Abstract
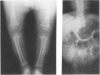
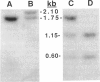
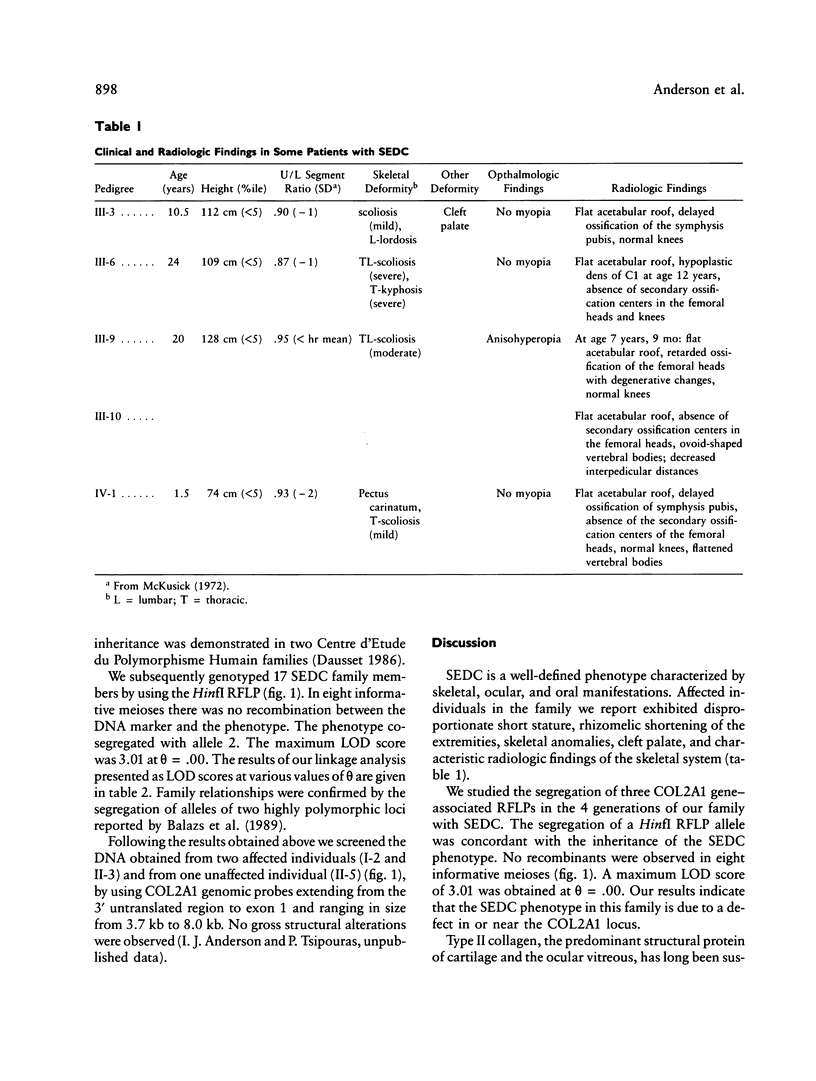
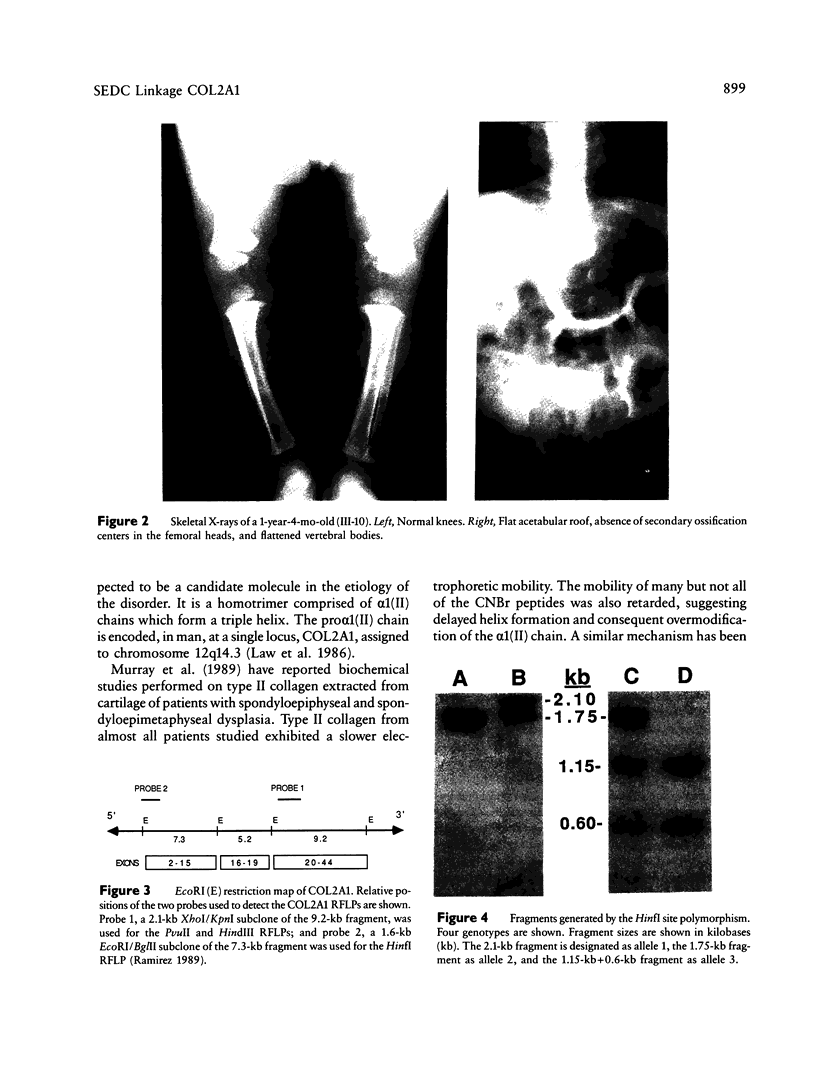
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita (SEDC) is an autosomal dominantly inherited chondrodysplasia characterized by disproportionate short stature (short trunk), abnormal epiphyses, and flattened vertebral bodies. Manifestations are present at birth. We ascertained a 4-generation family exhibiting the clinical manifestations of the disorder. Previous evidence suggesting defects of type II collagen associated with the SEDC phenotype led us to genotype the family for various COL2A1 gene-associated RFLPs. A total of 17 affected and unaffected members of this family were studied. The family was informative for a recently discovered HinfI RFLP. No recombinants between the marker and the phenotype were found in eight informative meioses. A maximum LOD score of 3.01 was obtained at a recombination fraction of .00. Our results indicate that the SEDC phenotype in this family is caused by mutations in or very close to the COL2A1 locus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balazs I., Baird M., Clyne M., Meade E. Human population genetic studies of five hypervariable DNA loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;44(2):182–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Bonadio J. F., Steinmann B. Osteogenesis imperfecta: update and perspective. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Feb;17(2):429–435. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J. Le centre d'étude du polymorphisme humain. Presse Med. 1986 Oct 18;15(36):1801–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Upton M. P., Shapiro F. D., Wilkinson R. H., Vawter G. F. Nonexpression of cartilage type II collagen in a case of Langer-Saldino achondrogenesis. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;39(1):52–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francomano C. A., Liberfarb R. M., Hirose T., Maumenee I. H., Streeten E. A., Meyers D. A., Pyeritz R. E. The Stickler syndrome: evidence for close linkage to the structural gene for type II collagen. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. R., Friedmann A. I., Maroteaux P., Glen-Bott A. M., Mittwoch U. Dysplasia spondyloepiphysaria congenita and related generalized skeletal dysplasias among children with severe visual handicaps. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Aug;44(236):490–498. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.236.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Hollister D. W. Type II achondrogenesis-hypochondrogenesis: identification of abnormal type II collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;43(6):904–913. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Keene D. R., Blank E., Hori H., Sakai L. Y., Sherwin L. A., Hollister D. W. Type II achondrogenesis-hypochondrogenesis: morphologic and immunohistopathologic studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;43(6):894–903. