Abstract
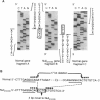
alpha 1-Antitrypsin (alpha 1AT) deficiency, a common hereditary disorder responsible for emphysema in Caucasians of northern European descent, is caused by single base substitutions, deletions, or additions in the seven exons (IA-IC and II-V), of the 12.2-kb alpha 1AT gene located on chromosome 14 at q31-32.3. Of the five known representatives of the "null" group of alpha 1AT-deficiency alleles (alpha 1AT genes incapable of producing alpha 1AT protein detectable in serum) evaluated at the gene level, all result from mutations causing the formation of stop codons in coding exons of the alpha 1AT gene. The present study identifies an alpha 1AT allele (referred to as "Null(isola di procida")) caused by complete deletion of the alpha 1AT coding exons. The Null(isola di procida) allele was identified in an individual with heterozygous inheritance of M(procida) (an allele associated with alpha 1AT deficiency) and a null allele. Although results of karyotypic analysis were normal, quantification of the copies of alpha 1AT genes in this individual revealed that the index case had only half the normal copies of alpha 1AT genes. Cloning and mapping of the Null(isola di procida) gene demonstrated a deletion of a 17-kb fragment that included exons II-V of the alpha 1AT structural gene. As a consequence of the deletion, the normal noncoding exons (IA-IC) were followed by exons II-V of the downstream alpha 1AT-like gene. Sequence analysis of the deletion demonstrated a 7-bp repeat sequence (GAGGACA) both 5' to the deletion and at the 3' end of the deletion, a 4-bp palindromic sequence (ACAG vs. CTGT) bracketing the deletion, and a novel inserted 4-bp sequence (CCTG) at the breakpoint, suggesting that the mechanism of the deletion may have been "slipped mispairing."
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bao J. J., Reed-Fourquet L., Sifers R. N., Kidd V. J., Woo S. L. Molecular structure and sequence homology of a gene related to alpha 1-antitrypsin in the human genome. Genomics. 1988 Feb;2(2):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brantly M., Nukiwa T., Crystal R. G. Molecular basis of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Med. 1988 Jun 24;84(6A):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Jeppsson J. O., Laurell C. B., Brennan S. O., Owen M. C., Vaughan L., Boswell D. R. Structure and variation of human alpha 1-antitrypsin. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):329–334. doi: 10.1038/298329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constans J., Viau M., Gouaillard C. Pi M4: an additional Pi M subtype. Hum Genet. 1980;55(1):119–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00329137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Johnson A. M., Fagerhol M. K. Report of Nomenclature Meeting for alpha 1-antitrypsin, INSERM, Rouen/Bois-Guillaume-1978. Hum Genet. 1980;53(3):429–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00287070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Brantly M. L., Hubbard R. C., Curiel D. T., States D. J., Holmes M. D. The alpha 1-antitrypsin gene and its mutations. Clinical consequences and strategies for therapy. Chest. 1989 Jan;95(1):196–208. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.1.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G. The alpha 1-antitrypsin gene and its deficiency states. Trends Genet. 1989 Dec;5(12):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiel D., Brantly M., Curiel E., Stier L., Crystal R. G. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency caused by the alpha 1-antitrypsin Nullmattawa gene. An insertion mutation rendering the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene incapable of producing alpha 1-antitrypsin. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1144–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI113994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish R., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G., Tolstoshev P. Copy number of a human type I alpha 2 collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13816–13822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagerhol M. K., Cox D. W. The Pi polymorphism: genetic, biochemical, and clinical aspects of human alpha 1-antitrypsin. Adv Hum Genet. 1981;11:1-62, 371-2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Fells G. A., Zimmerman R. L., Rennard S. I., Crystal R. G. Antielastases of the human alveolar structures. Implications for the protease-antiprotease theory of emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):889–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI110344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver R. I., Jr, Mornex J. F., Nukiwa T., Brantly M., Courtney M., LeCocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency and emphysema caused by homozygous inheritance of non-expressing alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 20;314(12):762–766. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603203141207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J. Maternal duplication associated with gene deletion in sporadic hemophilia. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;43(3):274–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görg A., Postel W., Weser J., Patutschnick W., Cleve H. Improved resolution of PI (alpha 1-antitrypsin) phenotypes by a large-scale immobilized pH gradient. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Sep;37(5):922–930. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Nelen M., Klasen E. C., Nukiwa T., Curiel D., Crystal R. G., Frants R. R. Cloning and characterization of an alpha 1-antitrypsin like gene 12 KB downstream of the genuine alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):634–642. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80542-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M., Curiel D., Brantly M., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the intracellular mechanism causing the alpha-1-antitrypsin Nullgranite falls deficiency state. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1662–1667. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B., Dunning A., Humphries S. Identification of deletions in the human low density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;24(3):144–147. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.3.