Abstract
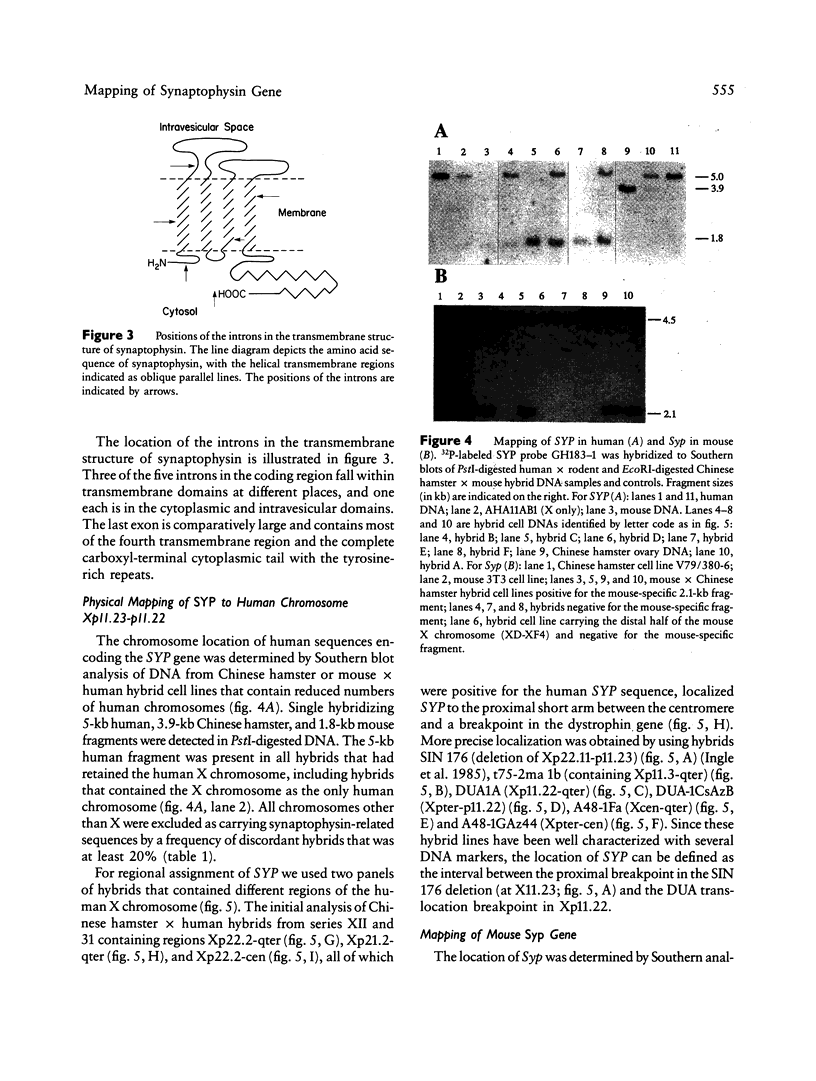
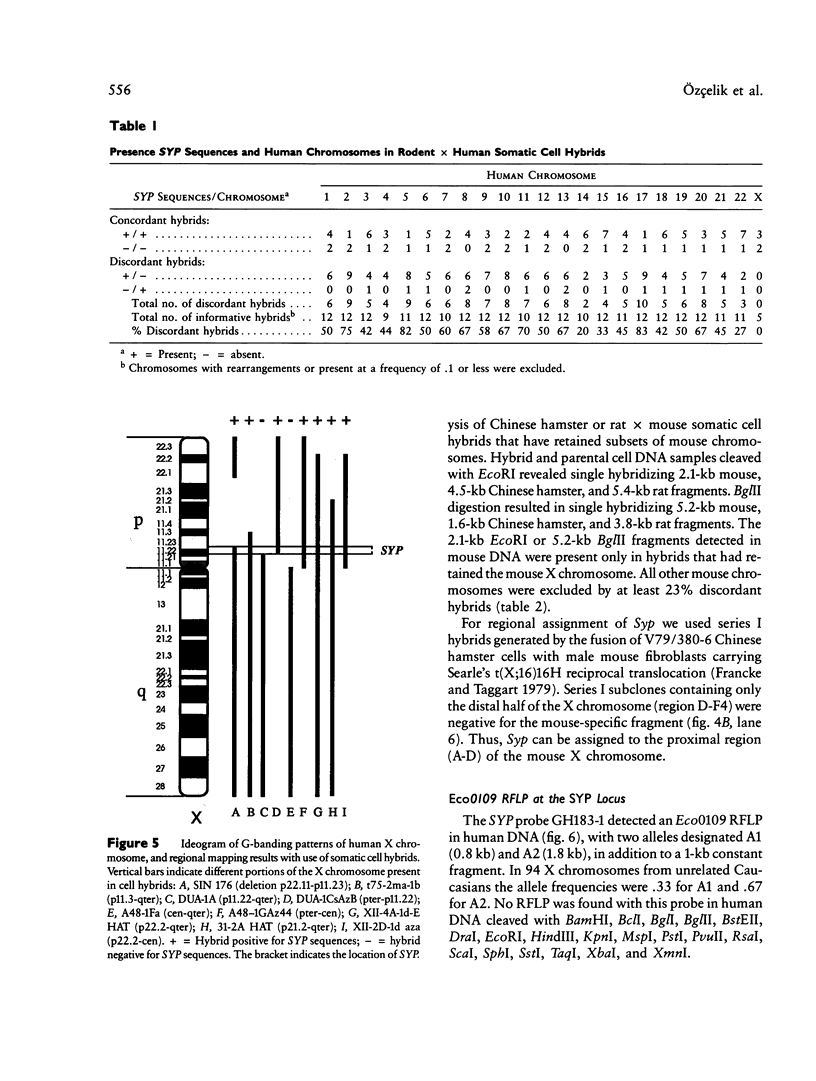
Synaptophysin is an integral membrane protein of small synaptic vesicles in brain and endocrine cells. We have determined the structure and organization of the human synaptophysin gene and have established the chromosome localizations in man and mouse. Analysis of a cosmid clone containing the human synaptophysin gene (SYP) revealed seven exons distributed over approximately 20 kb, when compared with the previously published cDNA sequence. The exon-intron boundaries have been identified and do not correlate with functional domains. One intron interrupts the 3' untranslated region. Chromosomal localization of the human and murine genes for synaptophysin established the human SYP locus on the X chromosome in subbands Xp11.22-p11.23 and the mouse synaptophysin gene locus (Syp) on the X chromosome in region A-D. In addition, an Eco0109 RFLP has been identified and used in genetic mapping of the human SYP locus and supports the order TIMP-SYP-DXS14 within a span of approximately 4-7 centimorgans.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arveiler B., Alembik Y., Hanauer A., Jacobs P., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Puissant H., Piet L. L., Mandel J. L. Linkage analysis suggests at least two loci for X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton D. E., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U. The human tyrosine aminotransferase gene mapped to the long arm of chromosome 16 (region 16q22----q24) by somatic cell hybrid analysis and in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1986 Mar;72(3):221–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00291881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop A. E., Power R. F., Polak J. M. Markers for neuroendocrine differentiation. Pathol Res Pract. 1988 Apr;183(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(88)80040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Willard H. F. Localization of a gene that escapes inactivation to the X chromosome proximal short arm: implications for X inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):273–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. M., Floor E., Kelly R. B. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding p38, a major synaptic vesicle protein. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2447–2456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Hecht F. Gene for incontinentia pigmenti maps to band Xp11 with an (X;10) (p11;q22) translocation. Clin Genet. 1987 Jul;32(1):66–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., McGee T. L., Reichel E., Hahn L. B., Cowley G. S., Yandell D. W., Sandberg M. A., Berson E. L. A point mutation of the rhodopsin gene in one form of retinitis pigmentosa. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):364–366. doi: 10.1038/343364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Darras B. T., Zander N. F., Kilimann M. W. Assignment of human genes for phosphorylase kinase subunits alpha (PHKA) to Xq12-q13 and beta (PHKB) to 16q12-q13. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):276–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Taggart R. T. Assignment of the gene for cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase (Sod-1) to a region of chromosome 16 and of Hprt to a region of the X chromosome in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5230–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Yang-Feng T. L., Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A. Chromosomal mapping of genes involved in growth control. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):855–866. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer W. L., Somani A. K., Kwong P. C., Peacocke M., Rubin L. A., Siminovitch K. A. Linkage relationships of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome to 10 loci in the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):568–571. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90489-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B., Aicardi J., Dias K., Ramos O. A progressive syndrome of autism, dementia, ataxia, and loss of purposeful hand use in girls: Rett's syndrome: report of 35 cases. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):471–479. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle C., Williamson R., de la Chapelle A., Herva R. R., Haapala K., Bates G., Willard H. F., Pearson P., Davies K. E. Mapping DNA sequences in a human X-chromosome deletion which extends across the region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutation. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):451–462. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Cameron P. L., Stukenbrok H., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin is targeted to similar microvesicles in CHO and PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Transmembrane topography and evolutionary conservation of synaptophysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Südhof T. C. The multisubunit structure of synaptophysin. Relationship between disulfide bonding and homo-oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8869–8873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasiter P. S., Kachele D. L. Postnatal development of protein P-38 ('synaptophysin') immunoreactivity in pontine and medullary gustatory zones of rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Jul 1;48(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc N., Beesley P. W., Brown I., Colonnier M., Gurd J. W., Paladino T., Hawkes R. Synaptophysin expression during synaptogenesis in the rat cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 8;280(2):197–212. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Kaiser P., Seiter A., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Rehm H., Knaus P., Prior P., Betz H., Reinke H. Synaptophysin: molecular organization and mRNA expression as determined from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3261–3268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Topogenesis and sorting of synaptophysin: synthesis of a synaptic vesicle protein from a gene transfected into nonneuroendocrine cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahtani M. M., Willard H. F. A primary genetic map of the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Willard H. F., Nussbaum R. L., Romeo G., Puck J. M., Davies K. E. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51(1-4):384–437. doi: 10.1159/000132801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews K. D., Ardinger H. H., Nishimura D. Y., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C., Bartley J. A. Linkage localization of Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;34(4):470–474. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. C., Koslow M., Budzilovich G. N., Burstein D. E. Synaptophysin: a sensitive and specific marker for ganglion cells in central nervous system neoplasms. Hum Pathol. 1990 Jan;21(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90080-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Yagasaki K., Horiguchi M., Kawase Y., Kanda T. Congenital stationary night blindness with negative electroretinogram. A new classification. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Jul;104(7):1013–1020. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1986.01050190071042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musarella M. A., Burghes A., Anson-Cartwright L., Mahtani M. M., Argonza R., Tsui L. C., Worton R. Localization of the gene for X-linked recessive type of retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP) to Xp21 by linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):484–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musarella M. A., Weleber R. G., Murphey W. H., Young R. S., Anson-Cartwright L., Mets M., Kraft S. P., Polemeno R., Litt M., Worton R. G. Assignment of the gene for complete X-linked congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB1) to Xp11.3. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):727–737. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Di Gioia G., Jahn R., Browning M., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Microvesicles of the neurohypophysis are biochemically related to small synaptic vesicles of presynaptic nerve terminals. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3425–3433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo J. T., Bateman J. B., Cortessis V., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Inana G., Spence M. A. Norrie disease: linkage analysis using a 4.2-kb RFLP detected by a human ornithine aminotransferase cDNA probe. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Wang J. K., Valtorta F., Benfenati F., Greengard P. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):762–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm H., Wiedenmann B., Betz H. Molecular characterization of synaptophysin, a major calcium-binding protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):535–541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling K., Barco E. B., Rhinehart D., Pilgrim C. Expression of synaptophysin and neuron-specific enolase during neuronal differentiation in vitro: effects of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Nov;24(3):347–354. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthers G. K., Turner G., Mulley J. C. A non-syndromal form of X-linked mental retardation (XLMR) is linked to DXS14. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Czernik A. J., Kao H. T., Takei K., Johnston P. A., Horiuchi A., Kanazir S. D., Wagner M. A., Perin M. S., De Camilli P. Synapsins: mosaics of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.2506642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. The cDNA and derived amino acid sequences for rat and human synaptophysin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9607–9607. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C. The structure of the human synapsin I gene and protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7849–7852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Hartung K., Langosch D., Rehm H., Bamberg E., Franke W. W., Betz H. Identification of synaptophysin as a hexameric channel protein of the synaptic vesicle membrane. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1050–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.2461586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Gedeon A., Mulley J., Sutherland G., Rae J., Power K., Arthur I. Börjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome: clinical manifestations and gene localization to Xq26-27. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Dec;34(4):463–469. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Durfy S. J., Mahtani M. M., Dorkins H., Davies K. E., Williams B. R. Regional localization of the TIMP gene on the human X chromosome. Extension of a conserved synteny and linkage group on proximal Xp. Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;81(3):234–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00278995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth B., Denton M. J., Chen J. D., Neugebauer M., Halliday F. B., van Schooneveld M., Donald J., Bleeker-Wagemakers E. M., Pearson P. L., Gal A. Two different genes for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S. S., Clayton J. F., Dempster M., Tippett P., McKeown C. M., Jay M., Jay B., Bird A. C. Linkage relationships between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and nine short-arm markers: exclusion of the disease locus from Xp21 and localization to between DXS7 and DXS14. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;41(4):635–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., DeGennaro L. J., Francke U. Genes for synapsin I, a neuronal phosphoprotein, map to conserved regions of human and murine X chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8679–8683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]