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGER L. O., Jr SPONDYLOEPIPHYSIAL DYSPLASIA TARDA. HEREDITARY CHONDRODYSPLASIA WITH CHARACTERISTIC VERTEBRAL CONFIGURATION IN THE ADULT. Radiology. 1964 May;82:833–839. doi: 10.1148/82.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. L., Tung L., Morse H. G., Berger R., Jones C., Cheah K. S., Solomon E. The human type II collagen gene (COL2A1) assigned to 12q14.3. Ann Hum Genet. 1986 May;50(Pt 2):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1986.tb01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Vissing H., Ramirez F., Rogers D., Rimoin D. Identification of the molecular defect in a family with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):978–980. doi: 10.1126/science.2543071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray L. W., Bautista J., James P. L., Rimoin D. L. Type II collagen defects in the chondrodysplasias. I. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasias. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):5–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray T. G., Green W. R., Maumenee I. H., Kopits S. E. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita. Light and electron microscopic studies of the eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985 Mar;103(3):407–411. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050030103032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Pidoux I., Reiner A., Rosenberg L., Hollister D., Murray L., Rimoin D. Kniest dysplasia is characterized by an apparent abnormal processing of the C-propeptide of type II cartilage collagen resulting in imperfect fibril assembly. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):579–589. doi: 10.1172/JCI113356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roaf R., Longmore J. B., Forrester R. M. A childhood syndrome of bone dysplasia, retinal detachment and deafness. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1967 Aug;9(4):464–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1967.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spranger J. W., Langer L. O., Jr Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita. Radiology. 1970 Feb;94(2):313–322. doi: 10.1148/94.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom C. M. A three allele restriction fragment length polymorphism within the human Col2A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9077–9077. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Smith R., Vipond S., Paterson C., Cheah K., Solomon E. Exclusion of the alpha 1(II) cartilage collagen gene as the mutant locus in type IA osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1985 Jun;22(3):187–191. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.3.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]