Abstract
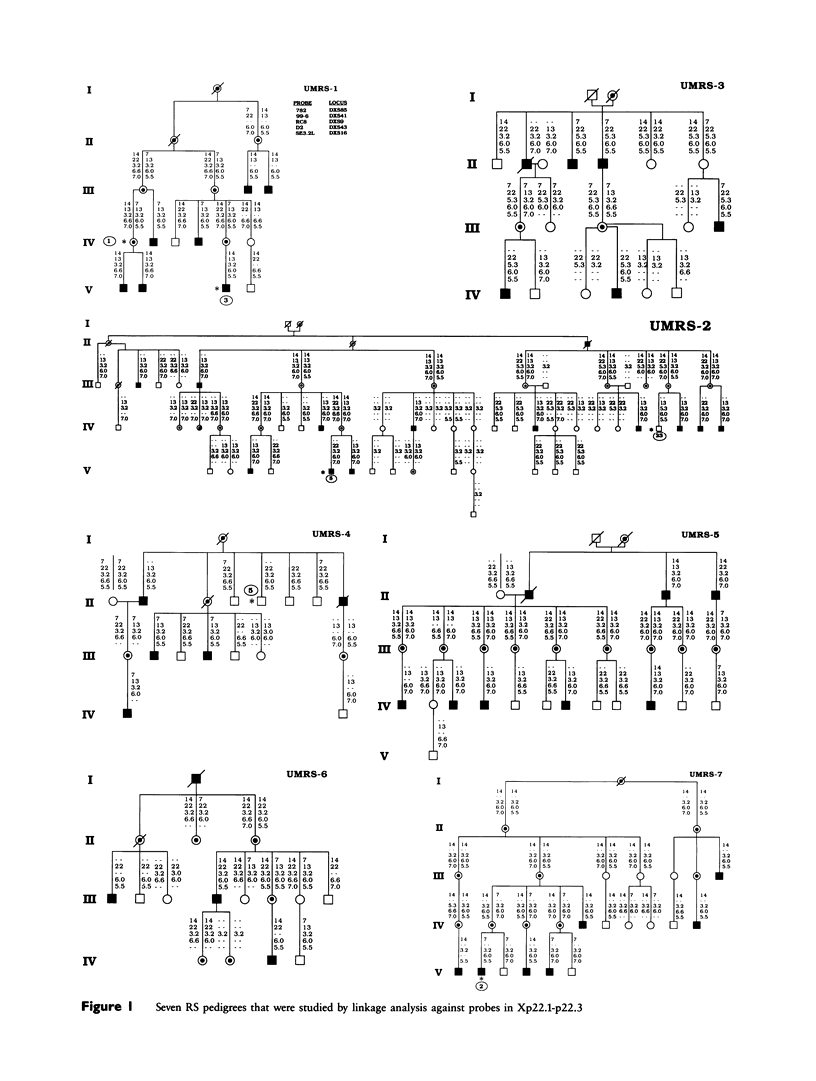
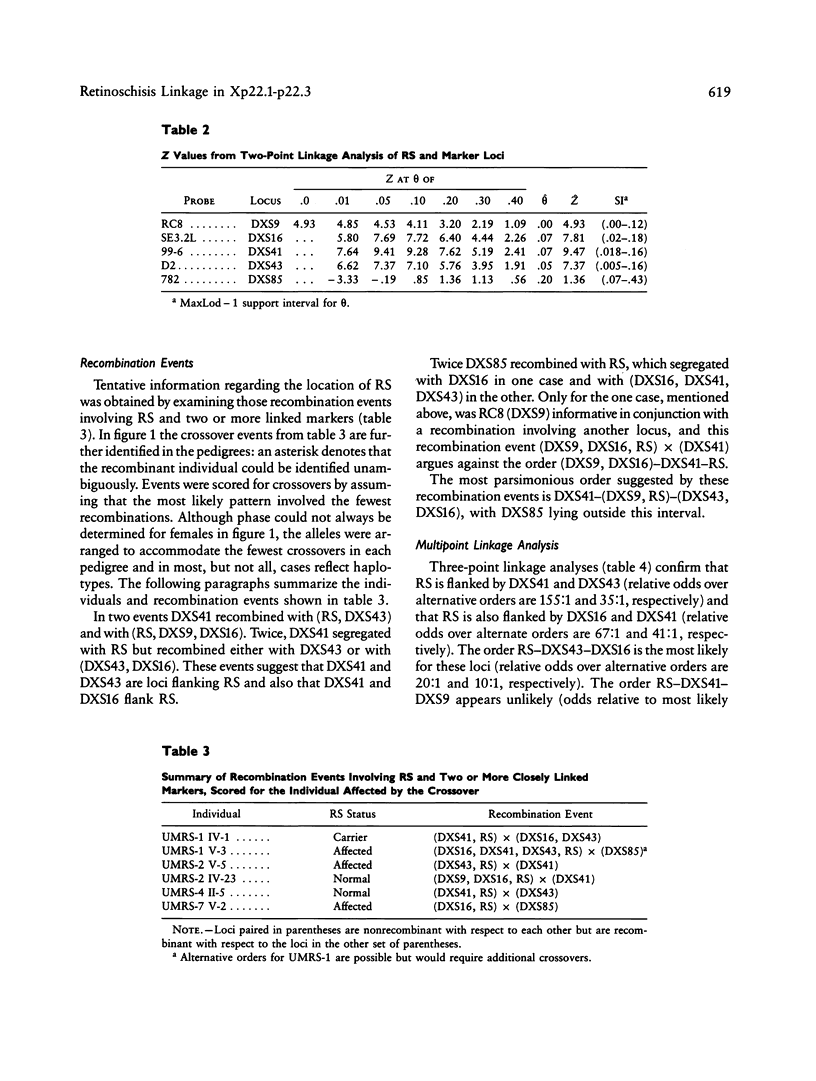
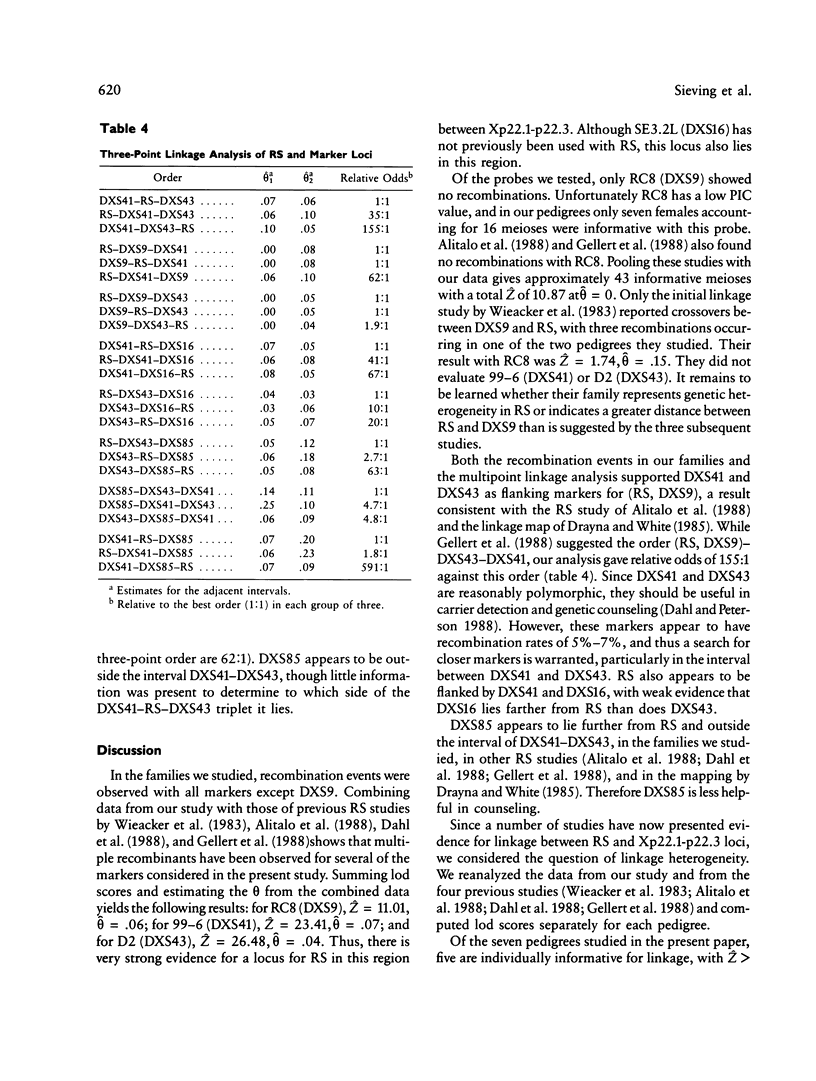
Linkage analysis was performed to evaluate the relationship between the locus for X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (RS) and five X-chromosomal markers-RC8 (DXS9), SE3.2L (DXS16), 99-6 (DXS41), D2 (DXS43), and 782 (DXS85)-all mapped to the interval Xp22.1-p22.3. Seven U.S. families with 56 affected males were studied. No recombinants were found between RS and DXS9 with a maximum lod score (Z) of 4.93 at a recombination fraction of zero. Obligate recombinants were found for RS with DXS16, DXS41, DXS43, and DXS85. Multipoint linkage analysis and consideration of recombination events within pedigrees suggest that DXS41 and DXS43, and also DXS41 and DXS16, flank RS and that DXS85 lies outside the interval DXS41-DXS43. Our pedigrees provide no evidence for genetic heterogeneity of RS, with five of our families individually showing evidence of linkage. (Z greater than 2.0) to the least one of these probes from Xp22.1-p22.3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo T., Forsius H., Kärnä J., Frants R. R., Eriksson A. W., Wood S., Kruse T. A., de la Chapelle A. Linkage relationships and gene order around the locus for X-linked retinoschisis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):476–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Willard H. F. MspI RFLP detected with chromosome-walk clone pXUT23-SE3.2L from DXS16 in Xp22.1-22.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9614–9614. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon G. P., Brownstein S., Wang N. S., Kearns J. A., Ewing C. C. Congenital hereditary (juvenile X-linked) retinoschisis. Histopathologic and ultrastructural findings in three eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Apr;104(4):576–583. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050160132029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Goonewardena P., Chotai J., Anvret M., Pettersson U. DNA linkage analysis of X-linked retinoschisis. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):228–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00291666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Pettersson U. Use of linked DNA probes for carrier detection and diagnosis of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Oct;106(10):1414–1416. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140578026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIESER E. P., FALLS H. F. Hereditary retinoschisis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Jun;51:1193–1200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)92457-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert G., Peterson J., Krawczak M., Zoll B. Linkage relationship between retinoschisis and four marker loci. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):382–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00282183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Eisenhard M., Latt S. A. Regional localization on the human X of DNA segments cloned from flow sorted chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1557–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Weeks D., Boehnke M. Programs for Pedigree Analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dGENE. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(6):471–472. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. S., Schnitzer B., Bingham E. L., Harnden C. E., Hyder D. M., Ginsburg D. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1988 May;131(2):331–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. A. TESTING FOR HETEROGENEITY OF RECOMBINATION FRACTION VALUES IN HUMAN GENETICS. Ann Hum Genet. 1963 Nov;27:175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1963.tb00210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Dallapiccola B., Bender K., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Linkage relationships between Retinoschisis, Xg, and a cloned DNA sequence from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):143–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00327111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilichowski E., Krawczak M., Seemanova E., Hanefeld F., Schmidtke J. Genetic linkage study between the loci for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy and nine X-chromosomal DNA markers. Hum Genet. 1987 Jan;75(1):32–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00273835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G., Cotlier E., Brodie S. A carrier state of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1985 Feb;5(1-2):13–17. doi: 10.3109/13816818509007850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