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Beta O-39 thalassemia gene: a premature termination codon causes beta-mRNA deficiency without affecting cytoplasmic beta-mRNA stability. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastases and emphysema. Current assessment of the protease-antiprotease hypothesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):417–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey G. D., Povey S., Bygrave A. E., Lovell-Badge R. H. Species- and tissue-specific expression of human alpha 1-antitrypsin in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):161–171. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois S., Kastelein J. J., Hayden M. R. Characterization of six partial deletions in the low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene causing familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;43(1):60–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long G. L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Complete sequence of the cDNA for human alpha 1-antitrypsin and the gene for the S variant. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4828–4837. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORHEAD P. S., NOWELL P. C., MELLMAN W. J., BATTIPS D. M., HUNGERFORD D. A. Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:613–616. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Rachmilewitz E. A., Ross J. Unstable beta-globin mRNA in mRNA-deficient beta o thalassemia. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalski J. P., McCombs C. C., Sheth S., McCarthy M., deShazo R. A modified double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measurement of alpha-1-antitrypsin in biologic fluids. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 24;83(1):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukiwa T., Brantly M. L., Ogushi F., Fells G. A., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the gene and protein of the common alpha 1-antitrypsin normal M2 allele. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Sep;43(3):322–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukiwa T., Brantly M., Ogushi F., Fells G., Satoh K., Stier L., Courtney M., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the M1(Ala213) type of alpha 1-antitrypsin, a newly recognized, common "normal" alpha 1-antitrypsin haplotype. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5259–5267. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukiwa T., Takahashi H., Brantly M., Courtney M., Crystal R. G. alpha 1-Antitrypsin nullGranite Falls, a nonexpressing alpha 1-antitrypsin gene associated with a frameshift to stop mutation in a coding exon. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11999–12004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Curiel D. T., Brantly M. L., Holmes M. D., Crystal R. G. Rapid, nonradioactive detection of mutations in the human genome by allele-specific amplification. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Aug;114(2):105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlino E., Cortese R., Ciliberto G. The human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene is transcribed from two different promoters in macrophages and hepatocytes. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2767–2771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M., Watson M., Kidd V., Woo S. L., Breg W. R., Ruddle F. H. Regional location of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes on human chromosome 14. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01560668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Tripodi M., Cortese R., Wagner E. F. The human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene is efficiently expressed from two tissue-specific promotors in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7519–7529. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Nukiwa T., Brantly M., Garver R. I., Jr, Hofker M., Courtney M., Crystal R. G. Emphysema associated with complete absence of alpha 1- antitrypsin in serum and the homozygous inheritance [corrected] of a stop codon in an alpha 1-antitrypsin-coding exon. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):77–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. F., Li Y., Sifers R. N., Wang H., Hardick C., Tsai S. Y., Woo S. L. Tissue-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene is controlled by multiple cis-regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8399–8415. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sifers R. N., Brashears-Macatee S., Kidd V. J., Muensch H., Woo S. L. A frameshift mutation results in a truncated alpha 1-antitrypsin that is retained within the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7330–7335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Nukiwa T., Satoh K., Ogushi F., Brantly M., Fells G., Stier L., Courtney M., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the gene and protein of the alpha 1-antitrypsin "deficiency" allele Mprocida. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15528–15534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita K., Forget B. G., Scarpa A., Benz E. J., Jr Intranuclear defect in beta-globin mRNA accumulation due to a premature translation termination codon. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewers M. D., Casolaro M. A., Sellers S. E., Swayze S. C., McPhaul K. M., Wittes J. T., Crystal R. G. Replacement therapy for alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency associated with emphysema. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1055–1062. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J., Dressler D. Bacteriophage T7 DNA replication. An electron microscopic study of the growing point and the role of the T7 gene 4 protein in the formation of DNA fragments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10490–10495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Sawa R., Okamoto N., Matsui A., Yanagisawa M., Ikemoto S. Deletion 14q(q24.3 to q32.1) syndrome: significance of peculiar facial appearance in its diagnosis, and deletion mapping of Pi(alpha 1-antitrypsin). Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):190–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00282092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Antonarakis S. E., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Phillips D. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of five partial deletions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]