Abstract
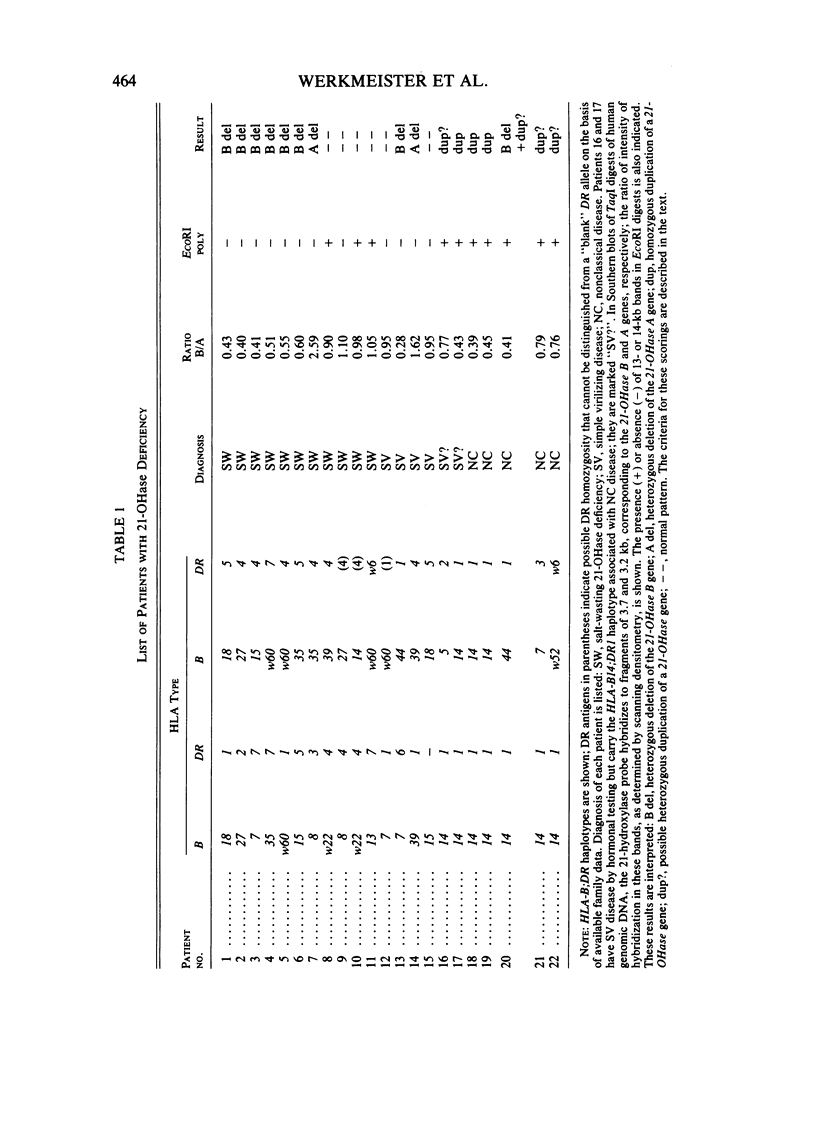
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase (21-OHase) deficiency is an HLA-linked disorder resulting from a mutation in the 21-OHase B gene encoding the adrenal cytochrome P450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. To identify polymorphisms associated with 21-OHase deficiency, DNA samples from 22 unrelated patients with this disorder were examined with a human cDNA clone encoding the enzyme. Deletions of the active 21-OHase gene were found in almost one-fourth of classical 21-OHase deficiency alleles. In contrast, mild, "nonclassical" 21-OHase deficiency is associated with a duplicated 21-OHase gene.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll M. C., Belt T., Palsdottir A., Porter R. R. Structure and organization of the C4 genes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):379–388. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. J., Reyes A. A., Morin C., Itakura K., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Detection of sickle cell beta S-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):278–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohoue P. A., Jospe N., Migeon C. J., McLean R. H., Bias W. B., White P. C., Van Dop C. Restriction maps and restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the human 21-hydroxylase genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 29;136(2):722–729. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Shaefer J. M. Inborn errors of steroid biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):353–406. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischnick E., Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Granados J., Alosco S. M., Crigler J. F., Jr, Gerald P. S., Giles C. M., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended MHC haplotypes in 21-hydroxylase-deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia: shared genotypes in unrelated patients. Lancet. 1983 Jan 22;1(8317):152–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlepp M. J., Wilton A. N., Dawkins R. L., White P. C. Rearrangement of 21-hydroxylase genes in disease-associated MHC supratypes. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(2):100–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00377968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New M. I., Dupont B., Pollack M. S., Levine L. S. The biochemical basis for genotyping 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Hum Genet. 1981;58(1):123–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00284159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Dupont B., Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., New M. I. Complement C4 allotypes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: further evidence for different allelic variants at the 21-hydroxylase locus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):312–322. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Anderson J., Strong L., Granados J., Teran L., Giblett E., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Human C4 haplotypes with duplicated C4A or C4B. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):72–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsby G., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R., Grant D. B., Hjelm M. Deletion of the steroid 21-hydroxylase and complement C4 genes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Med Genet. 1986 Jun;23(3):204–209. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., Dupont B., Rubinstein P., Piazza A., Kastelan A., New M. I. High frequency of nonclassical steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):650–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner E., Dimartino-Nardi J., Kuhnle U., Levine L. S., Oberfield S. E., New M. I. Is salt-wasting in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to the same gene as the fasciculata defect? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Jan;24(1):9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]