Abstract
Fundamental to maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening is the clinical utility of the laboratory report. It follows that the scientific form of expression in that report is vital. Professional societies concur that patient-specific risk reporting is the preferred form. However, some intermediate steps being taken to calculate patient-specific risks are invalid because of the erroneous assumption that multiples of the median (MoMs) represent an interlaboratory common currency. The numerous methods by which MoMs may be calculated belie the foregoing assumption.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. J., Jr, Windham G. C., James L. M., Greenberg F., Clayton-Hopkins J. A., Reimer C. B., Oakley G. P., Jr Clinical interpretation of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein concentrations. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Feb 1;148(3):241–254. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
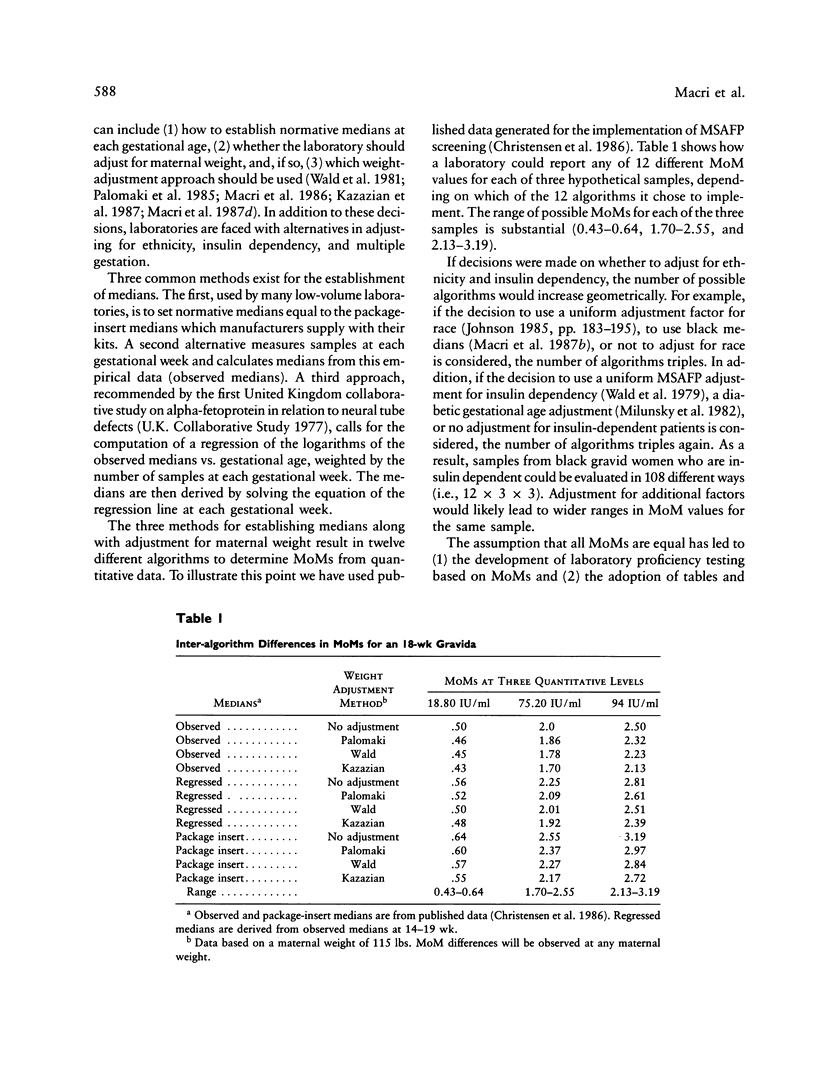
- Christensen R. L., Rea M. R., Kessler G., Crane J. P., Valdes R., Jr Implementation of a screening program for diagnosing open neural tube defects: selection, evaluation, and utilization of alpha-fetoprotein methodology. Clin Chem. 1986 Oct;32(10):1812–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Belsky R., Greb A., Dvorin E., Drugan A. Wide variation in maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein reports in one metropolitan area: concerns for the quality of prenatal testing. Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Sep;72(3 Pt 1):342–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Variability in predicted rates of Down syndrome associated with elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in older women. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;43(2):160–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian L. C., Niebyl J. R., Joseph J. M. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening: effects of weight adjustment. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Sep;157(3):782–784. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri J. N. Critical issues in prenatal maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening for genetic anomalies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Aug;155(2):240–246. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90798-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri J. N., Kasturi R. V., Hu M. G., Krantz D. A., Douros T. J., Sajda P., Cook E. J. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening. III. Pitfalls in evaluating black gravid women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Oct;157(4 Pt 1):820–822. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri J. N., Kasturi R. V., Krantz D. A., Hu M. G. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening. II. Pitfalls in low-volume decentralized laboratory performance. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Mar;156(3):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(87)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macri J. N., Kasturi R. V., Krantz D. A., Koch K. E. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein screening, maternal weight, and detection efficiency. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Oct;155(4):758–760. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(86)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Alpert E., Kitzmiller J. L., Younger M. D., Neff R. K. Prenatal diagnosis of neural tube defects. VIII. The importance of serum alpha-fetoprotein screening in diabetic pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Apr 15;142(8):1030–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palomaki G. E., Haddow J. E. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, age, and Down syndrome risk. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Feb;156(2):460–463. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(87)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palomaki G. E., Knight G. J., Kloza E. M., Haddow J. E. Maternal weight adjustment and low serum alpha-fetoprotein values. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):468–468. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauker S. G., Kassirer J. P. Decision analysis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 29;316(5):250–258. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701293160505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Przybyszewski V. A., Gary E. Results of the Centers for Disease Control experimental proficiency testing survey for serum alpha-fetoprotein. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.100-105.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N. J., Cuckle H., Boreham J., Stirrat G. M., Turnbull A. C. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and diabetes mellitus. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 Feb;86(2):101–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald N., Cuckle H., Boreham J., Terzian E., Redman C. The effect of maternal weight on maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Nov;88(11):1094–1096. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1981.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


