Abstract
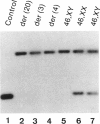
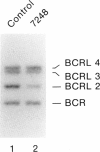
DiGeorge Syndrome (DGS) is often associated with loss of a portion of the proximal long arm of chromosome 22. Using a probe for the D22S9 locus, we have examined DNA from eight DGS cell lines and from one balanced-translocation carrier parent of a DGS proband. The D22S9 locus is deleted in four DGS patients, with deletion of 22pter----q11 because of unbalanced translocation. The locus is not deleted from three DGS probands with normal chromosomes or from two DGS probands with interstitial deletions of 22q11. The interstitial deletion DGS probands are also heterozygous for D22S43, another proximal 22q11 locus. This suggests that D22S9 and D22S43 are in a flanking but not critical region for DGS. One of the interstitial deletion DGS probands is monosomic for BCRL2 but has two copies of the flanking BCRL4 and BCR loci. Thus, the region critical to DGS (DGCR) may be in proximity to the BCRL2 locus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arinami T., Kondo I., Hamaguchi H., Nakajima S. Multifocal meningiomas in a patient with a constitutional ring chromosome 22. J Med Genet. 1986 Apr;23(2):178–180. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.2.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augusseau S., Jouk S., Jalbert P., Prieur M. DiGeorge syndrome and 22q11 rearrangements. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):206–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00282098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Stier R., Böhm N., Adlung A., Hameister H. Partial monosomy 22pter leads to q11 in a newborn with the clinical features of trisomy 13 syndrome. Ann Genet. 1980;23(4):244–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen P., Pabst H., Berry D., Collins-Nakai R., Hoo J. J. Thymus deficiency in an infant with a chromosome t(18;22)(q12.2;p11.2)pat rearrangement. Clin Genet. 1986 Feb;29(2):174–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M., Canaani E., Emanuel B. S. Linear order of the four BCR-related loci in 22q11. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):168–171. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budarf M., Sellinger B., Griffin C., Emanuel B. S. Comparative mapping of the constitutional and tumor-associated 11;22 translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):128–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Aronson M. M., Emanuel B. S. In situ hybridization and translocation breakpoint mapping. II. Two unusual t(21;22) translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(3):173–178. doi: 10.1159/000132130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. An improved method for G-banding chromosomes after in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):308–309. doi: 10.1159/000132079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Beckwith J. B., Mancer J. F., Tenckhoff L. The spectrum of the DiGeorge syndrome. J Pediatr. 1979 Jun;94(6):883–890. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Huebner K., Isobe M., Fainstain E., Lifshitz B., Shtivelman E., Canaani E. Mapping of four distinct BCR-related loci to chromosome region 22q11: order of BCR loci relative to chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia breakpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7174–7178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns W. B., Stratton R. F., Parke J. T., Greenberg F., Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Miller-Dieker syndrome: lissencephaly and monosomy 17p. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):552–558. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed M. J., Robertson J., Beck J. S., Cater J. I., Bose B., Madlom M. M. Features of di George syndrome in a child with 45,XX,-3,-22,+der(3),t(3;22)(p25;q11). J Med Genet. 1987 Apr;24(4):225–227. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.4.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah L. M., de Nazareth H. R., Dolnikoff M., Delascio D. Balanced homologous translocation t(22q22q) in a phenotypically normal woman with repeated spontaneous abortions. Humangenetik. 1975 Aug 25;28(4):357–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00284812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Crowder W. E., Paschall V., Colon-Linares J., Lubianski B., Ledbetter D. H. Familial DiGeorge syndrome and associated partial monosomy of chromosome 22. Hum Genet. 1984;65(4):317–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00291554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Elder F. F., Haffner P., Northrup H., Ledbetter D. H. Cytogenetic findings in a prospective series of patients with DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):605–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter A. G., Ray M., Wang H. S., Thompson D. R. Phenotypic correlations in patients with ring chromosome 22. Clin Genet. 1977 Oct;12(4):239–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I., Zackai E. H., Emanuel B. S., Kistenmacher M., Greenberg F., Punnett H. H. The association of the DiGeorge anomalad with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkels V. G., Hustinx T. W., Scheres J. M. Habitual abortion and translocation (22q;22q): unexpected transmission from a mother to her phenotypically normal daughter. Clin Genet. 1980 Dec;18(6):456–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb01794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELE K. P., PENROSE L. S., STALLARD H. B. CHROMOSOME DELETION IN A CASE OF RETINOBLASTOMA. Ann Hum Genet. 1963 Nov;27:171–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1963.tb00209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Opitz J. M. The DiGeorge anomaly as a developmental field defect. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1986;2:113–127. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer L. O., Jr, Krassikoff N., Laxova R., Scheer-Williams M., Lutter L. D., Gorlin R. J., Jennings C. G., Day D. W. The tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome with exostoses (or Langer-Giedion syndrome): four additional patients without mental retardation and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Sep;19(1):81–112. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Mascarello J. T., Riccardi V. M., Harper V. D., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J. Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: a follow-up report of 40 cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):278–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz B., Fainstein E., Marcelle C., Shtivelman E., Amson R., Gale R. P., Canaani E. bcr genes and transcripts. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarello J. T., Bastian J. F., Jones M. C. Interstitial deletion of chromosome 22 in a patient with the DiGeorge malformation sequence. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Jan;32(1):112–114. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid H. E., Duncan A. M., Brasch K. R., Holden J. J., Magenis E., Sheehy R., Burn J., Kardon N., Noel B., Schinzel A. Characterization of the supernumerary chromosome in cat eye syndrome. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.3961499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C. G., Schwartz S., Hodes M. E. Transmission of a balanced homologous t(22q;22q) translocation from mother to normal daughter. Clin Genet. 1980 Jun;17(6):418–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M., Sujansky E., Smith A. C., Francke U. Chromosomal imbalance in the Aniridia-Wilms' tumor association: 11p interstitial deletion. Pediatrics. 1978 Apr;61(4):604–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. B., Jr DiGeorge's or the III-IV pharyngeal pouch syndrome: pathology and a theory of pathogenesis. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1975;2:173–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Haines J. L., Bazanowski A., Colella-Crowley A., Trofatter J. A., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of the long arm of human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A. Microdeletion syndromes, balanced translocations, and gene mapping. J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;25(7):454–462. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.7.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. F., Dobyns W. B., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. New chromosomal syndrome: Miller-Dieker syndrome and monosomy 17p13. Hum Genet. 1984;67(2):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00273000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Herva R., Koivisto M., Aula P. A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]