Abstract
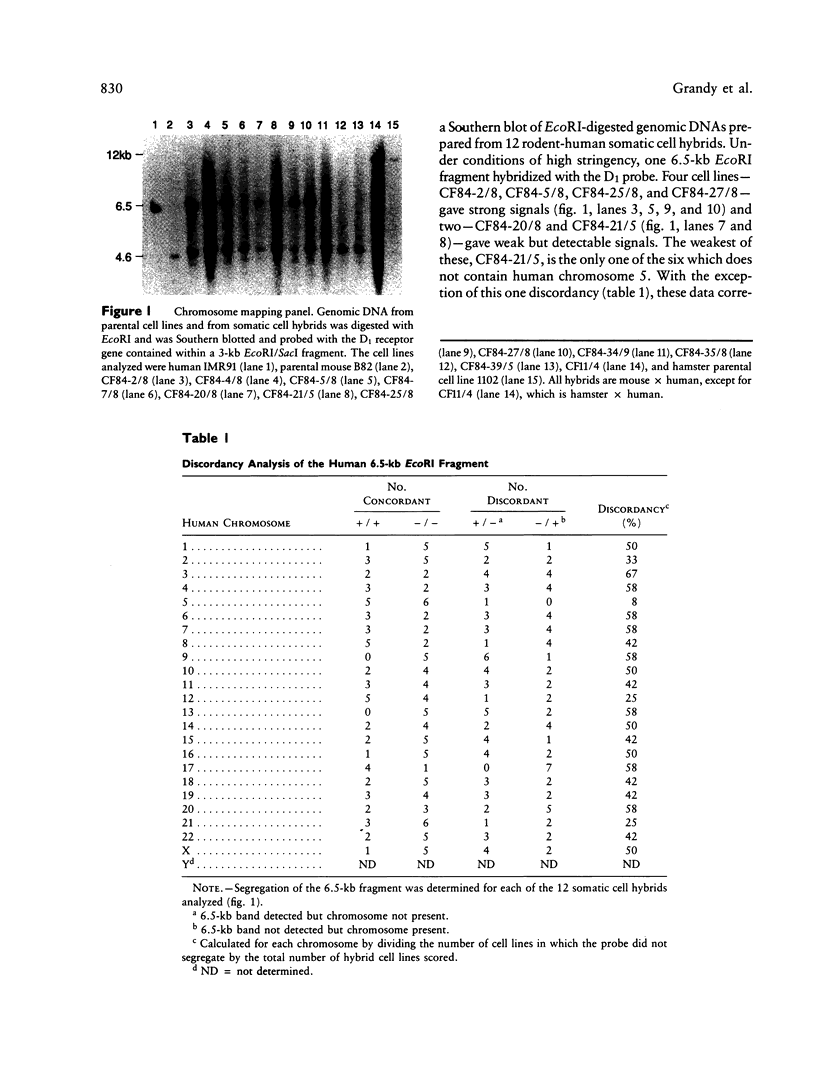
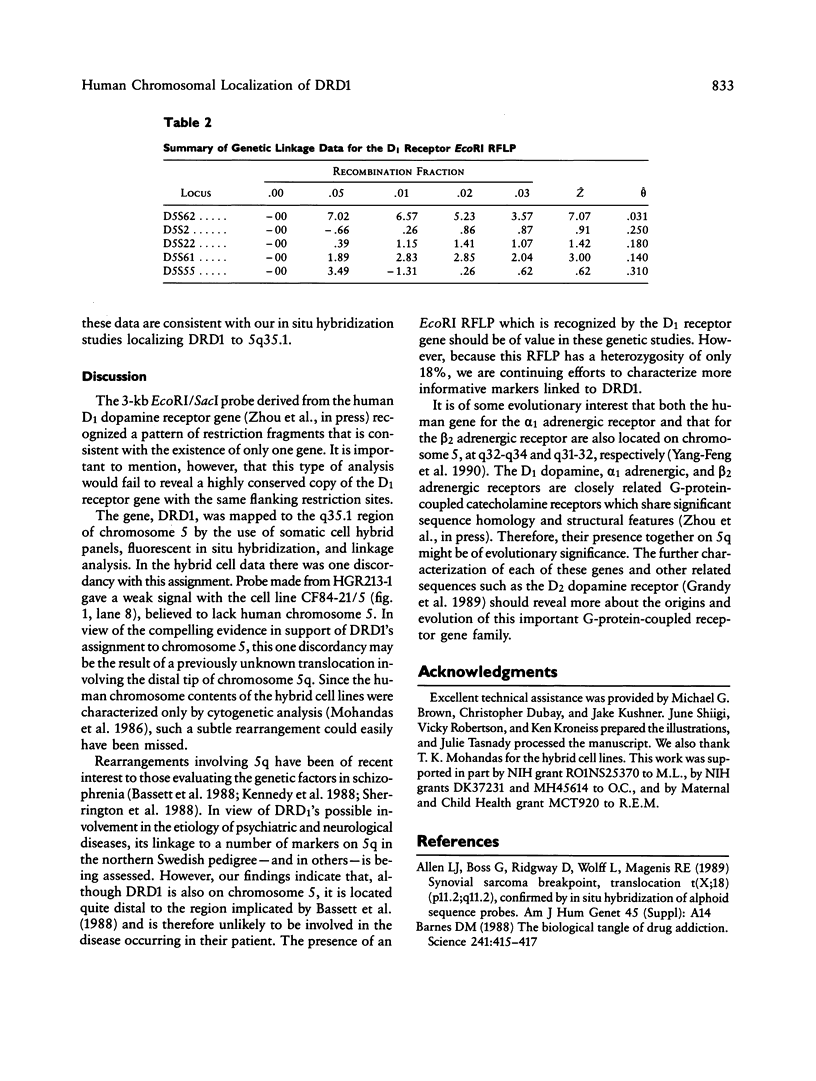
Dopaminergic neurons have been shown to affect voluntary movement, hormone secretion, and emotional tone. Mediating these activities are two receptor subtypes, D1 and D2, which are biochemically and pharmacologically distinct. The D1 subtype, the most abundant form of dopamine receptor in the central nervous system, stimulates adenylate cyclase, modulates D2 receptor activity, regulates neuron growth and differentiation, and mediates several behavioral responses. Recently we reported the cloning of a human D1 dopamine receptor gene (DRD1). High-stringency hybridization of the DRD1 clone to human genomic blots suggests that DRD1 is single copy. When used to probe a Southern blot made with DNAs from a rodent-human somatic cell hybrid panel, DRD1 hybridized to a 6.5-kb EcoRI restriction fragment which was assigned to chromosome 5. Fluorescent in situ hybridization of this gene to human metaphase chromosomes refined the location of DRD1 to 5q35.1. A search for RFLPs associated with DRD1 identified a two-allele EcoRI RFLP, allowing confirmation of DRD1's localization by linkage analysis in Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain families.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. M. The biological tangle of drug addiction. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3393909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett A. S., McGillivray B. C., Jones B. D., Pantzar J. T. Partial trisomy chromosome 5 cosegregating with schizophrenia. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):799–801. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91660-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu M. Clinical importance of D-1 and D-2 receptors. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3 Suppl):402–406. doi: 10.1017/s031716710003780x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. D., Toth-Fejel S. E., Gadi I. K., Litt M., Condon M. R., Kolbe M., Hagen I. K., Kurkinen M., Mackenzie J. W., Magenis E. The genes coding for human pro alpha 1(IV) collagen and pro alpha 2(IV) collagen are both located at the end of the long arm of chromosome 13. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):309–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R., Raisman R., Ploska A., Agid Y. Dopamine D-1 receptor and cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 1987 Oct;49(4):1075–1083. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb09996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D., White F. J. D1 dopamine receptor--the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse. 1987;1(4):347–388. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Burt D. R., Snyder S. H. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976 Apr 30;192(4238):481–483. doi: 10.1126/science.3854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dausset J., Cann H., Cohen D., Lathrop M., Lalouel J. M., White R. Centre d'etude du polymorphisme humain (CEPH): collaborative genetic mapping of the human genome. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):575–577. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90491-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandy D. K., Litt M., Allen L., Bunzow J. R., Marchionni M., Makam H., Reed L., Magenis R. E., Civelli O. The human dopamine D2 receptor gene is located on chromosome 11 at q22-q23 and identifies a TaqI RFLP. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):778–785. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B., Ott J., Conneally M. Report of the committee on linkage and gene order. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):459–502. doi: 10.1159/000132805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. L., Giuffra L. A., Moises H. W., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Pakstis A. J., Kidd J. R., Castiglione C. M., Sjogren B., Wetterberg L., Kidd K. K. Evidence against linkage of schizophrenia to markers on chromosome 5 in a northern Swedish pedigree. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):167–170. doi: 10.1038/336167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankford K. L., DeMello F. G., Klein W. L. D1-type dopamine receptors inhibit growth cone motility in cultured retina neurons: evidence that neurotransmitters act as morphogenic growth regulators in the developing central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4567–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4567-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T., Seeman P., Rajput A., Farley I. J., Hornykiewicz O. Receptor basis for dopaminergic supersensitivity in Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):59–61. doi: 10.1038/273059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Wasmuth J., Edwards P., Lusis A. J. Assignment of human 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene to q13----q23 region of chromosome 5. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jan;12(1):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01560731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Synder S. H. Relationship of neuroleptic drug effects at brain dopamine, serotonin, alpha-adrenergic, and histamine receptors to clinical potency. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Dec;137(12):1518–1522. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.12.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer D. Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):190–193. doi: 10.1159/000131482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Lee T. Antipsychotic drugs: direct correlation between clinical potency and presynaptic action on dopamine neurons. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1217–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.1145194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Ulpian C., Bergeron C., Riederer P., Jellinger K., Gabriel E., Reynolds G. P., Tourtellotte W. W. Bimodal distribution of dopamine receptor densities in brains of schizophrenics. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.6147018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Brynjolfsson J., Petursson H., Potter M., Dudleston K., Barraclough B., Wasmuth J., Dobbs M., Gurling H. Localization of a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 5. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):164–167. doi: 10.1038/336164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. R., Bergstrom D. A., Carlson J. H., Chase T. N., Braun A. R. D1 dopamine receptor activation required for postsynaptic expression of D2 agonist effects. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.2953072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Park C., Ferrell R. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 5. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):137–148. doi: 10.1159/000132789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann G. D. Note on an abnormality of the operator for the structural gene of the dopamine D1 receptor as a possible partial cause of schizophrenia. J Theor Biol. 1986 Jun 7;120(3):277–283. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Xue F. Y., Zhong W. W., Cotecchia S., Frielle T., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Francke U. Chromosomal organization of adrenergic receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1516–1520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]