Abstract
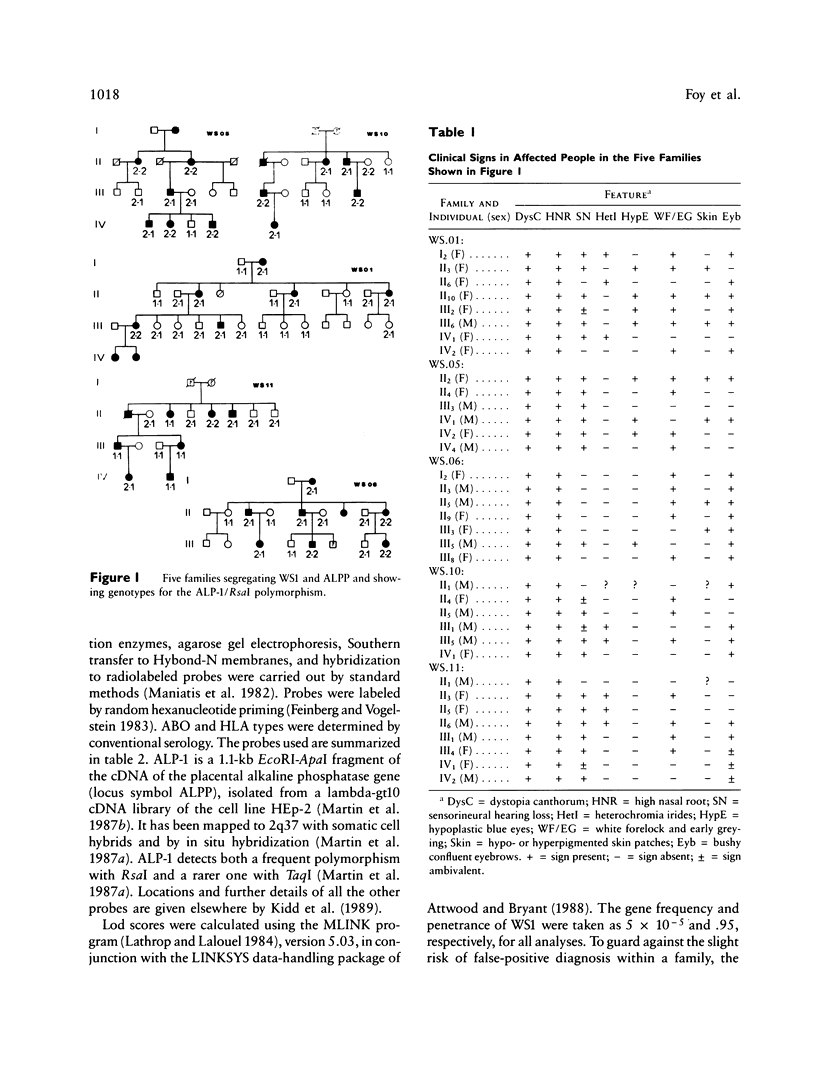
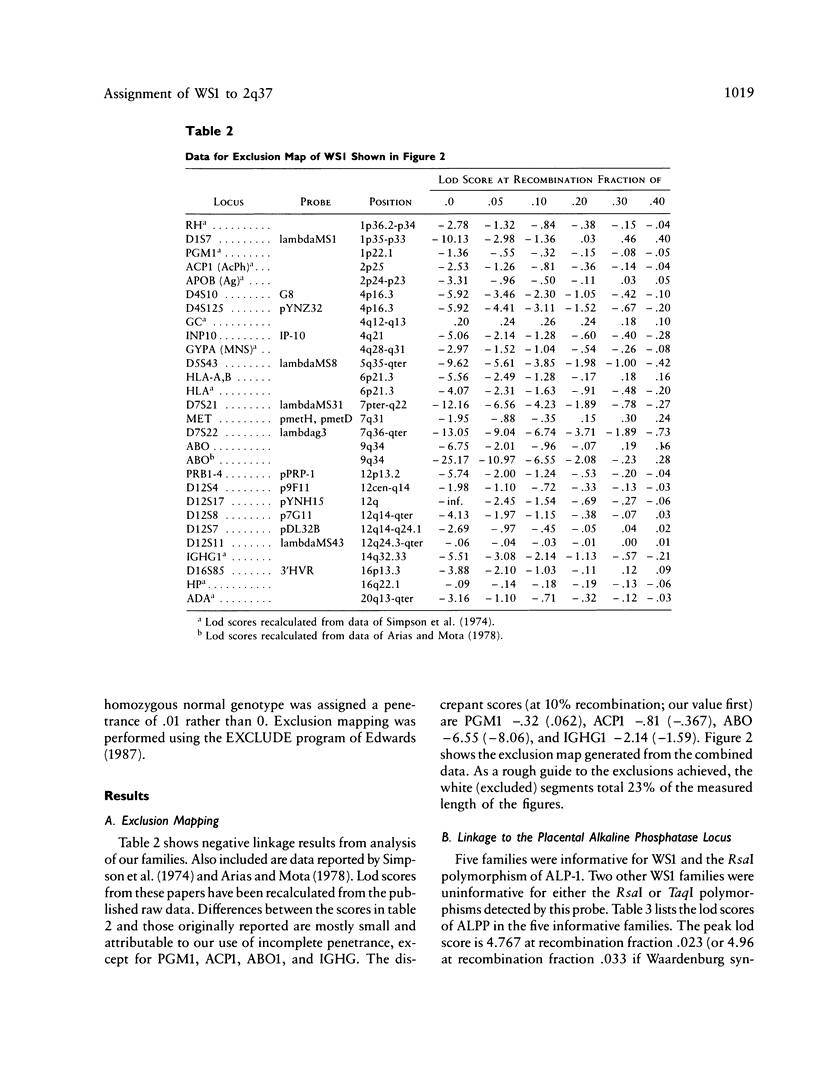
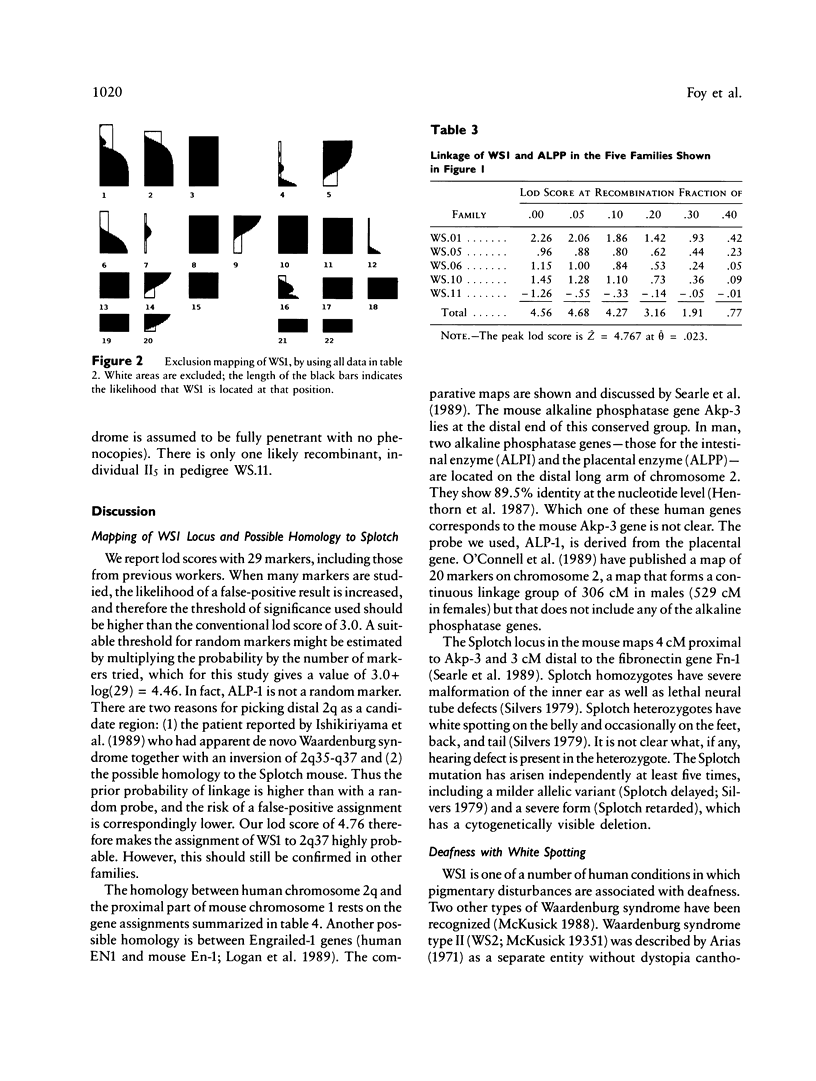
We have demonstrated close linkage between the locus for the autosomal dominant Waardenburg syndrome type I and the placental alkaline phosphatase locus on chromosome 2q37. In five families the peak lod score was 4.76 at a recombination fraction of .023. In the mouse the Splotch locus maps to near the homologous position. Splotch mice have white spotting and hearing defects, suggesting that Splotch may be the murine homologue of Waardenburg syndrome type I.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amer M., el-Shazly M. The association of familial hyperbetalipoproteinaemia with Waardenburg's syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1974 Mar;90(3):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb06399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias S. Genetic heterogeneity in the Waardenburg syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Mar;07(4):87–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias S., Mota M. Current status of the ABO-Waardenburg syndrome type I linkage. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):291–294. doi: 10.1159/000130956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias S., Mota M., Yánez A., Bolivar M. Probable loose linkage between the ABO locus and Waardenburg syndrome type I. Humangenetik. 1975;27(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00273330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton D. E., Yang-Feng T. L., Mason A. J., Seeburg P. H., Francke U. Mapping of genes for inhibin subunits alpha, beta A, and beta B on human and mouse chromosomes and studies of jsd mice. Genomics. 1989 Jul;5(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Haguenauer O., Barton P. J., Nguyen V. C., Serero S., Gross M. S., Jegou-Foubert C., de Tand M. F., Robert B., Buckingham M., Frézal J. Assignment of the human fast skeletal muscle myosin alkali light chains gene (MLC1F/MLC3F) to 2q 32.1-2qter. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00291237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Odland G. F. Partial albinism. JAMA. 1966 Feb 14;195(7):519–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David T. J., Warin R. P. Waardenburg's syndrome in two siblings, both parents and their maternal grandmother. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Jul;65(7):601–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deol M. S. Influence of the neural tube on the differentiation of the inner ear in the mammalian embryo. Nature. 