Abstract
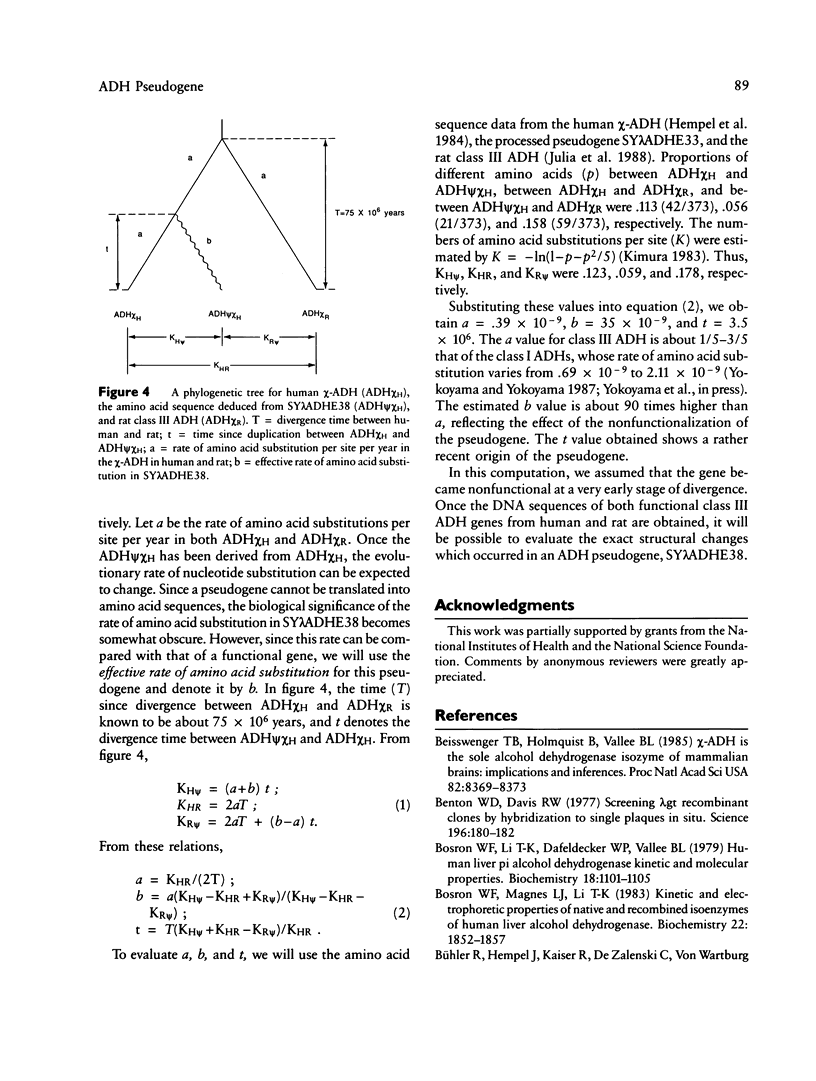
Current information on the molecular structure of human alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) genes is fragmentary. To characterize all ADH genes, we have isolated 63 ADH clones from human genomic libraries made from one individual. Fifty-nine clones have been classified into five previously known loci: ADH1 (18 clones), ADH2 (20 clones), and ADH3 class I (16 clones), ADH4 class II (4 clones), and ADH5 class III (1 clone). Sequencing of one of the remaining four unclassified clones, SY lambda ADHE38, about 1.1 kb in length, shows no introns and three frameshift mutations in the coding region, with a total of 10 internal termination codons. When its deduced amino acid sequence was compared with those of the class I, class II, and class III ADHs, the proportions of identical amino acids were 56.7%, 55.5%, and 88.7%, respectively, suggesting that the processed pseudogene was derived from an ADH5 gene. The duplication event seems to have occurred about 3.5 million years ago, and the pseudogene has undergone a rapid change since then.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beisswenger T. B., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. chi-ADH is the sole alcohol dehydrogenase isozyme of mammalian brains: implications and inferences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8369–8373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosron W. F., Li T. K., Dafeldecker W. P., Vallee B. L. Human liver pi-alcohol dehydrogenase: kinetic and molecular properties. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1101–1105. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosron W. F., Magnes L. J., Li T. K. Kinetic and electrophoretic properties of native and recombined isoenzymes of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1852–1857. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler R., Hempel J., Kaiser R., de Zalenski C., von Wartburg J. P., Jörnvall H. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. 2. The primary structure of the gamma 1 protein chain. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dafeldecker W. P., Vallee B. L. Organ-specific human alcohol dehydrogenase: isolation and characterization of isozymes from testis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1056–1063. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90358-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Smith M., Bilanchone V., Hatfield G. W. Molecular analysis of the human class I alcohol dehydrogenase gene family and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2027–2033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Bühler R., Kaiser R., Holmquist B., de Zalenski C., von Wartburg J. P., Vallee B., Jörnvall H. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. 1. The primary structure of the beta 1 beta 1 isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög J. O., von Bahr-Lindström H., Hedén L. O., Holmquist B., Larsson K., Hempel J., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H. Structure of the class II enzyme of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: combined cDNA and protein sequence determination of the pi subunit. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1926–1932. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta T., Szeto S., Yoshida A. Three human alcohol dehydrogenase subunits: cDNA structure and molecular and evolutionary divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):634–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julià P., Pareś X., Jörnvall H. Rat liver alcohol dehydrogenase of class III. Primary structure, functional consequences and relationships to other alcohol dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;172(1):73–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser R., Holmquist B., Hempel J., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H. Class III human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: a novel structural type equidistantly related to the class I and class II enzymes. