Abstract
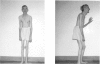
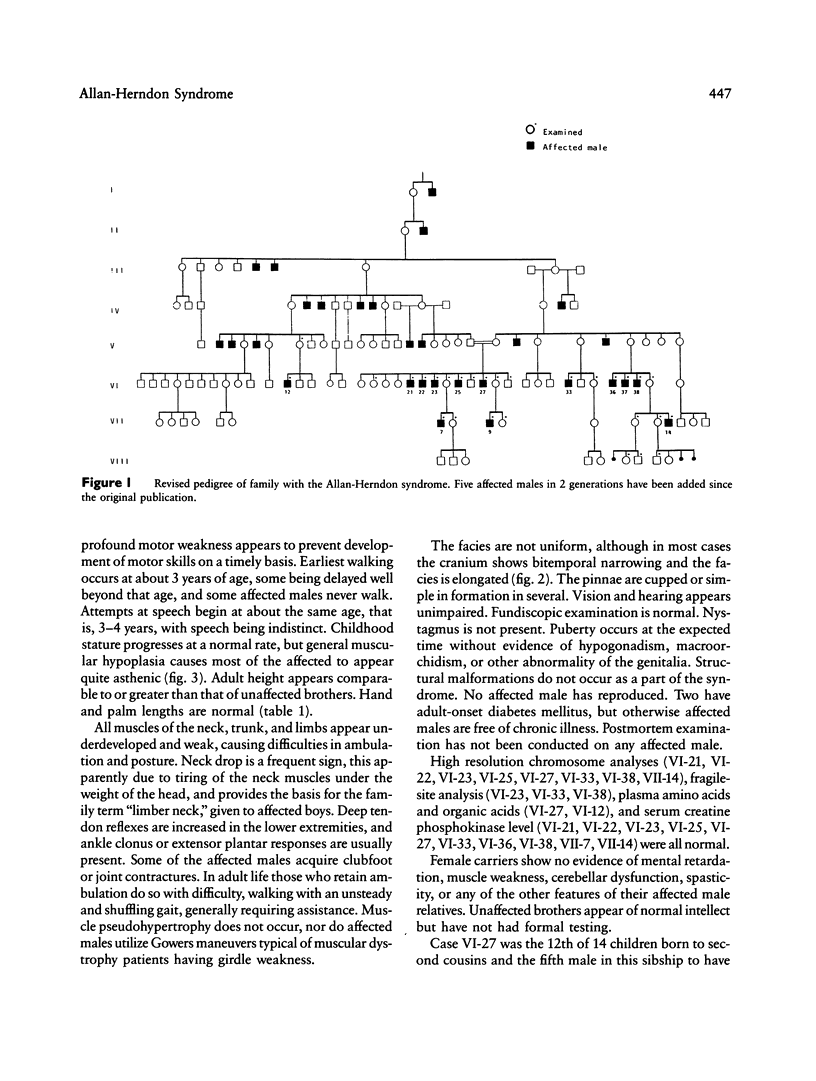
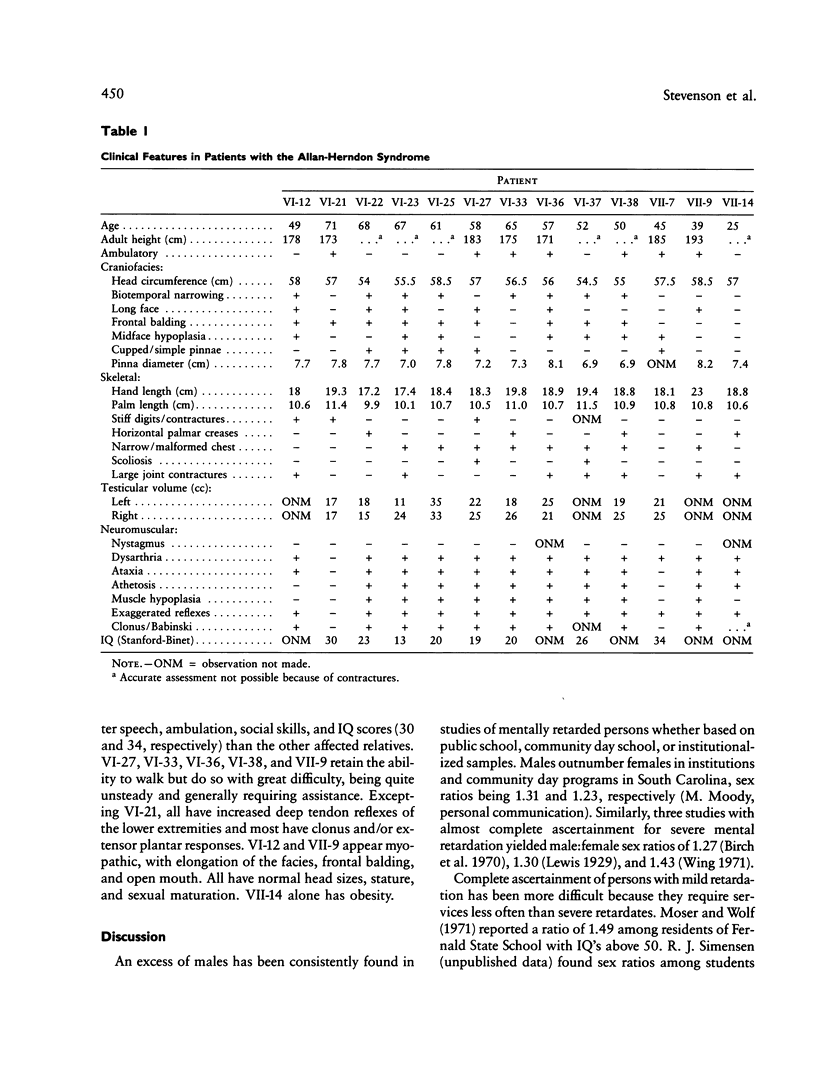
A large family with X-linked mental retardation, originally reported in 1944 by Allan, Herndon, and Dudley, has been reinvestigated. Twenty-nine males have been affected in seven generations. Clinical features include severe mental retardation, dysarthria, ataxia, athetoid movements, muscle hypoplasia, and spastic paraplegia with hyperreflexia, clonus, and Babinski reflexes. The facies appear elongated with normal head circumference, bitemporal narrowing, and large, simple ears. Contractures develop at both small and large joint. Statural growth is normal and macroorchidism does not occur. Longevity is not impaired. High-resolution chromosomes, serum creatine kinase, and amino acids are normal. This condition, termed the Allan-Herndon syndrome, appears distinct from other X-linked disorders having mental retardation, muscle hypoplasia, and spastic paraplegia.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apak S., Yüksel M., Ozmen M., Saka N., Darendeliler F., Neuhäuser G. Heterogeneity of X-linked recessive (spino)cerebellar ataxia with or without spastic diplegia. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Oct;34(2):155–158. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baar H. S., Gabriel A. M. Sex-linked spastic paraplegia. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 Jul;71(1):13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Griffiths M. I. Recurrence risks in families of children with symmetrical spasticity. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1977 Apr;19(2):179–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1977.tb07968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON A. W., McKUSICK V. A. A sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Mar;14:83–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K. E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00401241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz R., Bodensteiner J., Schaefer B., Gay C. X-linked olivopontocerebellar atrophy. Clin Genet. 