1966 Jan 8;209(5019):219–220. doi: 10.1038/209219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. Exclusion mapping. J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;24(9):539–543. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.9.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCH L. Deafness as part of an hereditary syndrome. J Laryngol Otol. 1959 Jun;73:355–382. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100055420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. M., Lewithal I., Solomon A., Klein D. Upper limb involvement in the Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Apr;11(4):425–433. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman M. J., Delleman J. W. Heterogeneity in Waardenburg syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):468–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Raducha M., Edwards Y. H., Weiss M. J., Slaughter C., Lafferty M. A., Harris H. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase: close homology to placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén M. A., Honeyman M. M., Mayne A. J., Tarlow M. J. Homozygosity in piebald trait. J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;24(9):568–571. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.9.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikiriyama S., Tonoki H., Shibuya Y., Chin S., Harada N., Abe K., Niikawa N. Waardenburg syndrome type I in a child with de novo inversion (2)(q35q37.3). Am J Med Genet. 1989 Aug;33(4):505–507. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd K. K., Bowcock A. M., Schmidtke J., Track R. K., Ricciuti F., Hutchings G., Bale A., Pearson P., Willard H. F., Gelernter J. Report of the DNA committee and catalogs of cloned and mapped genes and DNA polymorphisms. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):622–947. doi: 10.1159/000132810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan C., Willard H. F., Rommens J. M., Joyner A. L. Chromosomal localization of the human homeo box-containing genes, EN1 and EN2. Genomics. 1989 Feb;4(2):206–209. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubsen N. H., Renwick J. H., Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Schoenmakers J. G. A locus for a human hereditary cataract is closely linked to the gamma-crystallin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):489–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Spurr N. K., Trowsdale J. RFLP of the human placental alkaline phosphatase gene (PLAP). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9104–9104. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Tucker D. F., Gorman P., Sheer D., Spurr N. K., Trowsdale J. The human placental alkaline phosphatase gene and related sequences map to chromosome 2 band q37. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 May;51(Pt 2):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock B., Kozak C., Seldin M. F., Ruff N., D'Hoostelaere L., Szpirer C., Levan G., Seuanez H., O'Brien S., Banner C. A glutaminase (gis) gene maps to mouse chromosome 1, rat chromosome 9, and human chromosome 2. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemansky J., Hageman M. J. Tomographic findings of the inner ears of 24 patients with Waardenburg's syndrome. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975 Jun;124(2):250–255. doi: 10.2214/ajr.124.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P., Lathrop G. M., Nakamura Y., Leppert M. L., Lalouel J. M., White R. Twenty loci form a continuous linkage map of markers for human chromosome 2. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):738–745. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD F. C. The pathology of congenital deafness. J Laryngol Otol. 1960 Dec;74:919–950. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100057376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. B., Stone V. M., Boder E., Ziprkowski L. Pigmentary disorders in association with congenital deafness. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Feb;95(2):176–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Merck M. F., Simon-Chazottes D., Arpin M., Pringault E., Louvard D., Guénet J. L., Berger R. Localization of the villin gene on human chromosome 2q35-q36 and on mouse chromosome 1. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):130–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00278181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Peters J., Lyon M. F., Hall J. G., Evans E. P., Edwards J. H., Buckle V. J. Chromosome maps of man and mouse. IV. Ann Hum Genet. 1989 May;53(Pt 2):89–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skow L. C., Adkison L., Womack J. E., Beamer W. G., Taylor B. A. Mapping of the mouse fibronectin gene (Fn-1) to chromosome 1: conservation of the Idh-1-Cryg-Fn-1 synteny group in mammals. Genomics. 1987 Nov;1(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel K. P., Barkway C. Another role for melanocytes: their importance for normal stria vascularis development in the mammalian inner ear. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):453–463. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel K. P., Bock G. R. Hereditary inner-ear abnormalities in animals. Relationships with human abnormalities. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Jan;109(1):22–29. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800150026005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