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1132–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Polymorphism of DNA sequence adjacent to human beta-globin structural gene: relationship to sickle mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5631–5635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keung W. M. A genuine organ specific alcohol dehydrogenase from hamster testes: isolation, characterization and developmental changes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo Y., Yokoyama R., Yokoyama S. The genes for human alcohol dehydrogenases beta 1 and beta 2 differ by only one nucleotide. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):317–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo Y., Yokoyama S. Molecular structure of the human alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modiano G., Battistuzzi G., Motulsky A. G. Nonrandom patterns of codon usage and of nucleotide substitutions in human alpha- and beta-globin genes: an evolutionary strategy reducing the rate of mutations with drastic effects? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1110–1114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Gallwitz D. Structure of a human beta-actin-related pseudogene which lacks intervening sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7843–7849. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder A., Leder P. Unusual alpha-globin-like gene that has cleanly lost both globin intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savtchenko E. S., Schiff T. A., Jiang C. K., Freedberg I. M., Blumenberg M. Embryonic expression of the human 40-kD keratin: evidence from a processed pseudogene sequence. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):630–637. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C. Processed pseudogenes for rat cytochrome c are preferentially derived from one of three alternate mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2279–2288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. Genetics of human alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases. Adv Hum Genet. 1986;15:249–290. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8356-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Hopkinson D. A., Harris H. Alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes in adult human stomach and liver: evidence for activity of the ADH 3 locus. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;35(3):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Goldberg G. I., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. A mouse alpha-globin-related pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):222–226. doi: 10.1038/286222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F. Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:253–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner F. W., Parés X., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L. Physical and enzymatic properties of a class III isozyme of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: chi-ADH. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2193–2199. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cowan N. J. Diverse mechanisms in the generation of human beta-tubulin pseudogenes. Science. 1982 Aug 6;217(4559):549–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6178164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cripe T. P., Gwo-Shu Lee M., Cowan N. J. Evidence that a human beta-tubulin pseudogene is derived from its corresponding mRNA. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):83–84. doi: 10.1038/297083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S. J., Bosron W. F., Magnes L. J., Li T. K. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: purification and kinetic characterization of the beta 2 beta 2, beta 2 beta 1, alpha beta 2, and beta 2 gamma 1 "Oriental" isoenzymes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5847–5853. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., Yokoyama R. Molecular evolution of mammalian class I alcohol dehydrogenase. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Sep;4(5):504–513. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