1989 Jun;35(6):417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMUD N., COHEN P. Unusual form of cerebellar ataxia with sex-linked inheritance. Neurology. 1958 Apr;8(4):261–266. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.4.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Wolf P. A. The nosology of mental retardation: including the report of a survey of 1378 mentally retarded individuals at the Walter E. Fernald State School. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Feb;7(1):117–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidley J. W., Levinsohn M. W., Manetto V. Infantile X-linked ataxia and deafness: a new clinicopathologic entity? Neurology. 1987 Aug;37(8):1344–1349. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.8.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmon T. F., Walker B. A., Scott C. I., Abbott M. H. Two kindreds with a sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Feb;7(1):219–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wolff G., Wienker T. F., Sauer M. A new X-linked syndrome with muscle atrophy, congenital contractures, and oculomotor apraxia. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;20(4):597–606. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. Severely retarded children in a London area: prevalence and provision of services. Psychol Med. 1971 Nov;1(5):405–415. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700044792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. M., Davies K. E., Bell M. V., Huson S. M., Patterson M. N. MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00273999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz M., Penha-Serrano C., Otto P. A. X-linked recessive type of pure spastic paraplegia in a large pedigree: absence of detectable linkage with Xg. J Med Genet. 1976 Jun;13(3):217–222. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]