Abstract
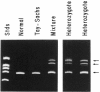
Mutations in the HEX A gene, encoding the alpha-subunit of beta-hexosaminidase A (Hex A), are the cause of Tay-Sachs disease as well as of juvenile, chronic, and adult GM2 gangliosidoses. We have examined the distribution of three mutations--a 4-nucleotide insertion in exon 11, a G----C transversion at a 5' splice site in intron 12, and a 269Gly----Ser amino acid substitution in exon 7--among individuals enzymatically diagnosed as carriers of Hex A deficiency. Mutation analysis included polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the relevant regions of genomic DNA, followed by allele-specific oligonucleotide hybridization; another test for heterozygosity of the exon 11 insertion was based on the formation of heteroduplex PCR fragments of low electrophoretic mobility. The percentage distribution of the exon 11, intron 12, exon 7, and unidentified mutant alleles was 73:15:4:8 among 156 Jewish carriers of Hex A deficiency and 16:0:3:81 among 51 non-Jewish carriers. Regardless of the mutation, the ancestral origin of the Jewish carriers was primarily eastern and (somewhat less often) central Europe, whereas for the non-Jewish carriers it was western Europe. Because a twelfth of the Jewish carriers and four-fifths of the non-Jewish carriers of Hex A deficiency had mutant alleles other than the three common ones tested, enzyme-based tests cannot be replaced by DNA-based tests at the present time. However, DNA-based tests for two-carrier couples could identify those at risk for the chronic/adult GM2 gangliosidoses rather than for infantile Tay-Sachs disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arpaia E., Dumbrille-Ross A., Maler T., Neote K., Tropak M., Troxel C., Stirling J. L., Pitts J. S., Bapat B., Lamhonwah A. M. Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):85–86. doi: 10.1038/333085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakai R., Chung D. W., Ratnoff O. D., Davie E. W. Factor XI (plasma thromboplastin antecedent) deficiency in Ashkenazi Jews is a bleeding disorder that can result from three types of point mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7667–7671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C. J., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., McCormick F., Marshall C. J. Analysis of RAS gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia by polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1629–1633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Kaback M. M. Estimation of the frequency of hexosaminidase a variant alleles in the American Jewish population. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):444–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Rozen R., Laframboise R., Laberge C., Scriver C. R. Novel PKU mutation on haplotype 2 in French-Canadians. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):905–909. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. A., Brody L. C., Sipila I., Looney J. E., Wong C., Engelhardt J. F., Patel A. S., Steel G., Obie C., Kaiser-Kupfer M. At least two mutant alleles of ornithine delta-aminotransferase cause gyrate atrophy of the choroid and retina in Finns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):197–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Costigan F. C. The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the alpha-chain of beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18587–18589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. Different mutations in Ashkenazi Jewish and non-Jewish French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1646–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.3754980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. Splice junction mutation in some Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease: evidence against a single defect within this ethnic group. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3955–3959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine C. M., Chan K., Lau Y. F. A PCR artifact: generation of heteroduplexes. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):337–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Adam A. Frequency of hexosaminidase A variant alleles among Ashkenazi Jews and prenatal diagnosis of GM2 gangliosidosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):1031–1033. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Kolodny E. H., Mitsumoto H., Thomas G. H., Proia R. L. Ashkenazi-Jewish and non-Jewish adult GM2 gangliosidosis patients share a common genetic defect. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):817–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon R., Proia R. L. The mutations in Ashkenazi Jews with adult GM2 gangliosidosis, the adult form of Tay-Sachs disease. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1471–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.2522679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F. Natural history and inherited disorders of a lysosomal enzyme, beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10927–10930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Okada S., Chen A., Fillerup D. L. Tay-sachs disease. Detection of heterozygotes and homozygotes by serum hexosaminidase assay. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 2;283(1):15–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007022830104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. Multiple abnormal beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain mRNAs in a compound-heterozygous Ashkenazi Jewish patient with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18563–18567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paw B. H., Kaback M. M., Neufeld E. F. Molecular basis of adult-onset and chronic GM2 gangliosidoses in patients of Ashkenazi Jewish origin: substitution of serine for glycine at position 269 of the alpha-subunit of beta-hexosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2413–2417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. M., Rotter J. I., Cantor R. M., Field L. L., Greenwald S., Lim J. S., Roy C., Schoenfeld V., Lowden J. A., Kaback M. M. The Tay-Sachs disease gene in North American Jewish populations: geographic variations and origin. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Nov;35(6):1258–1269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Diamond J. M. What maintains the frequencies of human genetic diseases? Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):289–290. doi: 10.1038/329289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S., Myerowitz R. A gel electrophoretic assay for detecting the insertion defect in Ashkenazi Jewish carriers of Tay-Sachs disease. Anal Biochem. 1990 Apr;186(1):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Berman P. H., Suzuki K. Detection of Tay-Sachs disease heterozygotes by assay of hexosaminidase A in serum and leukocytes. J Pediatr. 1971 Apr;78(4):643–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theophilus B., Latham T., Grabowski G. A., Smith F. I. Gaucher disease: molecular heterogeneity and phenotype-genotype correlations. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):212–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs-Raine B. L., Feigenbaum A. S., Natowicz M., Skomorowski M. A., Schuster S. M., Clarke J. T., Mahuran D. J., Kolodny E. H., Gravel R. A. Screening for carriers of Tay-Sachs disease among Ashkenazi Jews. A comparison of DNA-based and enzyme-based tests. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):6–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs-Raine B. L., Gravel R. A. Diagnostic heteroduplexes: simple detection of carriers of a 4-bp insertion mutation in Tay-Sachs disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):183–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Martin B. M., Barranger J. A., Stubblefield B. K., LaMarca M. E., Ginns E. I. Genetic heterogeneity in type 1 Gaucher disease: multiple genotypes in Ashkenazic and non-Ashkenazic individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2349–2352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]