4):279–286. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100025464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Franchini G., Love J., Simon M. I., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Chromosomal sublocalization of human c-myb and c-fes cellular onc genes. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):169–171. doi: 10.1038/304169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop M., Nakamura Y., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Woodward S., Lalouel J. M., White R. A mapped set of genetic markers for human chromosome 9. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Philip N., Passage E., Moisan J. P., Mandel J. L., Mattei J. F. DNA probe localization at 18p113 band by in situ hybridization and identification of a small supernumerary chromosome. Hum Genet. 1985;69(3):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00293038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Wolff S. New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):156–158. doi: 10.1038/251156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skre H. Friedreich's ataxia in Western Norway. Clin Genet. 1975 Apr;7(4):287–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb00331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Harding A. E., Baraitser M., Bravery M. B. Intrafamilial correlation in Friedreich's ataxia. Clin Genet. 1981 Dec;20(6):419–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]